1298
Microwaves guard weather forecasts, or that such a scatterometer
It's no secret that the wind blows just because the trees sway. However, the guys from NASA JPL (and not only them) have decided to go further than the famous comedy hero "Business People", and successfully studied the wind right out of space. How so? About this talk under the cut.

According to the tradition of attaching personal video that I translated and voiced specifically for this article. In it everything is explained as simply and without unnecessary details.
A few words about terminology: there are two almost equivalent concepts: reflectometry i> and scatterometer i>. However, I propose to call the study the Earth's surface from space is scatterometer, to avoid confusion with the translation and adaptation.
In simple terms, scatterometer - a method of measuring the size and shape of the object (usually - the relief of any surface) on the basis of how an object reflects and scatters light. Consequently, the scatterometer - is a microwave radar, which provides "fire" a beam of light and tries to catch the reflected rays.
Scatterometer can operate from space, for example, the trailer to the satellite, as well as during air travel within the earth's atmosphere, Nestled under the belly of the aircraft. To scan using the microwave, so NASA employees jokingly call phones "microwaves».
It is worth noting that the devices long and carefully calibrated, the error in the measurement of the reflected-scattered rays are very important. That's why NASA plans to use the already running scatterometers to accelerate the process of calibration of their latest device: RapidScat.
RapidScat - the most advanced and technologically scatterometer, which is scheduled for launch at the end of this year. SpaceX Dragon will bring the machine to the ISS, where it will begin to fulfill its primary function - to scan the surface of the Okan and seas. Any special requirements of the mission is not, however, NASA has formed for its "microwave" several purposes.
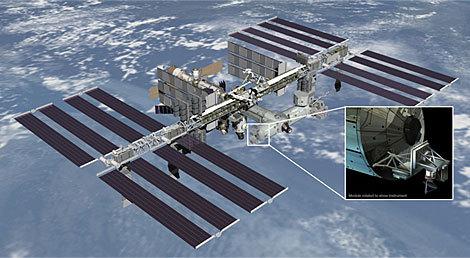
RapidScat, Attached to the International Space Station i>
Objectives RapidScat:
1) Create a new platform for the constellation scatterometers
RapidScat should provide a new platform for the calibration, which will improve the stability and accuracy of the data received by the rest of the scatterometer operating in Earth orbit.
2) To investigate the diurnal and semi-diurnal wind cycles in the ocean, as well as the evaporation of water from the surface of the Earth.
3) provide data for weather forecasting and sea storms, as well as data for the introduction of time cycles in space.
Besides the problem of studying winds RapidScat involved a constellation scatterometers: Seasat Scatterometer (SASS), launched in 1978, launched by the European Space Agency in 1991 European Remote-Sensing Satellite ERS-1, armed equipment Advanced Microwave Instrument (AMI), as well as running after the first ERS-2 (1995). In 1996 NASA launches the first NASA Scatterometer (NSCAT).
First scanning scatterometer, launched NASA, also known as ' SeaWinds ', entered "at work" in 1999. After him, in 2002, followed by a NASDA ADEOS-2 ASCAT In addition, the Indian space agency launched its own unit in 2009.
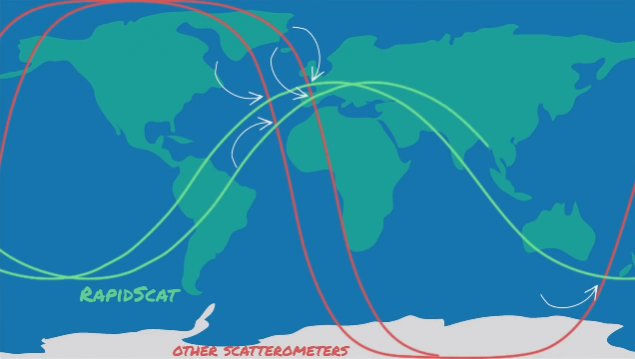
Crossing paths scatterometers and ISS i>
Thus, at the end of this year, NASA expects to begin to address the problems of meteorology and calibration of the entire constellation of devices.
The importance of such studies is due to the fact that we still call some of the physical phenomena of "mystery of nature».
The data obtained from ocean scatterometers will help scientists to better explore the interaction between atmosphere and ocean, ocean circulation, and their influence on global weather and climate.
These data can also be used to study the unusual weather such as Эль-Ниньо, long-term effects of tropical deforestation and changes in ice masses around the polar regions. All these phenomena play a central role in regulating the global climate.
When writing notes following materials were used:
About Scatteromerty by NASA JPL
Ocean Wind program by NASA JPL
Scatterometer on Wikipedia i>
P.S. It would be nice to supplement статью scatterometer on Wikipedia in Russian: the method itself, and the program deserves more detailed consideration.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/223419/

According to the tradition of attaching personal video that I translated and voiced specifically for this article. In it everything is explained as simply and without unnecessary details.
A few words about terminology: there are two almost equivalent concepts: reflectometry i> and scatterometer i>. However, I propose to call the study the Earth's surface from space is scatterometer, to avoid confusion with the translation and adaptation.
In simple terms, scatterometer - a method of measuring the size and shape of the object (usually - the relief of any surface) on the basis of how an object reflects and scatters light. Consequently, the scatterometer - is a microwave radar, which provides "fire" a beam of light and tries to catch the reflected rays.
Scatterometer can operate from space, for example, the trailer to the satellite, as well as during air travel within the earth's atmosphere, Nestled under the belly of the aircraft. To scan using the microwave, so NASA employees jokingly call phones "microwaves».
It is worth noting that the devices long and carefully calibrated, the error in the measurement of the reflected-scattered rays are very important. That's why NASA plans to use the already running scatterometers to accelerate the process of calibration of their latest device: RapidScat.
RapidScat - the most advanced and technologically scatterometer, which is scheduled for launch at the end of this year. SpaceX Dragon will bring the machine to the ISS, where it will begin to fulfill its primary function - to scan the surface of the Okan and seas. Any special requirements of the mission is not, however, NASA has formed for its "microwave" several purposes.

RapidScat, Attached to the International Space Station i>
Objectives RapidScat:
1) Create a new platform for the constellation scatterometers
RapidScat should provide a new platform for the calibration, which will improve the stability and accuracy of the data received by the rest of the scatterometer operating in Earth orbit.
2) To investigate the diurnal and semi-diurnal wind cycles in the ocean, as well as the evaporation of water from the surface of the Earth.
3) provide data for weather forecasting and sea storms, as well as data for the introduction of time cycles in space.
Besides the problem of studying winds RapidScat involved a constellation scatterometers: Seasat Scatterometer (SASS), launched in 1978, launched by the European Space Agency in 1991 European Remote-Sensing Satellite ERS-1, armed equipment Advanced Microwave Instrument (AMI), as well as running after the first ERS-2 (1995). In 1996 NASA launches the first NASA Scatterometer (NSCAT).
First scanning scatterometer, launched NASA, also known as ' SeaWinds ', entered "at work" in 1999. After him, in 2002, followed by a NASDA ADEOS-2 ASCAT In addition, the Indian space agency launched its own unit in 2009.

Crossing paths scatterometers and ISS i>
Thus, at the end of this year, NASA expects to begin to address the problems of meteorology and calibration of the entire constellation of devices.
The importance of such studies is due to the fact that we still call some of the physical phenomena of "mystery of nature».
The data obtained from ocean scatterometers will help scientists to better explore the interaction between atmosphere and ocean, ocean circulation, and their influence on global weather and climate.
These data can also be used to study the unusual weather such as Эль-Ниньо, long-term effects of tropical deforestation and changes in ice masses around the polar regions. All these phenomena play a central role in regulating the global climate.
When writing notes following materials were used:
About Scatteromerty by NASA JPL
Ocean Wind program by NASA JPL
Scatterometer on Wikipedia i>
P.S. It would be nice to supplement статью scatterometer on Wikipedia in Russian: the method itself, and the program deserves more detailed consideration.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/223419/