702
10 microscopic events with huge impacts on the Ground

The earth is very old and very big, and for many centuries it has accumulated many microscopic details that are not always possible to discern. Modern technologies demonstrate incredible view of tiny things that are either left over from the major natural and human events in the past or continue to keep the planet in check to this day.
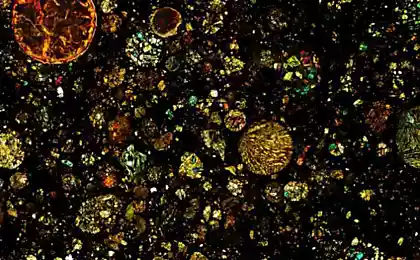
Freeze-frame of the formation of the Solar system
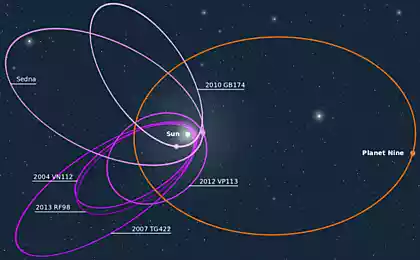
It's a thin slice of meteorite age four and a half billion years. Round spots, called chondrules (chondrule), to determine the name of these meteorites — chondrites. Today chondrites show scientists exactly how formed the Earth and the rest of the Solar system.
Chondrites older than dust, dirt and sand, literally. They were formed when the Solar system was just a cloud of interstellar dust, some of which melted in Hendry. The rest began to gather together into large objects with greater gravity. This process continued until the center of the cloud is not lit star — our Sun. What is left from dust and chondrules, became planets, moons, asteroids and comets.
After that, all planets and most moons have become large enough to develop independently. Original material to date remains, therefore, chondrites are important to study.
The asteroids and some other objects were too small to continue to evolve, and just hovered in the Solar system for billions of years, occasionally breaking and falling to the Ground. Now scientists know that bright Hendry, shown above, included in the material from the original interstellar cloud of dust, which formed our Solar system.
Possible blocks of life in space
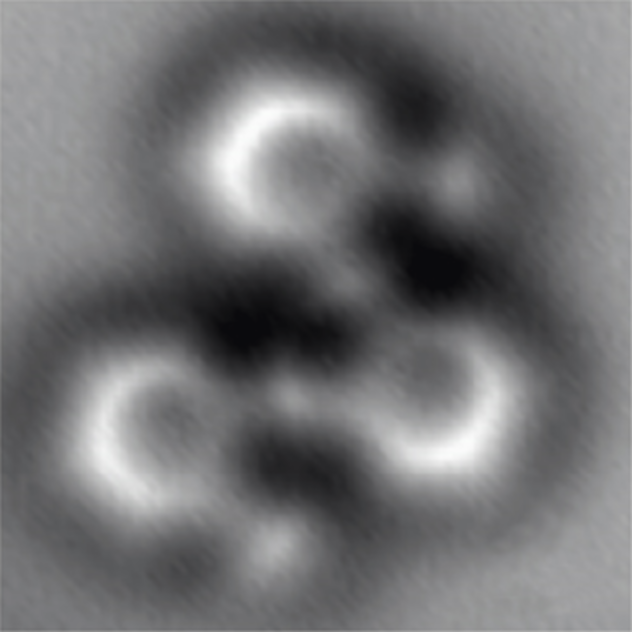

It's blurry and seems unfocused image is a real equivalent chemical formulas that you have seen in textbooks. It is made using a very interesting tool — "non-contact atomic force microscope" and shows atoms of carbon and hydrogen, linked together in three benzene rings.
Astrobiologists like hexagonal benzene structure, because it can gather a variety of types of molecules that can be found in space, including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). These and other organic molecules based on carbon is almost half of the dust and gas clouds, floating between the stars.
Because the basis of life on Earth is carbon, extremely interesting, not whether it came from these interstellar organic molecules. No one knows for sure, but NASA scientists made a startling discovery, studying PAH. They subjected the pyrimidine material like PAU, exposed to harsh space conditions reproduced in the laboratory. This resulted in uracil, cytosine and thymine — three material found in the genetic material of all life forms on Earth.
One day the experts will find out what started life on Earth. But we already know that since the emergence of life has undergone several mass extinctions. Perhaps worst of all were the following.
Cyanobacteria: cell, gave the Earth oxygen
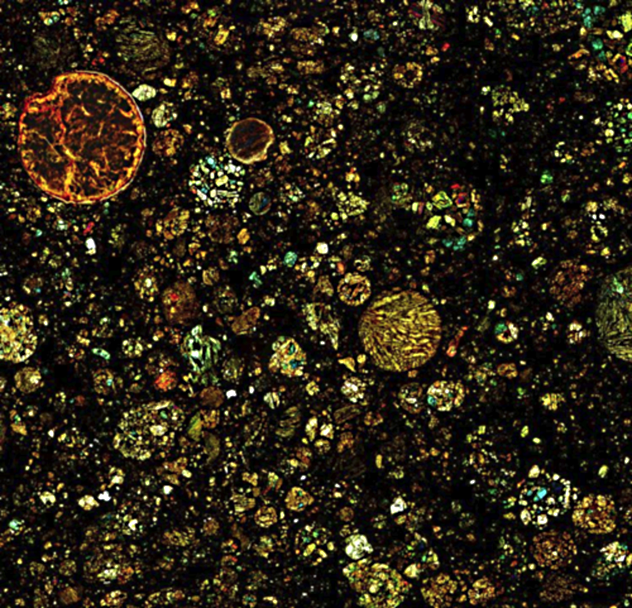
In this picture is exactly what you think: a bunch of bacterial cells under the microscope. These creatures were known as blue-green algae, but today are called "cyanobacteria". The first amazing fact about these cells: they are a billion years. The researchers extracted them from geological deposits in Australia age of a billion years, along with 29 other species.
How can bacteria leave fossils? More cyanobacteria and other bacteria have a thick cell wall. They live in mats that are layered structures — stromatolites and oncolites. Ancient stromatolites, being cut into extremely thin plates, sometimes reveal fossilized cyanobacteria — like in this picture.
Another amazing fact is that without these cyanobacteria in the picture and without any other similar to them, life on Earth as we know it, would not exist. In her youth the Earth's atmosphere resembled the smoke-filled air of the moon of Saturn the Titan. He was toxic modern life, but some microbes, including cyanobacteria, could get along with him. Approximately 2.3 billion years ago cyanobacteria evolved the ability to live off sunlight through photosynthesis. One of the side effects of photosynthesis is oxygen which was deadly to germs, prefer able. Because cyanobacteria were exceedingly many, so-called Oxygen catastrophe changed the atmosphere of the planet and likely caused a mass extinction on Earth. However, it also laid the Foundation for modern animals and plants.
There was another powerful event — the Great extinction — after which almost all life on Earth disappeared. One of the reasons for this extinction was...
The Siberian traps

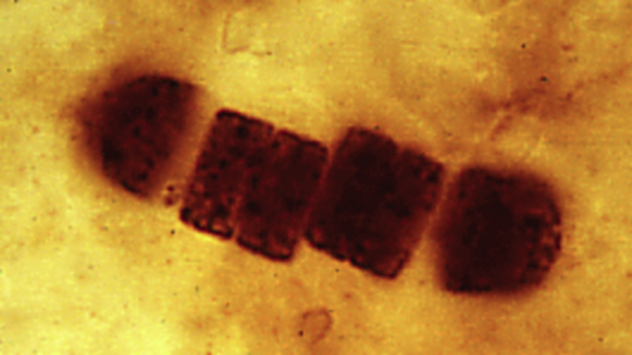
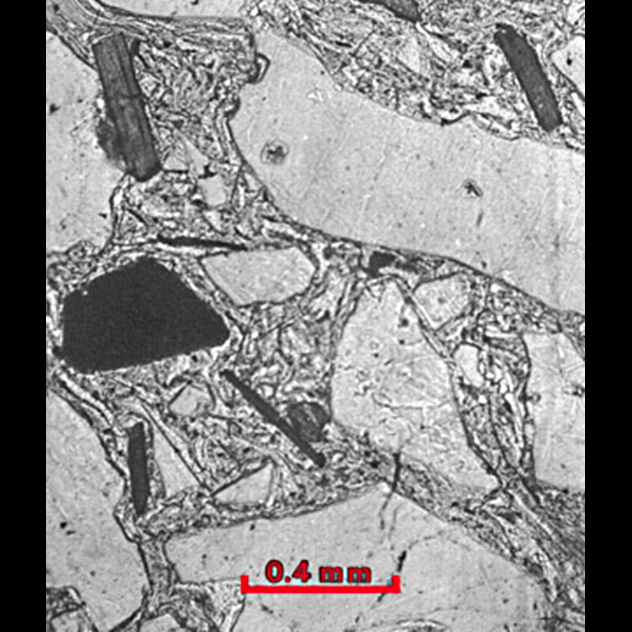
So geologists call a thin slice of rock is very thin. If you look at it under a microscope using polarized light, the color can be used to identify different minerals.
This thin section of a leucocratic gabbro. The white part of the picture — the mineral plagioclase, and blue — amphibole. Please note, as the minerals melted together; they are stuck in the flow of the black material, which can represent sluggish current, like Hawaiian lava, from left to right in this picture.
Once the material was spread in the Hawaiian style lava from the ground on the territory of what is now Siberia about 250 million years ago. The flooding of the Siberian traps occurred during the Permian period, almost simultaneously with the largest mass extinction of life on Earth. Basalt flood lasted one million years. There was a lot of lava — enough to drown Siberia under a kilometer-thick.
The earthly life had hard times. Although during the Great extinction is manifested and other factors, gases and the ash from the eruption blocked sunlight, and the lava escaped poisonous gases, poison the air and water. During this period on Earth disappeared 93-97% of life.
Some believe that the flood was caused by a mantle plume; others think that it is related to plate tectonics. Siberian lava silent, but silence is her deadliest crystals eloquently. The earth goes through cycles of life and death. Some are written in its rocks, but the atmosphere of record stores. Or stores?
The Earth's atmosphere 420 000 years ago
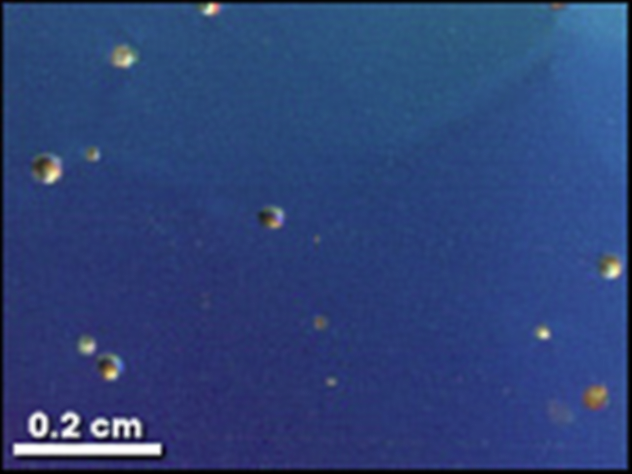
These tiny air bubbles appear in the water. They were frozen in the ice hundreds of thousands of years ago. Analysis of air and tell scientists much about the ancient climate of the Earth as it changed over time and how it may change in the future.
As the air trapped in the ice and how to determine its age? Snow crystals catch the air as you fall to the Ground. If the snow melts, it turns into a glacier with air bubbles. Sometimes glaciers move horizontally, floating in the water and the earth, but vertical, their location does not change. Thus, scientists can determine the age of various horizontal ice layers without carbon Dating — younger layers are always on top. Actually, it was determined that the air bubbles found in ice cores of Antarctica and Greenland, contain particles of the atmosphere by the age of 420,000 years.
Changes in the amount of carbon dioxide in the air would definitely affect the climate. Today it is considered a big problem, but, fortunately, the tiny sea creatures help us to cope with it.
The main processor of carbon
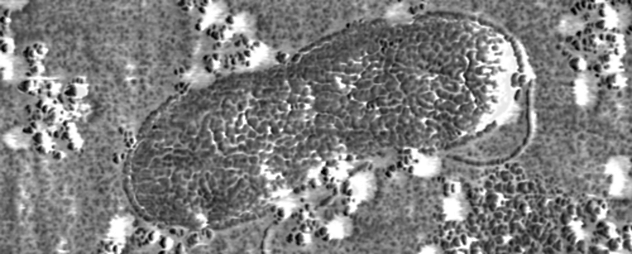
It's not a satellite image of a forest with a road around it. This is a microscopic view of Alteromonas, a newly discovered bacteria, which play an important role in retaining carbon dioxide (CO2) under control.
Carbon exists everywhere on Earth. It is present in the air in a certain concentration, which help to control the earth's oceans. Sea water absorbs and releases atmospheric carbon dioxide. The plankton feeds on coal, which is absorbed. When they die, their bodies sink to the bottom of the ocean, where they feed on bacteria. Then, the bacteria release carbon dioxide, which eventually returns to the Earth's atmosphere.
At least scientists think so. A large part of the process takes place deep under the ocean, where scientists can't reach it. It was once thought that the process involved many different bacteria. Recently, however, found that some Alteromonas eat for seven. This discovery greatly facilitated the creation of a model of the carbon cycle in the ocean.
Plants age of nine million years

Plants help to keep the atmosphere breathable. Pieces top is instantly fossilized plants during the fall of a meteorite millions of years ago. Scientists have no idea how an organic substance could withstand so much heat. Due to this discovery, we know that life on Mars, if it ever was, could be preserved in the same way.
Here's what happened: a series of seven different space objects fell on the territory of present-day Argentina about nine million years ago. The land there was covered by a powdery soil called loess, which melted quickly and turned into glass. The researchers conducted a series of experiments, and after several mishaps, it was found that at a temperature of about 1480 degrees Celsius water in the outer layers of plants absorbs enough heat to protect the internal fragile structure. Something similar happens when you bake food.
Mars is also covered with loess and has many craters. For billions of years on the red planet are no lakes and rivers, but once might have been. Mars could have life, and it is likely that in the case of coincidence, the fall of the meteorite, it could also protect the glass of loess, as in the case of plants on Earth.
Freeze-frame the largest of the recent eruptions

This picture is similar to a close - "Starry night" by van Gogh, but in reality it is another geological thin section of volcanic rock. Only there are a lot of sharp corners. This eruption was violent, this is not a sluggish Hawaiian lava.
Large pieces are broken fragments of minerals. They are in the molten rock that flowed around. If you look closely, you can see a dark void in the sawn stone that stretches like melted caramel.
It is a small piece of the super eruption of Toba, held about 75 000 years ago. This eruption was the largest in the history of mankind, throwing 2900 cubic kilometers of magma and three trillion kilograms of sulfur into the sky. Mineral crystals scattered into the chip, when the explosion occurred. After a few seconds they were prisoners in a hot gassy volcanic ash. The gas dissipates quickly, leaving spaces in the ash particles, which appear black in polarized light. Tens of thousands of years later, geologists study these pieces and marvel at the cruelty of war. The ash from the eruption scattered over East Africa over 7000 km.
The fire coaches
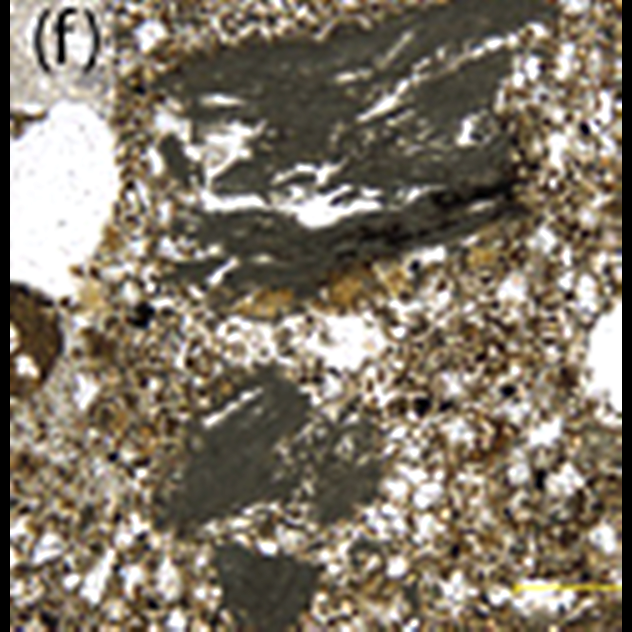
In this picture it's simple. The yellowish-brown stuff is dirt, particles lighter — ashes of a wood fire, and dark grey — material plants, which was partially burned. Surprisingly, this is proof that people tamed fire a million years ago — much earlier than expected.
Assessment the exact dates of the domestication of fire has always been shaky. It's hard to say whether the ancient layers of ash remnants of a forest fire, or appeared in the process of cooking. A few years ago, used the advanced technology of the ashes. Ashes took from the hearth in a cave in South Africa aged a million years. He was intact and could not be the result of natural processes. Were found near stone tools.
Before us the ashy remains of plants that someone, perhaps Homo erectus, brought to the cave one million years ago. And he was not a vegetarian, because the burned bones were also discovered nearby.
Dominion over fire has become a cornerstone in our conversion to the owners of the Land, which we feel today. However, are we really the owners? Scientists are beginning to understand that the largest mass of living organisms on Earth may in fact be hiding in the rocky crust under the oceans. And these tiny creatures are called...
Endolite

The simplest way to call these tiny green things: "mineral Twisted stems produced by iron oxidizing bacteria, extracted in experiments by incubation of minerals from wells Juan de Fuca".
The important word here is well. Scientists drilled the seabed and discovered that there are bacteria. The inhabitants of these tiny stones called andalite was there before. They live in a stone and eat it. Scientists have long known about them, but only recently began to suspect that andalites on the Ground can be very, very much.
A large part of the Earth is covered by oceanic crust. The ocean floor consists of basaltic lava that erupts at mid-ocean ridges and then moves it from the ridges along a kind of conveyor belt. There is a lot of water and heat necessary for the prosperity of life on earth. In addition, the life aquatic feels great in the mid-ocean ridges at hydrothermal vents. Why would it not flourish within the seabed?
Now imagine that all oceanic crust inhabited by living beings. The scientists who made this the green stems of andalites, I believe that the seabed may be more biomass than land and sea combined.published
Source: hi-news.ru