688
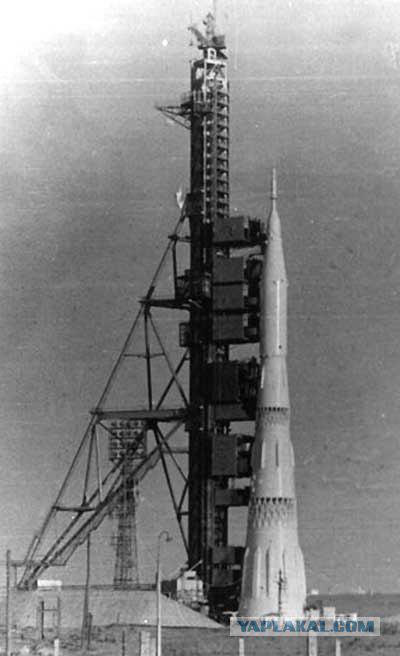
Soviet launch vehicle (H-1)
13 ph.
The Soviet draft of the lunar launch vehicle (H-1)
It is fragmentary and incomplete information can sometimes be seen in the various sources of information about the Soviet lunar program.

2. The program was launched after the policy statement of US President Kennedy in 1962 about the intentions before the end of the decade to land US astronauts to the moon on the program "Apollo".

3. The main political objective of this program was the desire to restore American prestige as a great space power (the first satellite and the first cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin was launched in the USSR).

4. Two of the world system - the capitalist and socialist continued competition in the space field. It was a political, scientific and economic race. In response to the US initiative in the Soviet Union began to work on the creation of a powerful carrier rocket, capable to bring to the moon manned spacecraft.

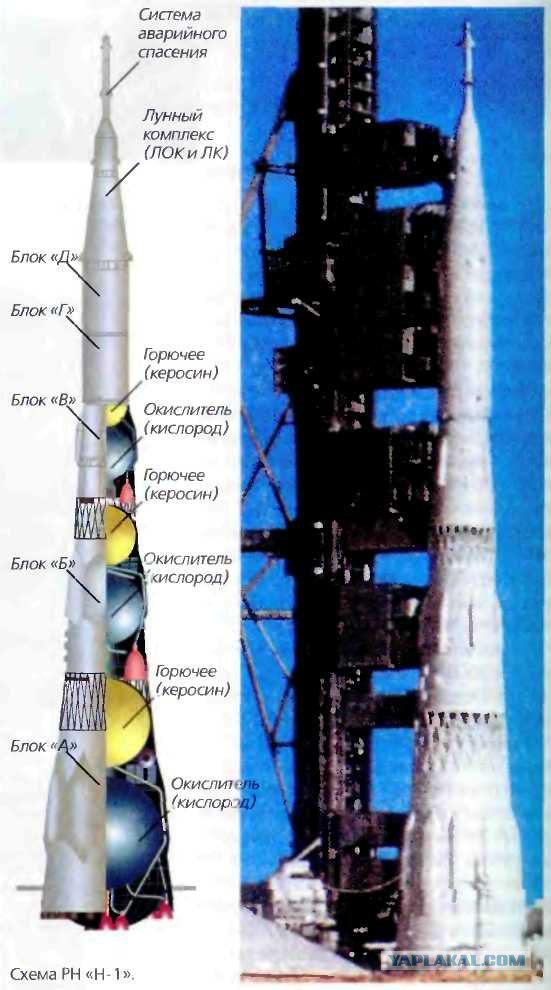
5. The project was named the H-1 (11A52). The development produced by OKB-1. Home work was led by SP Queen.
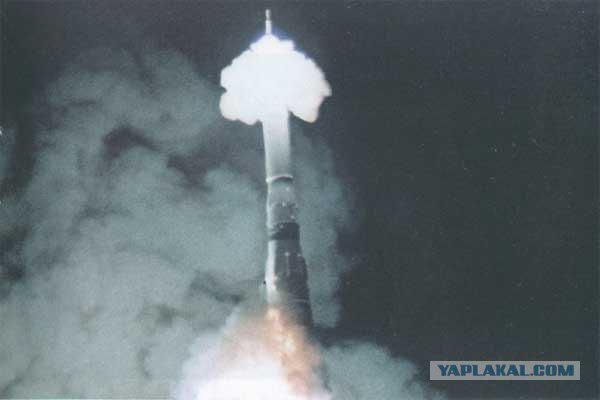
6. There were made four starts booster H-1 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome: 1) 2/20/69 2) 7/3/69 3) 7/27/71 4) 11/23/72 Unfortunately, all of them They were unsuccessful. By the end of 1972, the Americans have started to turn off the program "Apollo". Further work on the H-1 project was terminated.

7. Some specifications of the rocket:
• The weight of the payload into orbit output from 75 to 95 tons.
• Total weight: 2 682 tonnes.
• Length: 76, 6 m.
• The maximum diameter of 10 m.
The rocket had 4 stages (in the version for the flight to the Moon - 5 stages).
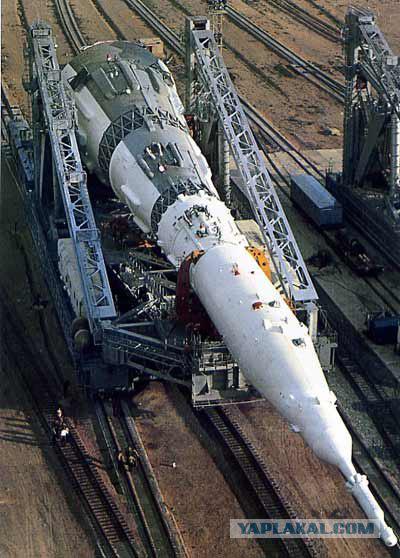

8. According to the United States, July 21, 1969 Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin landed on the moon. The main reason for stopping the lunar program of the USSR - the lack of a powerful booster similar to the American "Saturn-5," created under the direction of Wernher von Braun (designer of the German V-2, who worked for the United States after World War II).

9. The Soviet lunar orbiter consisted of a lander, the orbital module, which was located a special compartment with engines orientation and approach and docking system units, instrument-aggregate compartment cylindrical shape with a tapered "skirt", which was located a block and a missile, and power supply system for oxygen-hydrogen fuel cells.

10. Household compartment served concurrently airlock when moving astronauts in lunar ship through the open space (after donning a spacesuit lunar "Merlin").
Installing the H-1 launch pad.

11. During the start of the fourth set, the first stage work practically without remarks to 106, 93, when there was a failure of the pump motor oxidant N4, which led to the accumulation of the mixture
By the fifth launch of complex N1-L3 N 8L have been developed and have been all kinds of ground tests mnogoresursnye engines (11D111, 11D112 and 11D113) increased reliability, mounted on a missile after firing tests without bulkheads. However, the fifth launch did not take place, all for the same reason, the United States completed their program of lunar flight of spacecraft "Apollo 17" and the political interest in the lunar program was gone.

12. It is appropriate to mention one detail. Usually after the alarm starts organized search for the fallen parts of carrier rockets and GB. And when one of these searches was found the layout of the lunar ship, which stood alone in the wilderness on their regular four "legs", a little buried in the sand. The ship did not have much of any damage, except for small dents and deformations.
In June 1974 works on the complex N1-LZ were discontinued. The existing reserve was destroyed, the costs have been written off (in prices of the 70's costs amounted to 4 billion. Rub.).

13. Probably the death of the brilliant designer SP Queen in 1966, has served as one of the reasons for the failure of the project H-1.
The layout of the H-1, you can see at the Museum of Central House of Aviation and Cosmonautics.

Source:
The Soviet draft of the lunar launch vehicle (H-1)
It is fragmentary and incomplete information can sometimes be seen in the various sources of information about the Soviet lunar program.

2. The program was launched after the policy statement of US President Kennedy in 1962 about the intentions before the end of the decade to land US astronauts to the moon on the program "Apollo".

3. The main political objective of this program was the desire to restore American prestige as a great space power (the first satellite and the first cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin was launched in the USSR).

4. Two of the world system - the capitalist and socialist continued competition in the space field. It was a political, scientific and economic race. In response to the US initiative in the Soviet Union began to work on the creation of a powerful carrier rocket, capable to bring to the moon manned spacecraft.

5. The project was named the H-1 (11A52). The development produced by OKB-1. Home work was led by SP Queen.

6. There were made four starts booster H-1 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome: 1) 2/20/69 2) 7/3/69 3) 7/27/71 4) 11/23/72 Unfortunately, all of them They were unsuccessful. By the end of 1972, the Americans have started to turn off the program "Apollo". Further work on the H-1 project was terminated.

7. Some specifications of the rocket:
• The weight of the payload into orbit output from 75 to 95 tons.
• Total weight: 2 682 tonnes.
• Length: 76, 6 m.
• The maximum diameter of 10 m.
The rocket had 4 stages (in the version for the flight to the Moon - 5 stages).

8. According to the United States, July 21, 1969 Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin landed on the moon. The main reason for stopping the lunar program of the USSR - the lack of a powerful booster similar to the American "Saturn-5," created under the direction of Wernher von Braun (designer of the German V-2, who worked for the United States after World War II).

9. The Soviet lunar orbiter consisted of a lander, the orbital module, which was located a special compartment with engines orientation and approach and docking system units, instrument-aggregate compartment cylindrical shape with a tapered "skirt", which was located a block and a missile, and power supply system for oxygen-hydrogen fuel cells.

10. Household compartment served concurrently airlock when moving astronauts in lunar ship through the open space (after donning a spacesuit lunar "Merlin").
Installing the H-1 launch pad.

11. During the start of the fourth set, the first stage work practically without remarks to 106, 93, when there was a failure of the pump motor oxidant N4, which led to the accumulation of the mixture
By the fifth launch of complex N1-L3 N 8L have been developed and have been all kinds of ground tests mnogoresursnye engines (11D111, 11D112 and 11D113) increased reliability, mounted on a missile after firing tests without bulkheads. However, the fifth launch did not take place, all for the same reason, the United States completed their program of lunar flight of spacecraft "Apollo 17" and the political interest in the lunar program was gone.

12. It is appropriate to mention one detail. Usually after the alarm starts organized search for the fallen parts of carrier rockets and GB. And when one of these searches was found the layout of the lunar ship, which stood alone in the wilderness on their regular four "legs", a little buried in the sand. The ship did not have much of any damage, except for small dents and deformations.
In June 1974 works on the complex N1-LZ were discontinued. The existing reserve was destroyed, the costs have been written off (in prices of the 70's costs amounted to 4 billion. Rub.).

13. Probably the death of the brilliant designer SP Queen in 1966, has served as one of the reasons for the failure of the project H-1.
The layout of the H-1, you can see at the Museum of Central House of Aviation and Cosmonautics.

Source:























