263
Mysteries of the cosmos: 5 phenomena that science still can not explain

Introduction: Secrets that the universe hides
Space is a vast space full of mysteries that challenge the human mind. Despite all the achievements of science, many cosmic phenomena remain unexplained. From dark matter, which makes up most of the universe, to mysterious fast radio bursts that last only milliseconds, these phenomena have scientists scratching their heads.
In this article, we will look at five of the most intriguing cosmic mysteries that have not yet found their explanation. Why are they important to science? What can they tell us about the nature of the universe? Let's go on a journey through the unknown corners of space.
1. Dark Matter: The Invisible Mystery
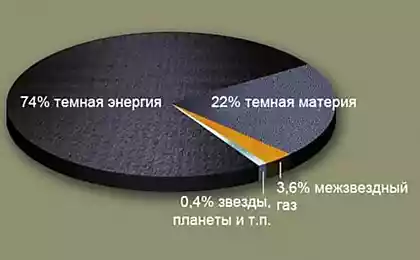
Dark matter is one of the biggest mysteries of modern astrophysics. Scientists estimate that it makes up about 85 percent of all matter in the universe, but it’s impossible to see or record directly. Its existence is only proved by its gravitational influence on visible objects such as galaxies and stars.
What is dark matter? What is it made of? These questions remain unanswered. Some theories suggest that it consists of unknown particles that do not interact with light. However, all attempts to detect these particles have not yet been successful.

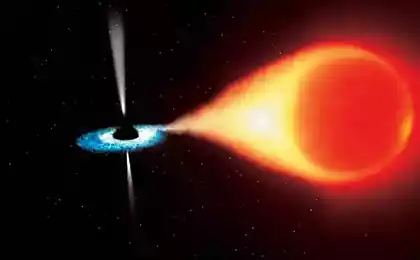
2. Quasars: The Luminous Monsters of the Universe
Quasars are some of the brightest objects in the universe. They are located in the centers of galaxies and emit a huge amount of energy. Scientists believe that the source of this energy are supermassive black holes that absorb surrounding matter.
However, the nature of quasars is not fully understood. How do they form? Why can their brightness change over short periods of time? These questions remain the subject of active research. Quasars not only help us study black holes, but also serve as beacons for exploring the early universe.
3. Fast radio bursts: Signals from deep space
Fast radio bursts (FRBs) are short but powerful radio signals that last only a few milliseconds. They come from distant galaxies, but their source is still unknown. Some scientists speculate that they may be associated with neutron stars or even alien civilizations.
Although the first FRBs were discovered in 2007, their nature remains a mystery. Why are they so short-lived? What causes such powerful bursts of energy? Answering these questions could change our understanding of the cosmos.

4. Dark Energy: The Mysterious Force of the Universe's Expansion
Dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that is responsible for the accelerated expansion of the universe. It makes up about 68% of all the energy in the universe, but its nature remains unknown. Scientists suggest that dark energy may be associated with the vacuum of space or with new physical laws.
Why is the universe expanding with acceleration? What is dark energy? These questions are among the most complex in modern cosmology. Understanding dark energy can help us predict the future of the universe.
5. The Great Attractor: The Mystery of Gravitational Anomaly
The Great Attractor is a gravitational anomaly that attracts galaxies, including our own Milky Way. It is about 220 million light-years from Earth, but its nature remains a mystery. Scientists suggest that it may be a supermassive cluster of galaxies or even a manifestation of dark matter.
What is hidden in the center of the Great Attractor? Why does he have such an attractive force? These questions continue to excite the minds of astronomers. Studying this anomaly could shed light on the structure and evolution of the universe.
Conclusion: Space is an eternal mystery
Space continues to amaze us with its secrets. From dark matter to fast radio bursts, each of these phenomena raises new questions for science. But it is these mysteries that make the study of the universe so fascinating.
Perhaps one day we will find answers to these questions. In the meantime, space remains for us an endless field for exploration and discovery. As Carl Sagan said, “Somewhere something incredible is waiting to be discovered.”
Why We Fear Change and How to Learn to Accept It
The History of Things: How Ordinary Objects Changed the World