1648
Superfast star reveals the secrets of dark matter
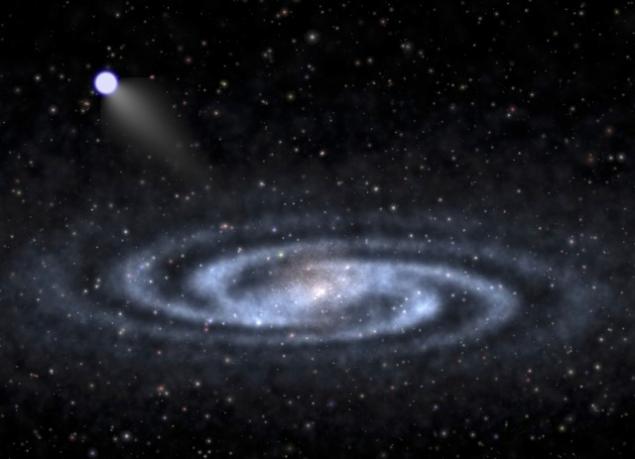

The artistic representation of the Milky Way and star bullet that flies almost perpendicular to the plane of our galaxy i>
Astronomers from the University of Utah found ultrafast star LAMOST-HVS1 , which in many ways stands out among the two dozen such strange stars, seen so far ( first ultrafast star discovered in 2005). Firstly, it is the second luminance among them. Second, is the closest to us. Third, it flies much faster than conventional high-speed stars. These features allow the use of LAMOST-HVS1 as a tool for scientific measurements.
LAMOST-HVS1 moves at a speed of about 2 to 25 million km / h relative to the solar system and about 1, 77 million km / h relative to the center of our galaxy. It is interesting that her age, scientists estimate only 32 million years, which can be called infancy by stellar standards.
LAMOST-HVS1 lies about 42400 light years from Earth and 62,000 light years from the galactic center. Although she could fly far enough, but the star still represents exceptional value for science. Most importantly, it will allow to test the theory of the existence of dark matter halos around galaxies.

Photo ultrafast stars found among pictures Sloan Digital Sky Survey i>
A halo of dark matter (dark matter halo) - hypothetical component of the galaxy surrounding the galactic disk and extends far beyond the visible area. According to calculations of scientists, the mass of dark matter in the halo must exceed the total mass of the visible galaxies. Although dark matter is, by definition, can not be observed directly, but the presence of her as we can judge by some specific interactions with other objects, including interstellar gas and the individual stars. According to scientists, only 5% of the mass of the universe belongs to the visible matter. Another 27% is invisible (dark matter), and the remaining 68% - even more mysterious dark energy, introduced in cosmology to explain the fact of the universe's expansion.
Draw a path around the galaxy, LAMOST-HVS1 provide information on the impact of external forces on it, including the hypothetical dark matter halo.
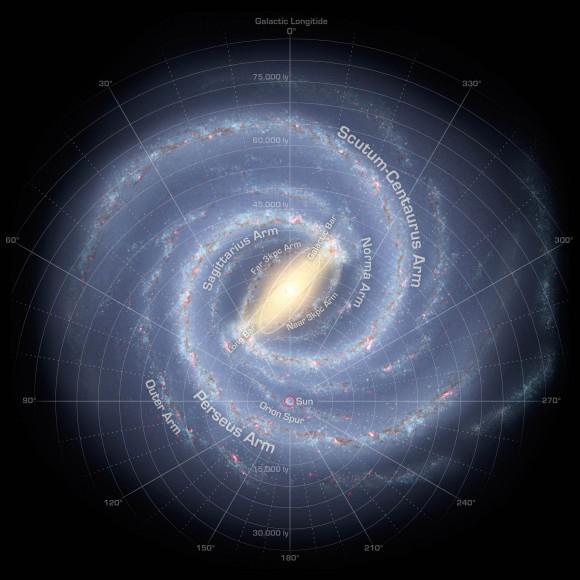
The Milky Way and the approximate location of the Sun i>
The diameter of the visible part of the Milky Way is a spiral galaxy is at least 100 000 light-years. If you add a halo of dark matter, the diameter increases to 1 million light years.
Over the past decade, scientists have discovered about 20 bullet stars that for some strange reason, it is quickly removed from our galaxy. One of the most likely versions - they broke up an exceptionally large size black hole at the center of the Milky Way, the presence of which also has not yet been confirmed. Nevertheless, the search for new high-speed stars and calculate their trajectories can provide data on the presence of such a black hole and its characteristics. It is assumed that its mass about 4 million times the mass of the sun.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/222699/