442
The reverse side of the Internet — a huge energy loss

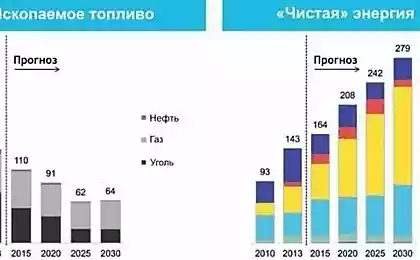
Currently, approximately 14 billion electronic devices connected to the Internet worldwide, annually wasted consume electricity worth about 80 billion dollars due to inefficient technologies, and by 2020, the estimated expenditure for the lost electricity will rise to $ 120 billion a year, according to a study published by the International Energy Agency.
According to the report, in 2013, the electronic devices connected to the Internet, such as modems, printers and game consoles, consumed amount of energy in the 616 terawatt - hours, in most cases, the devices were in standby mode. In addition, about 400 terawatts was wasted because of imperfections in the technology.
"The problem is not that these devices are often in standby mode, but rather that they use more electricity than necessary to support communication and data exchange in the network," said Director of the IEA, Maria van der Hoeven.
"Only through the use of more modern technologies available nowadays, such devices can perform the same functions in the standby mode, while consuming 65% less energy," she added.
The IEA reports that electricity consumption is increasing as network connectivity spreads to devices such as refrigerators or washing machines. Thus, according to experts, the number of devices that have access to the network will reach 50 billion units by 2020 and 100 billion in the next decade.
In this regard, energy efficiency of devices connected to the network, can save the amount of energy equal to 600 TWh, which is equivalent to 200 standard coal-fired power plants with a capacity of 500 megawatts.
Source: www.ecology.md