813
DARPA creates an alternative to terrestrial GPS and other innovative projects

One of the most promising projects DARPA: System Airborne Launch Assist Space Access (ALASA) to deliver satellites to 45 kg into orbit worth up to $ 1 million to launch, while satellites are sent from an airplane in the upper atmosphere i>
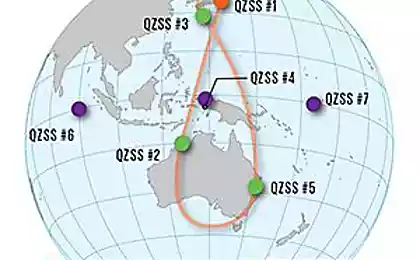
Research agency DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) promulgated plan (pdf, 41 p.) A > on advanced scientific and technological developments for the future (such reports published every two years). There's a lot of interesting things, and among them - a fundamentally new Global Positioning System navigation and time synchronization , which does not depend on satellites and defies jamming as GPS.
The design of the new system has not been defined (see discussion geopositioning systems. P. 30-31 of the report). One option involves the installation of hundreds of thousands of transmitters. Such an infrastructure is very difficult to deploy, and then serve.
Another option - a differential GPS, which is now used in the navy. But in this case still uses satellite signals, so that it is vulnerable to jamming.
Another technique - LORAN, ground-based radio navigation system, which was first used during World War II. Now it has been renewed interest because it really is protected from jamming. But it has a drawback: the positioning accuracy is not high enough.
The document DARPA is not clear what exactly it is going to bring the system up to date. But it is clear that it will not need a satellite. The document says: "The need to operate effectively in areas where GPS is unavailable, unreliable or potentially vulnerable to intruders, requires the creation of alternatives for precise navigation and time synchronization. To do this, DARPA is investing in a revolutionary new technologies that have the potential to ensure the accuracy of GPS, navigation and time synchronization for military purposes, including innovative inertial measuring devices, which use interferometry to cold atoms, with self-calibrating chip gyroscopes, accelerometers and watches, as well as pulse -Laser atomic clocks and microwave sources ».
Whatever it was, but after decades of such systems can be used and civilians, including it can be implemented in mobile phones and car navigators.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/248020/