696
Who is a Forex broker and what is its function in the market?

The Forex broker is the intermediary between the trader and the Forex market. Simply put, without a broker, there would be no access to the interbank market. For the services provided, the broker charges a small fee in the form of a commission or spreads. In most cases, both commission and spreads are part of a Forex broker's income.
The idea of brokerage is to help the trader to be active in the market, regardless of whether the trades are profitable or losing. It is in the broker's best interest to have active traders as this is the only way to earn commissions. If traders stop trading, or if traders quickly lose their deposits, the broker will also lose business. Thus, making a profit is both in the interests of the forex broker and in the interests of the trader. In any case, you should always pay attention to the reviews of traders, for example, the broker eToro.
Types of Forex Brokers
Forex brokers fall into two main categories: market makers or brokers who outsource their trades to liquidity providers. Brokers falling into the first category are dealing bureaus, while others are non-dealing counters. A true Forex broker is a broker that fits into the second category because that is the true meaning of a brokerage house: intermediate access to the interbank market. When it comes to market makers, there is a fine line between ethics and business practices.
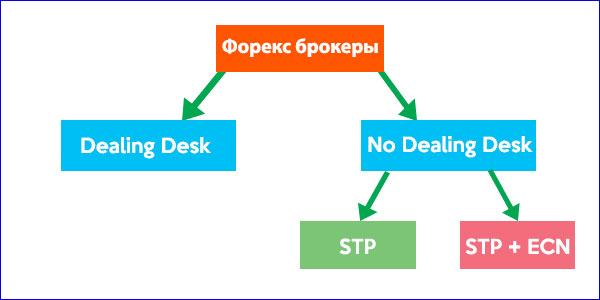
Brokers STP (Straight Through Processing)
This type of broker transfers or routes their trader's trades to liquidity providers for execution. Most STP brokers have their own trading department and divide traders into two categories. Traders who have a chance to survive in the Forex market or be profitable, and traders who are more likely to lose their deposit.
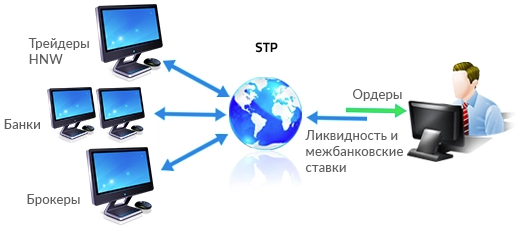
Those likely to be the winner will receive their orders from liquidity providers and the forex broker will switch sides of the trade for other traders. How can a Forex broker know in advance if a person is going to be a winner or a loser? There are things that can show in advance what the chances of a trader are to be a winner or a loser. For example, if a trader's initial deposit is small, chances are he will end up losing.
This was just an example, but the general verification process is more complex and based on many other things. As you can see, the STP broker operates in the so-called gray zone, but, nevertheless, the business is better organized than the brokerage of a single market maker.
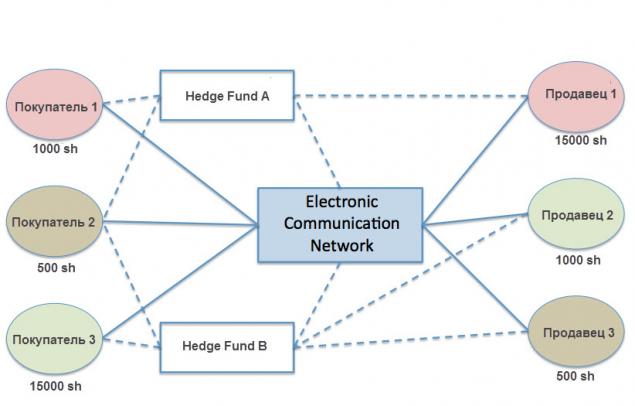
ECN (Electronic Communications Network)
With such a broker, traders can effectively see the interbank market. Other parties in the interbank market may take the opposite side of their trades, and such parties are other Forex brokers, institutional investors, other liquidity providers, banks, etc. compared to other types of brokers. Especially if the pending order is filled during an important economic release, the execution has some flows.

For this reason, few brokers are true ECNs, it is more likely that the broker will be a mixture between ECN and STP.