2536
A fistful of relays, or a computer on the electromagnetic relay. Part 1 - ALU
I'll tell you how you can create a computer (or rather, while only part of it) on the electromagnetic relay his own hands.

How it all began
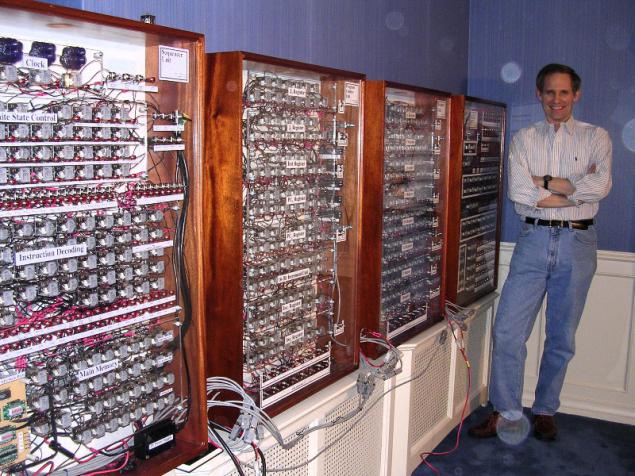
It all started with the fact that I had read about the computer on electromagnetic relays created Harry Porter - an enthusiast of the University of Portland. Here's a picture of him next to this computer:

Since I am fond of old computers (part of my collection can be seen in this album ), then I also wanted to create something similar. I began to look for other projects and found many
Other modern computers on electromagnetic relays
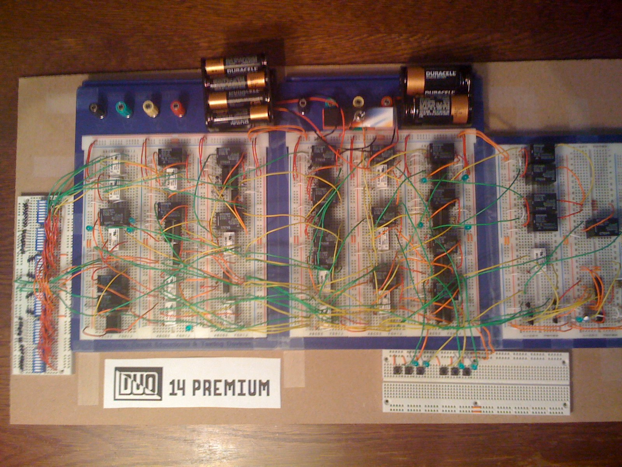
Some of them are more or less repeated the project Harry part only demonstrated that the creation of such a computer is possible. For example, DUO 14 Premium , shown below, can execute a program containing up to 8 simple commands.
Project
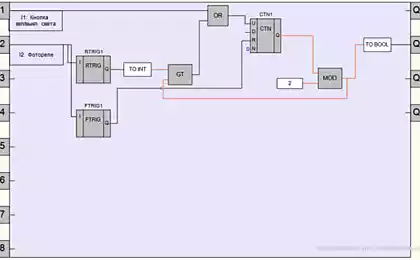
So, I planned to create a computer-like HPRC abbr>. Wished it could have been anything real to count, as well as to all of its elements were visual - could be traced work ALU, registers, counters, etc. instructions
Start making I decided to ALU. To determine the requirements applied to him, I am in general has developed a set of instructions, and figured what needed tires and signals. The ALU has a parallel structure (all bits are evaluated simultaneously) and is intended for an 8-bit calculations.
I immediately decided that I needed to do the subtraction module. In many other computers, this module is not implemented, as his work can be performed using the negation and addition. Thus, the ALU will perform the following operations: addition, subtraction (with or without transfer), logical AND, OR, NOT, XOR, and shifts to the right (with the transfer or in a circle). Scheme for addition and logical operations, I took out HPRC.
Another feature is rarely found in the fact that the calculation result is latched in the shadow register. It is needed to the same general purpose register may be used as both input and output.
As long as the ALU should work without the other components of the computer, so it debugging to relay coils are connected tumblers, supplies power. The calculation results can be observed by means of LEDs connected to the output of the circuit. Regardless of the latched result, computational units operate continuously, so with the help of indicators can simultaneously observe the results of all operations.
Relays
Was selected voltage supply 24 and not 12, as in most other modern computers on electromagnetic relays to make the wire thinner. Later it turned out that this solution has a drawback - LED with integrated resistor rated at 24 does not happen, so had to buy the resistors and solder separately.
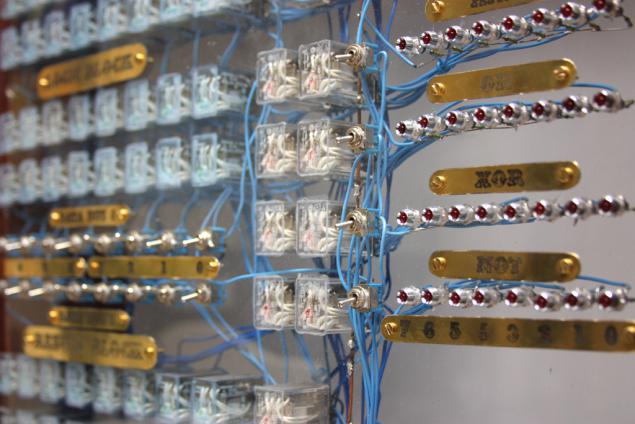
Since one of the main properties of the computer should be clarity, I chose a relay with a transparent body and a built-in LEDs. In addition, they look beautiful, it allows you to not install the extra LEDs for indicating the input signals.
After the start of assembly of the computer I'm reading one of the blogs, realized that I was missing the protective diodes, prevents arcing and knocking indicators when open relays. So I bought 100 pieces 1N4448 diodes and solder them in parallel with each of the coils.
Materials
Since the computer has to be clear, why should he not be beautiful? Harry used for mahogany body. I found a suitable material merbau wood , in the form of planed boards of the same thickness.
All components are mounted on a 6 mm sheet of Plexiglas. Relays are glued, and everything else, or is installed in a specially drilled holes, or screwed. Plates with inscriptions carved brass. The most difficult part was to find the appropriate size brass screws for mounting plates. In Russia, the book did not work anywhere else, but then I almost accidentally found them in a hobby store in Helsinki.
Job
I began by saying that he had bought the power supply, three dozen relay, wires, and switches to control inputs and the internal signals generated by the ALU. Relays contain 4 DIP switches. In some cases, all 4 switches are not used, but save by using a relay with a smaller number of contacts received hardly.
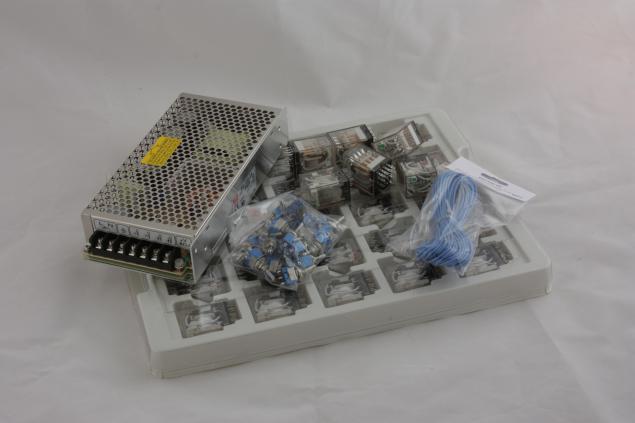

These relays have cost me about 200 rubles, so I started looking for cheaper options, as the whole unit ALU according to preliminary estimates of their required about 100 pieces. One batch of 100 pieces I was able to order at wholesale price slightly more than $ 100 for the relay. But this supplier themselves appear relay should not be soon, so I continued to search.
It turned out that the relay can be ordered directly from China is much cheaper. I ordered another batch of 100 pieces for about $ 1 apiece (dollar then cost around 30 rubles). Later it turned out that some relay received from China, obviously defective. For example, the following picture shows that the wires inside the relay been reversed. Fortunately, for correction of this bug was enough similarly reversed external connections to the relay.
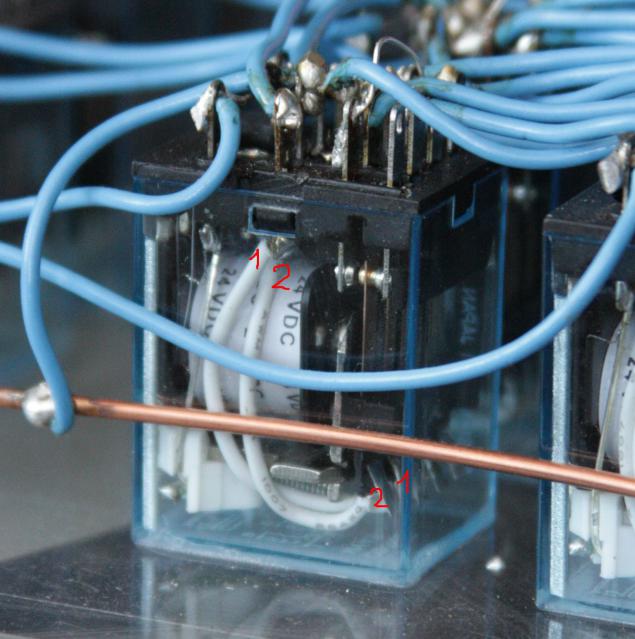
Moreover, there were many relay oxidised. In some cases it proved critical, and had to throw relay. But sometimes it still managed to throw the inputs and outputs to other contacts - played a role redundancy relay with 4 switches.
In the manufacture of the body had to learn some simple work on the processing of timber, but most of the time took brazing - for many of the relay had to solder wires to all 14 pins.
Results
Article was not very long and slightly superficial. More information can be found on the project website . If the community will be interested, I can write more about the characteristics and principles of operation as the ALU, and the projected computer.
From the moment that I decided to make my computer, it's been a year and a half. During this time I broadly designed architecture and instruction set, and also created the first computer module - arithmetic logic unit. Formally, of course, in the ALU used semiconductors - in LEDs for indication and protection diodes. But the logic is built on electromechanical relays. In this unit lacks only the external connections, but I'll do after the other blocks will appear, which will connect the ALU. Next I plan to make a block of registers.
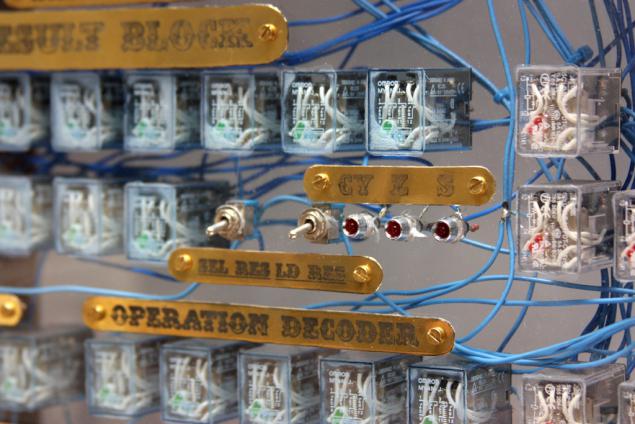

Statistics
ALU consists of 88 relay debug signals are fed with 43 toggle switches, the outputs are displayed using 70 LEDs. Unit Dimensions - 74x56x14 centimeters.
Relay with defects of various kinds was found about 10. Just count difficult, as some remained in slightly altered about this scheme.
Costs
Links
Project website: sourceforge.net/p/relay
Other computers:
Harry Porter's Relay Computer: web.cecs.pdx.edu/ ~ harry / Relay / li > Relay Computer Two: www.electronixandmore.com/projects/relaycomputertwo/index.html RC-3 Relay Computer: www.computerculture.org/projects/rc3/ Edmund Berkeley's Simon Relay Processor: www.cs.ubc.ca/ ~ hilpert / e / simon / index.html TIM: www.northdownfarm.co.uk/rory/tim/tim-8.htm DUO 14 Premium: www.ostracodfiles.com/ostracod/relay.html Relay computer «trainer»: relaysbc.sourceforge.net/ i² 8-Bit Relay Computer: isquared.weebly.com/ Kilian Leonhardt's relay computer: www.relaiscomputer.de/ Der Relaisrechner: www.schlaefendorf.de/relaisrechner/dokumentation/index.html Ul>
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/220865/

How it all began
It all started with the fact that I had read about the computer on electromagnetic relays created Harry Porter - an enthusiast of the University of Portland. Here's a picture of him next to this computer:

Since I am fond of old computers (part of my collection can be seen in this album ), then I also wanted to create something similar. I began to look for other projects and found many
Other modern computers on electromagnetic relays
Some of them are more or less repeated the project Harry part only demonstrated that the creation of such a computer is possible. For example, DUO 14 Premium , shown below, can execute a program containing up to 8 simple commands.

Project
So, I planned to create a computer-like HPRC abbr>. Wished it could have been anything real to count, as well as to all of its elements were visual - could be traced work ALU, registers, counters, etc. instructions
Start making I decided to ALU. To determine the requirements applied to him, I am in general has developed a set of instructions, and figured what needed tires and signals. The ALU has a parallel structure (all bits are evaluated simultaneously) and is intended for an 8-bit calculations.
I immediately decided that I needed to do the subtraction module. In many other computers, this module is not implemented, as his work can be performed using the negation and addition. Thus, the ALU will perform the following operations: addition, subtraction (with or without transfer), logical AND, OR, NOT, XOR, and shifts to the right (with the transfer or in a circle). Scheme for addition and logical operations, I took out HPRC.
Another feature is rarely found in the fact that the calculation result is latched in the shadow register. It is needed to the same general purpose register may be used as both input and output.
As long as the ALU should work without the other components of the computer, so it debugging to relay coils are connected tumblers, supplies power. The calculation results can be observed by means of LEDs connected to the output of the circuit. Regardless of the latched result, computational units operate continuously, so with the help of indicators can simultaneously observe the results of all operations.

Relays
Was selected voltage supply 24 and not 12, as in most other modern computers on electromagnetic relays to make the wire thinner. Later it turned out that this solution has a drawback - LED with integrated resistor rated at 24 does not happen, so had to buy the resistors and solder separately.
Since one of the main properties of the computer should be clarity, I chose a relay with a transparent body and a built-in LEDs. In addition, they look beautiful, it allows you to not install the extra LEDs for indicating the input signals.
After the start of assembly of the computer I'm reading one of the blogs, realized that I was missing the protective diodes, prevents arcing and knocking indicators when open relays. So I bought 100 pieces 1N4448 diodes and solder them in parallel with each of the coils.
Materials
Since the computer has to be clear, why should he not be beautiful? Harry used for mahogany body. I found a suitable material merbau wood , in the form of planed boards of the same thickness.
All components are mounted on a 6 mm sheet of Plexiglas. Relays are glued, and everything else, or is installed in a specially drilled holes, or screwed. Plates with inscriptions carved brass. The most difficult part was to find the appropriate size brass screws for mounting plates. In Russia, the book did not work anywhere else, but then I almost accidentally found them in a hobby store in Helsinki.
Job
I began by saying that he had bought the power supply, three dozen relay, wires, and switches to control inputs and the internal signals generated by the ALU. Relays contain 4 DIP switches. In some cases, all 4 switches are not used, but save by using a relay with a smaller number of contacts received hardly.

These relays have cost me about 200 rubles, so I started looking for cheaper options, as the whole unit ALU according to preliminary estimates of their required about 100 pieces. One batch of 100 pieces I was able to order at wholesale price slightly more than $ 100 for the relay. But this supplier themselves appear relay should not be soon, so I continued to search.
It turned out that the relay can be ordered directly from China is much cheaper. I ordered another batch of 100 pieces for about $ 1 apiece (dollar then cost around 30 rubles). Later it turned out that some relay received from China, obviously defective. For example, the following picture shows that the wires inside the relay been reversed. Fortunately, for correction of this bug was enough similarly reversed external connections to the relay.

Moreover, there were many relay oxidised. In some cases it proved critical, and had to throw relay. But sometimes it still managed to throw the inputs and outputs to other contacts - played a role redundancy relay with 4 switches.
In the manufacture of the body had to learn some simple work on the processing of timber, but most of the time took brazing - for many of the relay had to solder wires to all 14 pins.
Results
Article was not very long and slightly superficial. More information can be found on the project website . If the community will be interested, I can write more about the characteristics and principles of operation as the ALU, and the projected computer.
From the moment that I decided to make my computer, it's been a year and a half. During this time I broadly designed architecture and instruction set, and also created the first computer module - arithmetic logic unit. Formally, of course, in the ALU used semiconductors - in LEDs for indication and protection diodes. But the logic is built on electromechanical relays. In this unit lacks only the external connections, but I'll do after the other blocks will appear, which will connect the ALU. Next I plan to make a block of registers.

Statistics
ALU consists of 88 relay debug signals are fed with 43 toggle switches, the outputs are displayed using 70 LEDs. Unit Dimensions - 74x56x14 centimeters.
Relay with defects of various kinds was found about 10. Just count difficult, as some remained in slightly altered about this scheme.
Costs
- Relay - 6120
- LEDs - 2660
- Toggle Switches - 1510
- Power supply - 2520
- Cable and other Details - 1220
- Inscription (materials, engraving, and hardware) - 3340
- Materials for housing - 4300
- Total - 21670 b >
What can we do better
At the end of the first module of my computer, I came to realize that some things could be done better:
- Probably, the number used in the ALU relay could be reduced by combining modules addition and subtraction. I think that in this way could save 8 relays.
Links
Project website: sourceforge.net/p/relay
Other computers:
Harry Porter's Relay Computer: web.cecs.pdx.edu/ ~ harry / Relay / li > Relay Computer Two: www.electronixandmore.com/projects/relaycomputertwo/index.html RC-3 Relay Computer: www.computerculture.org/projects/rc3/ Edmund Berkeley's Simon Relay Processor: www.cs.ubc.ca/ ~ hilpert / e / simon / index.html TIM: www.northdownfarm.co.uk/rory/tim/tim-8.htm DUO 14 Premium: www.ostracodfiles.com/ostracod/relay.html Relay computer «trainer»: relaysbc.sourceforge.net/ i² 8-Bit Relay Computer: isquared.weebly.com/ Kilian Leonhardt's relay computer: www.relaiscomputer.de/ Der Relaisrechner: www.schlaefendorf.de/relaisrechner/dokumentation/index.html Ul>
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/220865/
The Government of Denmark has created a model country in Minecraft in 1: 1 scale
Mom's wisdom guard your marketing