839
Kalinin NPP.
A look from the inside. Machine rooms.
Kalinin NPP is situated in the north of Tver region on the shores of Lake Udomlya near the same city. It is the closest nuclear power plant to Moscow - distance from the Moscow Ring Road 330 km. The station consists of 3 units of VVER-1000 power 1000MVt each. Units built and commissioning gradually in 1985, 1987, 2005.
Currently, the works on the construction of the 4th unit of the same type, it will be put into operation this year. VVER (water-water) were developed at the Kurchatov Institute since the 1950s, under the leadership of Kurchatov. The first unit of this type was launched at Novovoronezh NPP in 1964. BMU VVER-1000 are the most common ekspluataruemyh worldwide. Learn more about them here.
Kalinin NPP takes the electricity generated in the 8 regions of Russia, including Moscow, Leningrad, Tver and Vladimir.
20 photos
via Docent

02
Before the entrance to the museum there is such installation

03
Here you can see the layout of Kalinin NPP with a description of all its units.

04
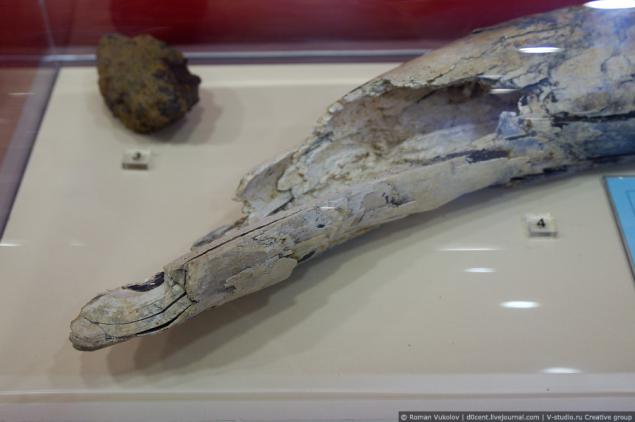
Mammoth tusk and other archaeological finds discovered during the construction of the station.

05
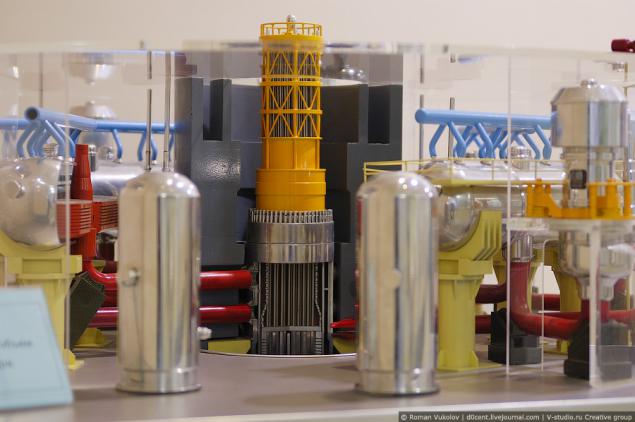
and of course models of VVER sectional

06
as well as other components in the composition of the first circuit.

07
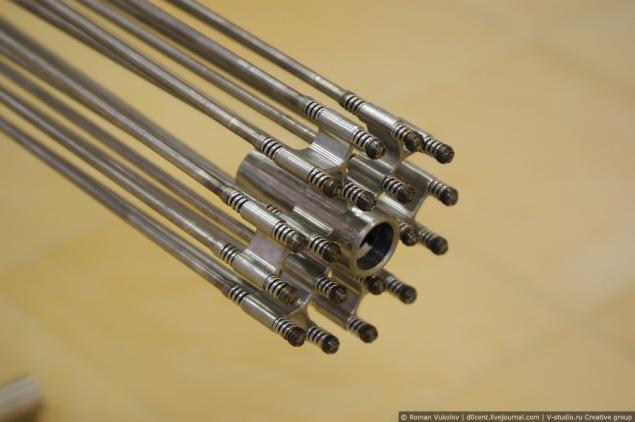
And this is a real TVEL (fuel element): the main element of a heterogeneous core of a nuclear reactor. (exposed as the sample).

08
In TVEL is a division of the nuclei 235U (Uranium-235), 239Pu (Plutonium-239) and 233U (Uranium-233), with the release of heat.

09
Fuel elements (cartridges) - the main structural component of a heterogeneous core of a nuclear reactor containing the nuclear fuel. The fuel rods occurs fission of heavy nuclei 235U, 239Pu or 233U, accompanied by the release of heat energy, which is then transferred to the heat carrier. The fuel rods consist of fuel core, sheath and end fittings. Type of fuel element is determined by the type and purpose of the reactor coolant parameters. TVEL is to provide a reliable heat transfer from the fuel to the coolant.
Most modern power reactors (VVER, RBMK), fuel rod is a rod diameter of 9, 1-13, 5 mm and a length of several meters.
Read more here

10
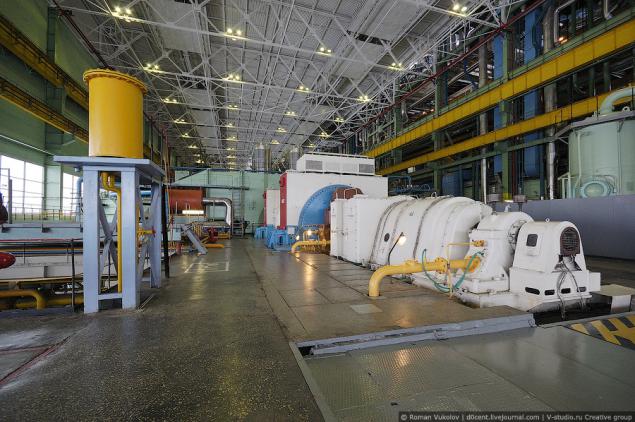
The machine room consists of two levels: at the top are the generators and turbines at the bottom - condensers, pumps and piping. In a nutshell, it works all the way: the reactor converts the energy released in a chain reaction of nuclear fission of uranium in the thermal energy of the coolant (water) of the first circuit. The heated coolant is supplied by means of circulating pumps in the steam generators where part gives its heat to the water of the second circuit. Produced in the steam generators steam enters the steam turbine that drives the turbine generator that produces electricity (source Wikipedia).

11
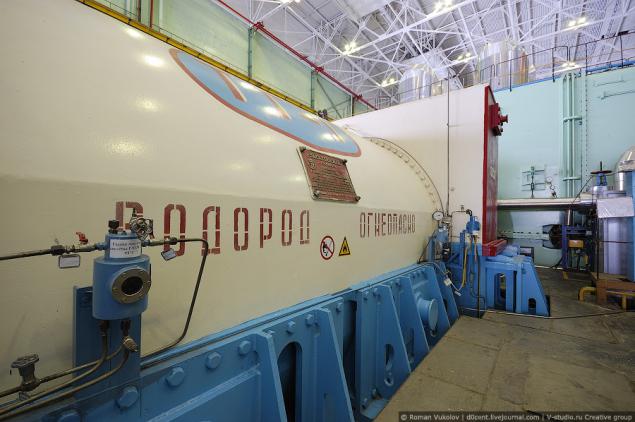
Turbogenerator.

12

13
Capacitors.

14
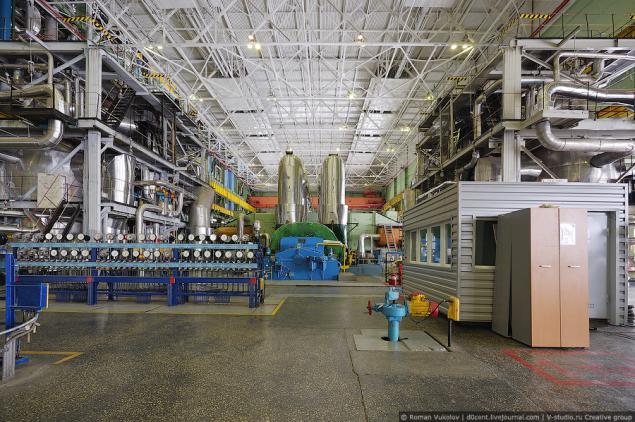
Workers in the hall is not a lot - the system is controlled remotely from the control panels.

15
It can be clearly seen both the level of the machine room.
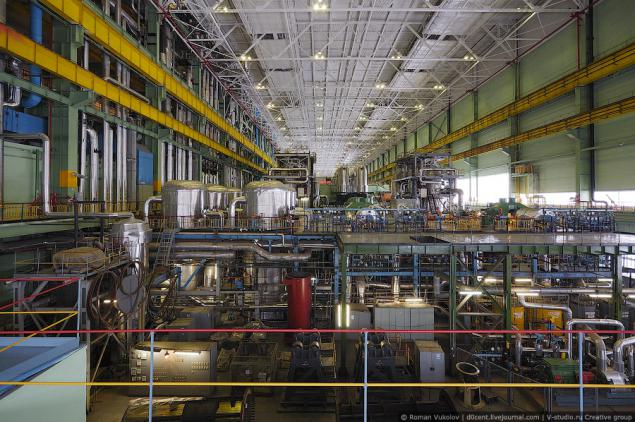

16
In the next room is a turbine, is the second in complexity and importance of the unit at the nuclear plant.

17.
Here, the thermal energy is converted into electrical energy.

18.
It is so large and powerful that the floor is shaking constantly underfoot.

19
On the territory of the Kalinin nuclear power plant, as well as on the territories of many other large enterprises are several bunkers for the temporary shelter personnel in case of emergency situation. It not only can stay for several days, but also to monitor the radiation environment on the surface, keep in touch, including the video to the outside world. However, the equipment for monitoring environmental conditions established in silos and the clock used currently. You can be calm - the radiation background in the territory of the Kalinin NPP and around Udomlya is within normal limits, and it is even lower than in Moscow.
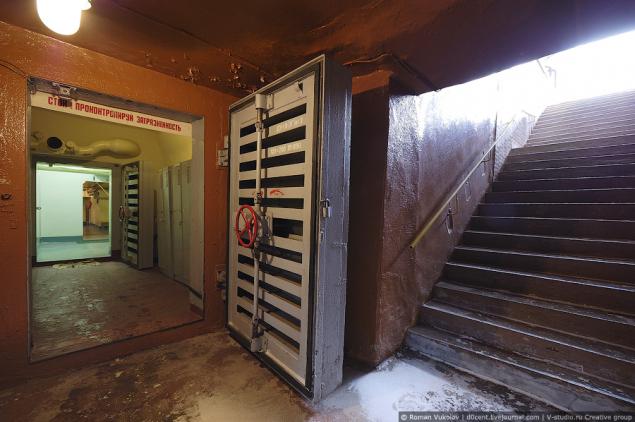

20
For each employee the station previously separate fixed bed.

Source:
Kalinin NPP is situated in the north of Tver region on the shores of Lake Udomlya near the same city. It is the closest nuclear power plant to Moscow - distance from the Moscow Ring Road 330 km. The station consists of 3 units of VVER-1000 power 1000MVt each. Units built and commissioning gradually in 1985, 1987, 2005.
Currently, the works on the construction of the 4th unit of the same type, it will be put into operation this year. VVER (water-water) were developed at the Kurchatov Institute since the 1950s, under the leadership of Kurchatov. The first unit of this type was launched at Novovoronezh NPP in 1964. BMU VVER-1000 are the most common ekspluataruemyh worldwide. Learn more about them here.
Kalinin NPP takes the electricity generated in the 8 regions of Russia, including Moscow, Leningrad, Tver and Vladimir.
20 photos
via Docent

02
Before the entrance to the museum there is such installation

03
Here you can see the layout of Kalinin NPP with a description of all its units.

04
Mammoth tusk and other archaeological finds discovered during the construction of the station.

05
and of course models of VVER sectional

06
as well as other components in the composition of the first circuit.

07
And this is a real TVEL (fuel element): the main element of a heterogeneous core of a nuclear reactor. (exposed as the sample).

08
In TVEL is a division of the nuclei 235U (Uranium-235), 239Pu (Plutonium-239) and 233U (Uranium-233), with the release of heat.

09
Fuel elements (cartridges) - the main structural component of a heterogeneous core of a nuclear reactor containing the nuclear fuel. The fuel rods occurs fission of heavy nuclei 235U, 239Pu or 233U, accompanied by the release of heat energy, which is then transferred to the heat carrier. The fuel rods consist of fuel core, sheath and end fittings. Type of fuel element is determined by the type and purpose of the reactor coolant parameters. TVEL is to provide a reliable heat transfer from the fuel to the coolant.
Most modern power reactors (VVER, RBMK), fuel rod is a rod diameter of 9, 1-13, 5 mm and a length of several meters.
Read more here

10
The machine room consists of two levels: at the top are the generators and turbines at the bottom - condensers, pumps and piping. In a nutshell, it works all the way: the reactor converts the energy released in a chain reaction of nuclear fission of uranium in the thermal energy of the coolant (water) of the first circuit. The heated coolant is supplied by means of circulating pumps in the steam generators where part gives its heat to the water of the second circuit. Produced in the steam generators steam enters the steam turbine that drives the turbine generator that produces electricity (source Wikipedia).

11
Turbogenerator.

12

13
Capacitors.

14
Workers in the hall is not a lot - the system is controlled remotely from the control panels.

15
It can be clearly seen both the level of the machine room.

16
In the next room is a turbine, is the second in complexity and importance of the unit at the nuclear plant.

17.
Here, the thermal energy is converted into electrical energy.

18.
It is so large and powerful that the floor is shaking constantly underfoot.

19
On the territory of the Kalinin nuclear power plant, as well as on the territories of many other large enterprises are several bunkers for the temporary shelter personnel in case of emergency situation. It not only can stay for several days, but also to monitor the radiation environment on the surface, keep in touch, including the video to the outside world. However, the equipment for monitoring environmental conditions established in silos and the clock used currently. You can be calm - the radiation background in the territory of the Kalinin NPP and around Udomlya is within normal limits, and it is even lower than in Moscow.

20
For each employee the station previously separate fixed bed.

Source: