644
Mind reading has become closer to reality
Create a map of the brain regions that are responsible for understanding different words
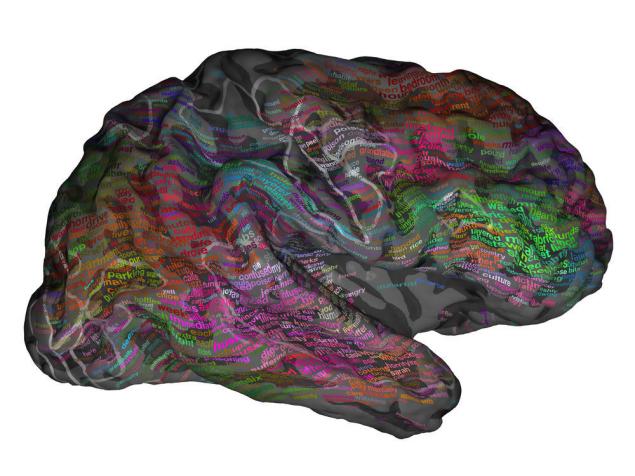
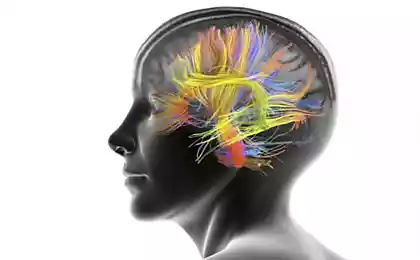
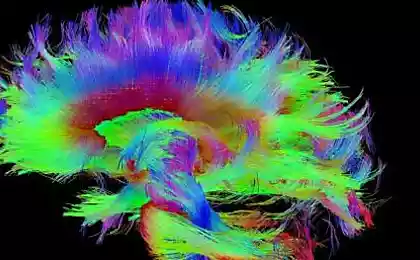
The group of neuroscientists from the University of California at Berkeley for the first time in the world was "semantic atlas" of the cerebral cortex. It not only shows where it is processed by the values of different words, but also demonstrates that the semantic processing of words involves large areas of the brain, not just the individual sections in the left hemisphere.
From previous studies it was known that the same parts of the brain are activated when processing different words meaning the same group.
Authors of new research have gone further. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging, they examined the brain activity of seven volunteers while listening to a large fused text, not single words and phrases, as in previous studies. For several hours the brain activity recorded in each volunteer MRI apparatus. Such a long and detailed study has allowed to identify in detail what specific areas of the brain are activated and at what point.
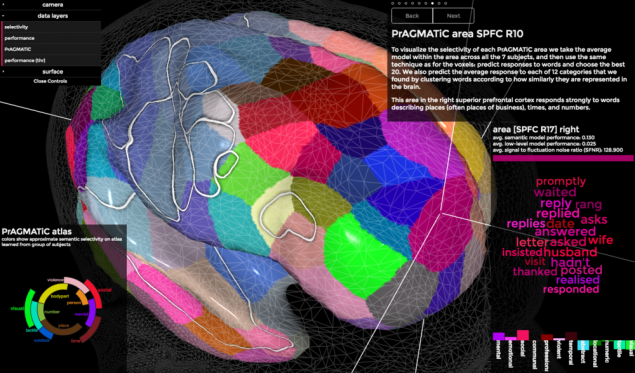
Scientists were able to determine which areas of the brain responsible for processing of words related to numbers, visual images, social phenomena, different professions, emotions, people, geographical objects, etc. Total identified 12 thematic categories, which were very similar for all participants in the experiment. For example, the lateral parietal cortex is responsible for the sense of the words associated with the people, and its surrounding areas - for the processing of numbers and words related to visual images
.
According to some experts, it is a big step to a real reading thoughts.
"Our semantic models predict well how large regions of the cortex react to the sounds of the language. Moreover, we can now get more specific information, which allows us to determine which brain regions are responsible for the representation of a word. That is why we believe that this technology is a huge potential ", - said Alex Hut (Alex Huth) from the University of California at Berkeley
. By combining brain scans of seven people using statistical modeling, the scientists made a three-dimensional atlas of the brain. Interactive version of the atlas is published here.
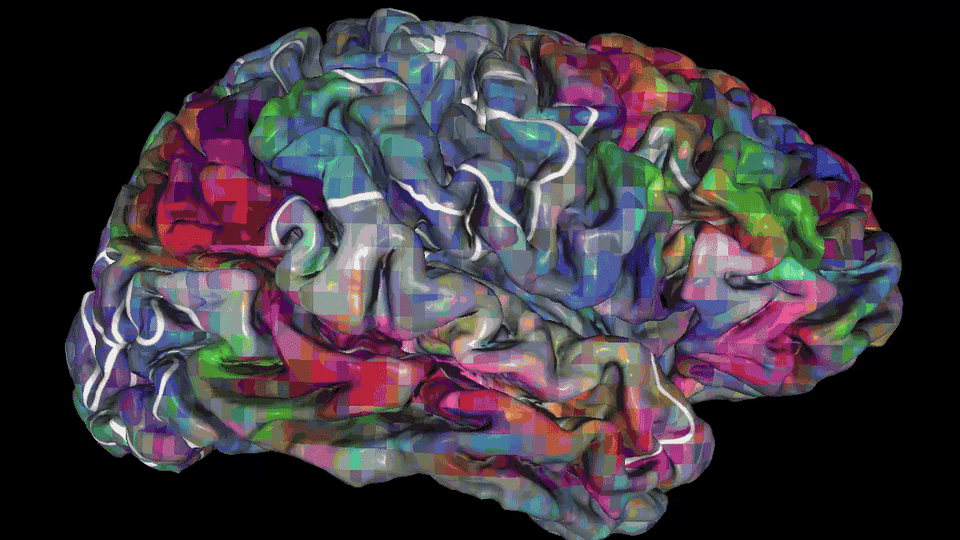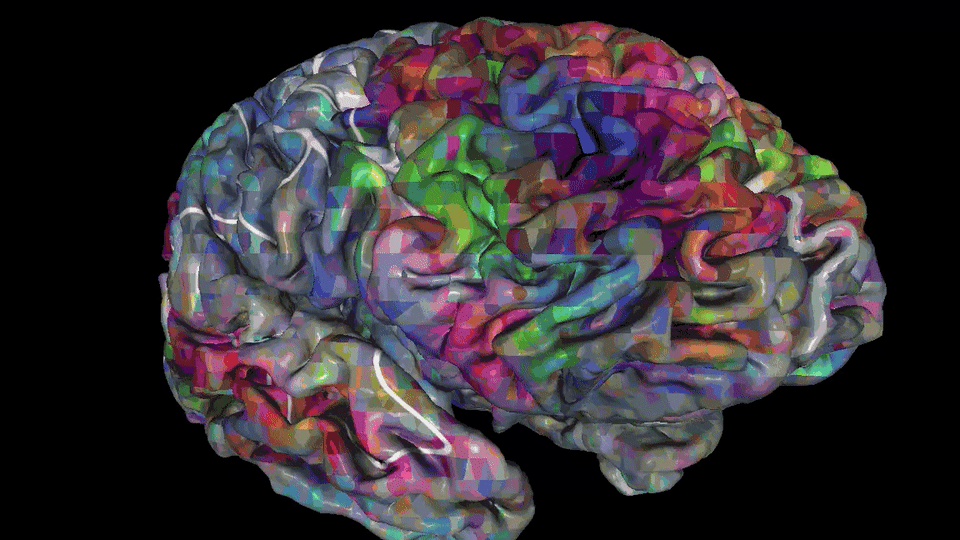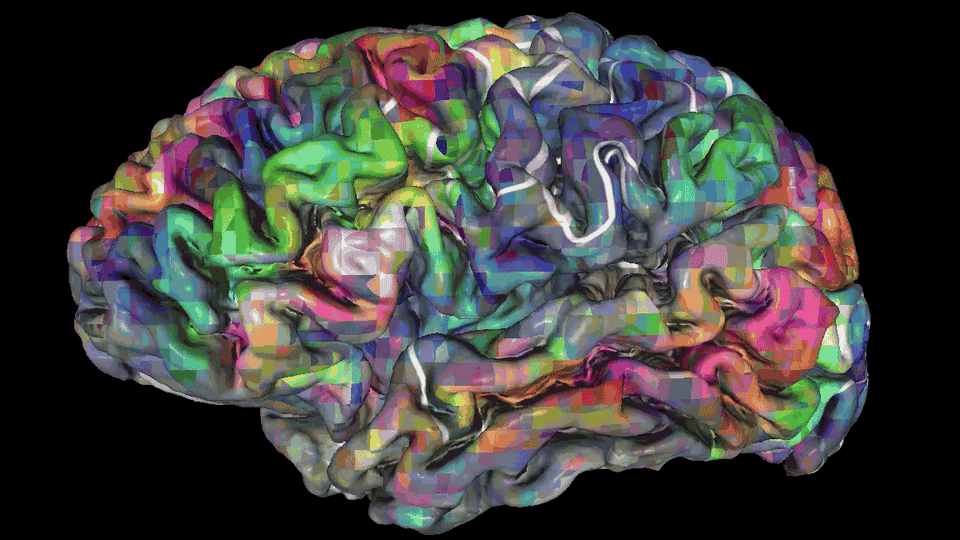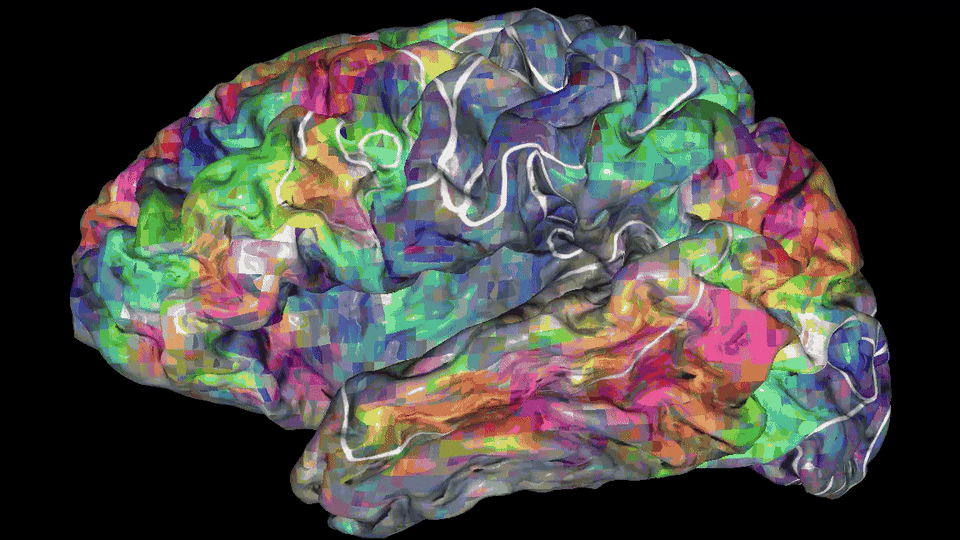
Depending on the meaning of words, their treatment will involve one or more of 100 individual parts of the cerebral cortex in both hemispheres.
According to the scientists, with the help of advanced brain scanners, for example, suffered a stroke people will be able to communicate their thoughts and feelings to others, even if they damaged the brain does not control the vocal apparatus.
Semantic atlas will help in the study of various diseases related to brain injuries. We will understand how these diseases affect speech and understanding of speech.
In addition, the atlas allows you to understand about the brain scans at that person reads a text and hear what they think.
It is too early to talk about some kind of "universal language map" in the cerebral cortex, because the scan was performed in all seven volunteers. Moreover, they all - English speakers to give the same way voice data through a voice synthesizer. In the future, scientists will expand the experiment to check whether the processing by the brain meanings of words different people from different cultures, reading instead of listening to the text, as well as people in an altered state of consciousness.
Scientific work published April 27, 2016 in the journal Nature (doi: 10.1038 / nature17637; pdf).
Source: geektimes.ru/post/275110/

The group of neuroscientists from the University of California at Berkeley for the first time in the world was "semantic atlas" of the cerebral cortex. It not only shows where it is processed by the values of different words, but also demonstrates that the semantic processing of words involves large areas of the brain, not just the individual sections in the left hemisphere.
From previous studies it was known that the same parts of the brain are activated when processing different words meaning the same group.
Authors of new research have gone further. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging, they examined the brain activity of seven volunteers while listening to a large fused text, not single words and phrases, as in previous studies. For several hours the brain activity recorded in each volunteer MRI apparatus. Such a long and detailed study has allowed to identify in detail what specific areas of the brain are activated and at what point.
Scientists were able to determine which areas of the brain responsible for processing of words related to numbers, visual images, social phenomena, different professions, emotions, people, geographical objects, etc. Total identified 12 thematic categories, which were very similar for all participants in the experiment. For example, the lateral parietal cortex is responsible for the sense of the words associated with the people, and its surrounding areas - for the processing of numbers and words related to visual images
.

According to some experts, it is a big step to a real reading thoughts.
"Our semantic models predict well how large regions of the cortex react to the sounds of the language. Moreover, we can now get more specific information, which allows us to determine which brain regions are responsible for the representation of a word. That is why we believe that this technology is a huge potential ", - said Alex Hut (Alex Huth) from the University of California at Berkeley
. By combining brain scans of seven people using statistical modeling, the scientists made a three-dimensional atlas of the brain. Interactive version of the atlas is published here.

Depending on the meaning of words, their treatment will involve one or more of 100 individual parts of the cerebral cortex in both hemispheres.
According to the scientists, with the help of advanced brain scanners, for example, suffered a stroke people will be able to communicate their thoughts and feelings to others, even if they damaged the brain does not control the vocal apparatus.
Semantic atlas will help in the study of various diseases related to brain injuries. We will understand how these diseases affect speech and understanding of speech.
In addition, the atlas allows you to understand about the brain scans at that person reads a text and hear what they think.
It is too early to talk about some kind of "universal language map" in the cerebral cortex, because the scan was performed in all seven volunteers. Moreover, they all - English speakers to give the same way voice data through a voice synthesizer. In the future, scientists will expand the experiment to check whether the processing by the brain meanings of words different people from different cultures, reading instead of listening to the text, as well as people in an altered state of consciousness.
Scientific work published April 27, 2016 in the journal Nature (doi: 10.1038 / nature17637; pdf).
Source: geektimes.ru/post/275110/