1128
Dark matter can collide with the atoms in our bodies more often than expected
Invisible dark matter particles may regularly pass through our bodies, and tens of thousands of these particles can collide with the atoms of our every year, according to new research. However, the radiation from these impacts is unlikely to cause cancer, the researchers added.
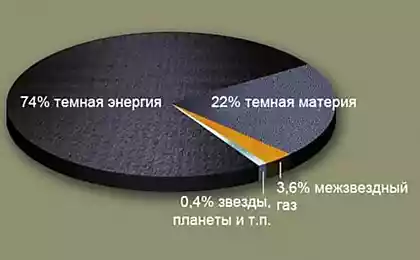
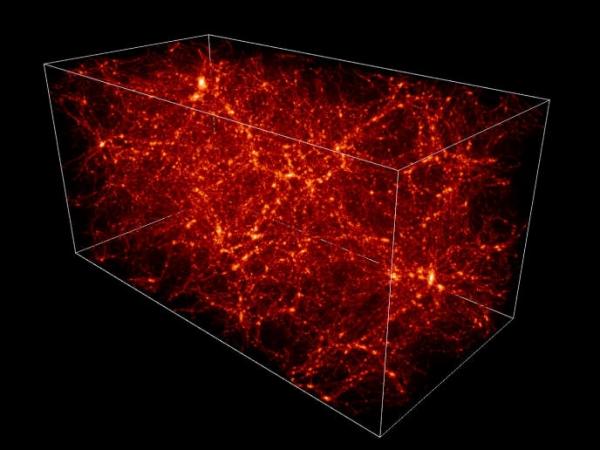
Dark matter - one of the biggest scientific mysteries of our time - the invisible substance that is thought to be five-sixths of all matter in the universe. Scientists think it may be composed of particles called weakly interacting massive particles, or a WIMP, which normally interact with gravity, but very weakly with all other known forces of the universe.
Their ghostly character makes it extremely difficult to direct evidence, there is dark matter really, or what its actual properties. Dark matter how suspect, is intangible, its presence can be detected only through gravity, which it manifests.
However, although the dark matter particles rarely interact with normal matter of the Earth, all the world should rush through the dense sea of dark matter with billions of these particles rushing through us every second. Although the great majority of these particles would pass right through us without hitting any of the atoms that make up our bodies, several clashes were likely to be. And the consequences of such impacts could shed light on the properties of dark matter.
Scientists have calculated how much dark matter particles must collide with atomic nuclei in the body of an adult - about 154 pounds (70 kilograms) of weight, largely composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.
Dark matter must often collide with the nuclei of hydrogen and oxygen in the body - the first 60 percent of the atoms in the body, while the latter is about 60 percent of the total body weight. Considering the most common assumptions about what the dark matter is about 35 impacts between the particles of dark matter and atoms in your body should take place annually.
However, if the latest models are correct, and the interaction of dark matter is more common than previously thought, perhaps about 100,000 collisions each year for every person on the planet.
"Before we did these calculations, I had the impression that an average of one WIMP will hit one of the nuclei in the human body in about 100 years. In fact, I used to joke about 'deadly theory WIMP' »said researcher Katherine Freese, a theoretical physicist at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. "Instead, it appears that the number of interactions WIMP would be more frequent - one collision per minute».
The researchers also calculated, would the energy released from the impact of the human body dark matter, cause cancer. "We found that WIMP is safe for the human body," said Fries.
«WIMP - a source of radiation, and the collision could potentially be dangerous for people," says Fries. "However, we found that the answer is no. Other natural sources of radiation from radon or cosmic rays are much more of a problem for us. This is not unexpected, as WIMP only interact through the weak connections, while cosmic rays - charged particles and thus have electromagnetic interactions, which are much more common and produce more energy. "
The picture of the distant future solar system as an example of detected white dwarfs
Ancient lava spirals on Mars can reveal the secrets of the Red Planet