782
NASA is ready to build a space station for repair and refueling satellites

More than 1,100 satellites are now orbiting the Earth. They transmit TV signals and telephone calls, collect scientific data and spy on enemy territory. Most of them are quite expensive: dozens or hundreds of millions of dollars required for the development, construction and start-up.
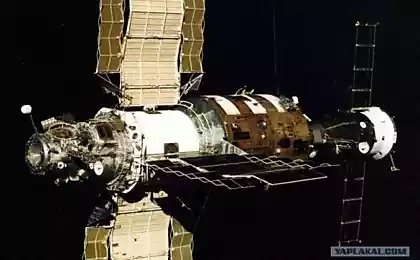
It's a shame when a satellite fails after only a few years of operation due to the abnormal situation: a fuel leak or malfunction. NASA is thinking about how to remedy the situation. For example, you can build a space station maintenance, repair and refuel satellites.
"There is a way to work together humans and robots to increase the useful life of satellites, repairing them and not allowing fuel to pour out, and vice versa, refueling, clogging and sent back into orbit?» - задаётся Questions Benjamin Reed (Benjamin Reed), deputy director of the management program of satellite services (Satellite Servicing Program Office) Space Flight Center Goddard in NASA. And immediately he replied: "Yes. We have the technology to do it ».
NASA astronauts on the International Space Station have carried out two training missions to refuel satellites in 2011 and 2014. At the same time, engineers Center. Goddard worked on the creation of new types of fuel injectors and other tools necessary to equip robots: wire cutters, drills and so on. D.
In addition, the layout is constructed six-meter Landsat-7 satellite for breaking maneuvers for rendezvous and docking required for refueling satellites in orbit.
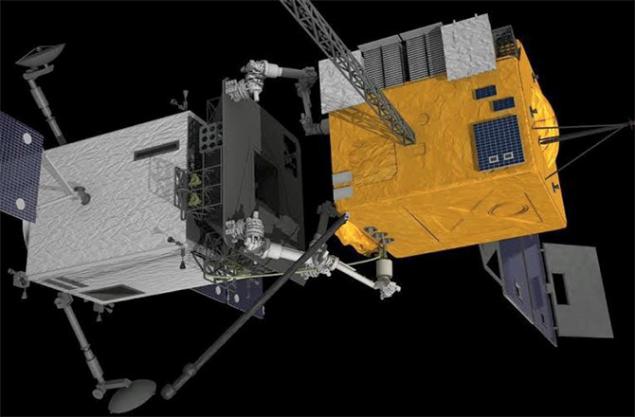
Among other developed technologies - laser sensor Raven, which produces the exact orbital path of approaching objects. This is a key piece for two relatively small satellites that are going to be joined to the fuel injector inserted into the hole just a few centimeters in diameter.

Replace the nozzle on the satellite fuel injector i>
Benjamin Reed believes that such service station, NASA can fly in low orbit and connect to the satellite that needs refilling or adjustment.
Some of the technologies for such stations can be used simultaneously in another program Asteroid Redirect Mission, which NASA hopes to land the module to the surface of an asteroid, and then break off a big piece and send to Earth for study and mining materials. This program has already funded and scheduled for December 2020.
NASA says that a greater interest in the establishment of a satellite service station showing a commercial company and not the NASA. In orbit is about 360 commercial satellites.
In addition, it should solve a number of legal issues before starting. What happens if you accidentally damage the service station commercial satellite and bring it down, or send another satellite into orbit as a result of a failed docking? Forced the space agency to pay any expenses and to pay a penalty? We need to create some sort of insurance system against such situations.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/252282/
American scientists warn that the planet begins the next great extinction of species
California chemists figured out how to make high-performance plastic solar panels