646
Superzrenie babies

In three or four months old, the child has the ability to see such fine details in the picture of the world that no adult will ever notice. But after the fifth month of life little man begins to lose the ability to super-vision, - said the researcher Suzanne Martinez-Conde.
But, in truth, is not particularly jealous of babies is about this: the loss of the ability of super-vision is explained by the development of other skills - to recognize what is really worth, and what is not worth attention
.
For example, when an adult looks at the image below snails, they are the first to notice the similarity of brilliant specimens A and B. With the snail does not shine, so it takes a separate position. But baby, if I could speak, would say that snails and C the most common. Adults it is difficult to see, but it is the snail And here unlike instance - its surface reflects a completely different lighting conditions. Infants are very sensitive to the most seemingly insignificant changes in the picture.
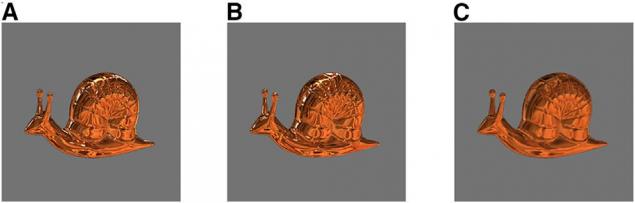
"Over time, we learn to ignore certain types of changes to be able to identify the same object as a constant in a variety of the most diverse situations," - says Martinez-Conde. So, in other words, due to the loss of the super-view, we were able to learn the same snail, as if it did not fall on the light.
A series of experiments confirmed this hypothesis, the research team conducted in Tokyo (Japan), with the participation of 42 children aged between three and eight months. As talk at this age children can not yet, scientists have recorded changes in their perception of the image by measuring the time that the baby looks at a particular picture.
Previous studies have shown that babies are the longest-held view of the objects that appear to be new to them, while the familiar objects given only a cursory glance.
Using this method, the researchers found that three or four month old children to notice the difference in pixel intensity and much less react to the difference between glossy and matte surfaces. However, closer to seven or eight months the children have lost the ability to distinguish the intensity of pixels, and in general, their perception of the image approaching the perception of an adult.
Another study found that children younger than six months can easily distinguish between monkeys only by their physiognomy, while the nine-month only able to distinguish people by their faces.
Your text to link ...