525
Do you need sugar for the brain during mental work
Indeed, the brain with carbohydrates (glucose) relationship difficult. The fact that the brain consumes a lot of energy and does so at the expense solely of glucose. Muscles, for example, can use both glucose and fats. In the calculation of the whole mass of the brain glucose is about 750 mg. Per 1 min, the brain tissue is oxidized 75 mg of glucose. Consequently, the amount of glucose present in the tissue of the brain, could be sufficient only for 10 min a person's life. Therefore, the glucose blood is vital.

The main points of the article:
1. We have many sources of glucose, are the three principal depots of glucose: glucose from digested food, glucose from the glycogen of the liver, glucose is obtained by synthesis from amino acids.
2. The level of glucose in the blood falls. The absolute number of people the glucose level never falls below the normal level.
3. The level of glucose in the blood does not depend on the share of carbohydrates in the diet (except if you do sports and at the same time sit on a low carbohydrate diet, in this case, the muscles will Rob the brain will develop so-called "carb flu")
4. The only way to reduce the level of glucose in the blood relatively healthy person is to do heavy physical work on an empty stomach.
5. Why snacking stimulate?

Ready? Go!
Our brain does a great job. The human brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons in gorillas and orangutans, the closest to us in brain size of primates, there are about 33 billion.
The most powerful electronic brain in the world at the present time can perform 17.6 quadrillion floating point operations per second, or 17.6 petaflops. Taking into account that the mind and computers is not entirely comparable, it is believed that the computational power of the human brain is 1 exaflop (57 times more than the computer).
A day in a person weighing 70 kg the brain consumes about 100 grams of glucose. In an adult the proportion of cerebral metabolism of the total energy needs of the body is 9% during sleep and 20-25% at the time of intense intellectual work, which is significantly more than other primates (8-10%), not to mention other mammals (3-5%).
So, just to maintain necessary life functions, the transmission of nerve signals and playback basic operations the brain of the average person needs about 400-500 kcal.
In the amplification of intellectual work, the cost of the brain active more than two times. And most of the energy consumed for the section of the brain that works the hardest. More calories have to spend on unusual tasks. So, if you force the Humanities to solve the puzzle of geometry, the energy consumption of the brain will greatly increase.
But keep in mind that to overclock your brain can people, who are systematically engaged in intellectual work, in other words, knows how to think. To bring themselves in mental exercises to the extent of physical exhaustion, not everyone can. Typically, this reaction to mental work have scientists, mathematicians, chess players.
A lot of effort is experiences, the emotional experiences of the energy costs increase by 10-20%. Unusually large and intelligent load coupled with the stress accompanying any exam or test, increase energy the body all at 30-40%.
Let's compare the energy consumption of the brain and muscles. A minute walk body burns 4 calories. And doing kickboxing consuming 10 calories per minute. But the brain, if nothing is busy, burns 0.1 calories per minute. Actually it is not so small if you take into account that the brain is an inert mass, component only two percent of the human body. But with a lot of cognitive load the amount of burned calories can increase up to 1.5 per minute. In any case, this is less than during normal walking!
In the process of active thinking involved mainly the frontal lobes of the brain. The problem is that we do not use these shares constantly. Therefore, although the brain is, on average, per day burns about 300 calories, it is always the possibility to burn more.
Our total reserve of glucose is around 20 grams of which about 5 grams are in the blood. Twenty grams of glucose to produce enough energy for approximately 40 minutes of operation. If you just sit, you can use all your stocks in less than one hour. If you go, glucose can disappear in about 15 minutes. Moderate work can exhaust the reserves of glucose for 4 minutes. Where does it come from?
So, where the brain takes the glucose?
Their stocks had not, he takes it from the blood. But in the blood glucose comes from food and supplies. Also glucose can be produced by the body from amino acids. And now two points.
1.Three main depots of glucose: glucose from digested food, glucose from the glycogen of the liver, glucose is obtained by synthesis from amino acids.
A) Glucose from digested food. If you have a good meal, glucose from a long (slow) carbs continues to act for two to three hours. The completion of this process gives a small signal that we could be mistaken for hunger. But it's not hunger, but a signal that the body is moved to the consumption of glycogen. And once the liver is forced to give up glycogen for energy needs, it immediately sends a signal to the brain. But this does not mean that the glycogen is over, which means that its decomposition has only just begun. If you start eating earlier than spend part of glycogen, to replenish the deficit will require not so much food, and everything else, eaten by you, will turn into fats and will take place in your body.
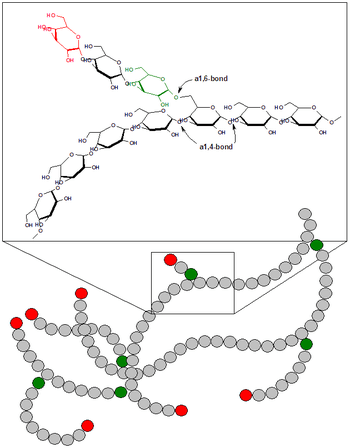
Glycogen
B) Glycogen is animal starch, the spare form of glucose. In our body it accumulates in the liver and in your muscles. Muscles accumulate glycogen for themselves, and the liver is mostly for the brain and for some types of cells (erythrocytes, etc.). Insulin inhibits the breakdown of glycogen and the stress increases. The total mass of glycogen in the liver can reach 100-120 grams in adults. An untrained person total glycogen reserves amount to about 450 grams (about 1800 kcal), and trained people can reach up to 750 g, which gives about 3,000 calories. But it is mainly muscle glycogen.
C) Gluconeogenesis. It is the synthesis of glucose from amino acids. The body can take proteins from food or your muscles. Daily the possibility of gluconeogenesis – 400 g of glucose a day. If you don't eat, gluconeogenesis vkluchaetsia only after 10-12 hours and increases only towards the end of the second day.
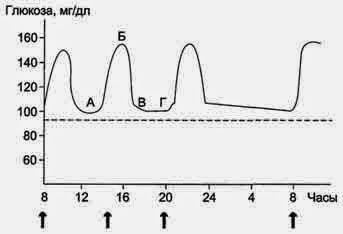
2. The level of glucose in the blood falls. The absolute number of people the glucose level never falls below the normal level, it is ranging from 4.5 to 5.5 mmol / l and varies within the range of about 10-15%. Sugar fluctuations can occur in diabetics, athletes and people with severe liver disease, but it is unlikely that you. We have several mechanisms that are very effective in controlling the level of glucose in the blood and raise him almost as soon as it is reduced.
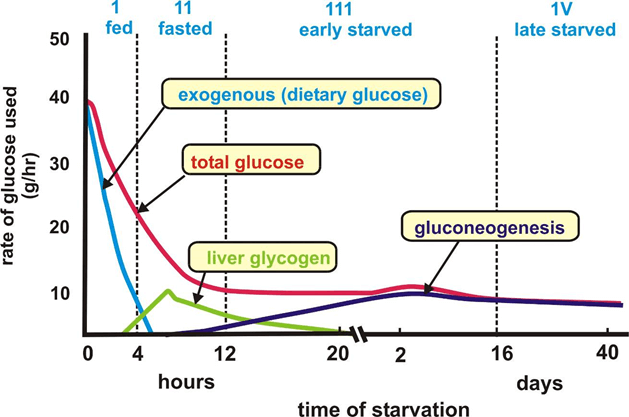
Various sources of glucose
3. The level of glucose in the blood does not depend on the share of carbohydrates in the diet (it can vary from 10 to 80% in the diet). Low starch and sugar reduces the level of glucose in the blood: we can maintain normal levels of blood glucose, despite significant fluctuations in the intake of carbohydrates and consumption of starch. This is because our liver and kidneys can synthesize glucose from amino acids (derived from proteins in the diet, or our muscles). (except if you do sports and at the same time sit on a low carbohydrate diet, in this case, the muscles will Rob the brain will develop so-called "carb flu")
4. The only way to reduce the level of glucose in the blood relatively healthy person is to do heavy physical work on an empty stomach. Hard physical labour and fasting really can drastically reduce the level of glucose in the blood and lead to loss of consciousness. Increase metabolism in the muscle cell increases the uptake of glucose from the blood, in this case muscle mass to "steal" glucose from the brain, and can lead to loss of consciousness. However, this rarely happens. Remember that no mental load was not able to burn as much glucose to reduce its level in the blood.
5. Why snacking stimulate? They are known to interfere with hormones and cause the release of insulin, cortisol, dopamine and serotonin. It's invigorating and fun, short-term boost of power. But high rise of these hormones will change the low drop, and we once again feel the nervousness, irritability and fatigue. But it's not really fatigue and not real hunger, but the result of hormonal and neurotransmitter imbalance. All of these changes (diabetes or insulin swings) is not allowed to operate and highly distracting.
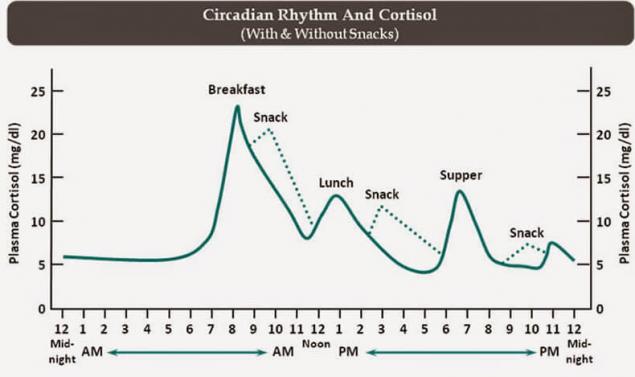
Snacks cause the rise of cortisol, a stress hormone
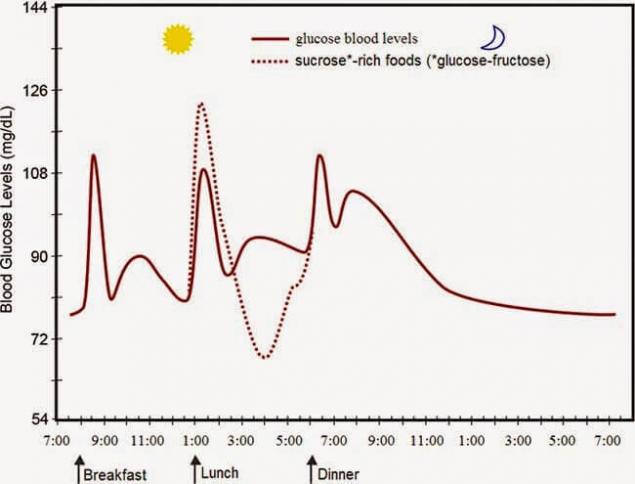
The principle of operation of a sugar swing
Snacking is very dangerous for the brain. This habit can be compared with caffeine or abuse of breaks. The fact that snacks sweet cause the same release of dopamine. And besides they are slightly Prime, as a sweet snack causes the release of the stress hormone cortisol. This will give some strength in the short term, but will cause exhaustion in the long term. So do all drugs. Sugar cravings and increased appetite during stress reflects only an eating disorder and nothing more. Of glucose to you enough!
The satiety hormone: why willpower is powerless against leptin
10 effective exercises to relieve muscle clips
6. The brain consists mainly of fat and need fat-soluble compounds, many of which are in vegetables and berries. Don't forget to add in the diet of fats (e.g., olive oil) as fats greatly enhance the absorption of fat-soluble compounds. For example, curcumin, sideridis in the spice turmeric, has potent neuroprotective effect and is a fat-soluble compound. But that's a topic for another article.
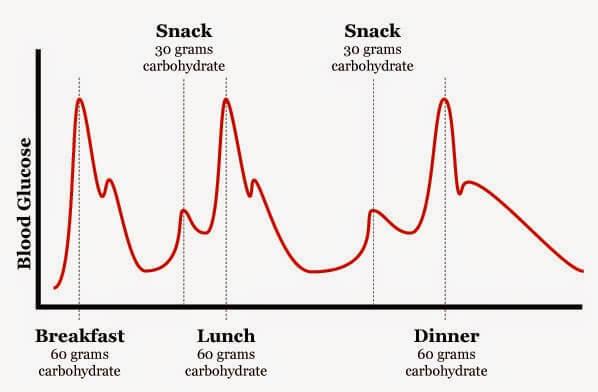
7. Don't forget that sugar is glucose only 50%, and 50% is fructose. Excess fructose is extremely dangerous, I wrote about it. In addition, fructose directly affects the brain, in experiments with rats found that fructose with regular inclusion in the diet in large quantities, quickly led to the deterioration of connections between brain cells.published
Author: Andrey Blueskin
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.beloveshkin.com/2015/04/Nuzhen-li-sahar-dlja-mozga-pri-umstvennoj-rabote.html

The main points of the article:
1. We have many sources of glucose, are the three principal depots of glucose: glucose from digested food, glucose from the glycogen of the liver, glucose is obtained by synthesis from amino acids.
2. The level of glucose in the blood falls. The absolute number of people the glucose level never falls below the normal level.
3. The level of glucose in the blood does not depend on the share of carbohydrates in the diet (except if you do sports and at the same time sit on a low carbohydrate diet, in this case, the muscles will Rob the brain will develop so-called "carb flu")
4. The only way to reduce the level of glucose in the blood relatively healthy person is to do heavy physical work on an empty stomach.
5. Why snacking stimulate?

Ready? Go!
Our brain does a great job. The human brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons in gorillas and orangutans, the closest to us in brain size of primates, there are about 33 billion.
The most powerful electronic brain in the world at the present time can perform 17.6 quadrillion floating point operations per second, or 17.6 petaflops. Taking into account that the mind and computers is not entirely comparable, it is believed that the computational power of the human brain is 1 exaflop (57 times more than the computer).
A day in a person weighing 70 kg the brain consumes about 100 grams of glucose. In an adult the proportion of cerebral metabolism of the total energy needs of the body is 9% during sleep and 20-25% at the time of intense intellectual work, which is significantly more than other primates (8-10%), not to mention other mammals (3-5%).
So, just to maintain necessary life functions, the transmission of nerve signals and playback basic operations the brain of the average person needs about 400-500 kcal.
In the amplification of intellectual work, the cost of the brain active more than two times. And most of the energy consumed for the section of the brain that works the hardest. More calories have to spend on unusual tasks. So, if you force the Humanities to solve the puzzle of geometry, the energy consumption of the brain will greatly increase.
But keep in mind that to overclock your brain can people, who are systematically engaged in intellectual work, in other words, knows how to think. To bring themselves in mental exercises to the extent of physical exhaustion, not everyone can. Typically, this reaction to mental work have scientists, mathematicians, chess players.
A lot of effort is experiences, the emotional experiences of the energy costs increase by 10-20%. Unusually large and intelligent load coupled with the stress accompanying any exam or test, increase energy the body all at 30-40%.
Let's compare the energy consumption of the brain and muscles. A minute walk body burns 4 calories. And doing kickboxing consuming 10 calories per minute. But the brain, if nothing is busy, burns 0.1 calories per minute. Actually it is not so small if you take into account that the brain is an inert mass, component only two percent of the human body. But with a lot of cognitive load the amount of burned calories can increase up to 1.5 per minute. In any case, this is less than during normal walking!
In the process of active thinking involved mainly the frontal lobes of the brain. The problem is that we do not use these shares constantly. Therefore, although the brain is, on average, per day burns about 300 calories, it is always the possibility to burn more.
Our total reserve of glucose is around 20 grams of which about 5 grams are in the blood. Twenty grams of glucose to produce enough energy for approximately 40 minutes of operation. If you just sit, you can use all your stocks in less than one hour. If you go, glucose can disappear in about 15 minutes. Moderate work can exhaust the reserves of glucose for 4 minutes. Where does it come from?
So, where the brain takes the glucose?
Their stocks had not, he takes it from the blood. But in the blood glucose comes from food and supplies. Also glucose can be produced by the body from amino acids. And now two points.
1.Three main depots of glucose: glucose from digested food, glucose from the glycogen of the liver, glucose is obtained by synthesis from amino acids.
A) Glucose from digested food. If you have a good meal, glucose from a long (slow) carbs continues to act for two to three hours. The completion of this process gives a small signal that we could be mistaken for hunger. But it's not hunger, but a signal that the body is moved to the consumption of glycogen. And once the liver is forced to give up glycogen for energy needs, it immediately sends a signal to the brain. But this does not mean that the glycogen is over, which means that its decomposition has only just begun. If you start eating earlier than spend part of glycogen, to replenish the deficit will require not so much food, and everything else, eaten by you, will turn into fats and will take place in your body.

Glycogen
B) Glycogen is animal starch, the spare form of glucose. In our body it accumulates in the liver and in your muscles. Muscles accumulate glycogen for themselves, and the liver is mostly for the brain and for some types of cells (erythrocytes, etc.). Insulin inhibits the breakdown of glycogen and the stress increases. The total mass of glycogen in the liver can reach 100-120 grams in adults. An untrained person total glycogen reserves amount to about 450 grams (about 1800 kcal), and trained people can reach up to 750 g, which gives about 3,000 calories. But it is mainly muscle glycogen.
C) Gluconeogenesis. It is the synthesis of glucose from amino acids. The body can take proteins from food or your muscles. Daily the possibility of gluconeogenesis – 400 g of glucose a day. If you don't eat, gluconeogenesis vkluchaetsia only after 10-12 hours and increases only towards the end of the second day.

2. The level of glucose in the blood falls. The absolute number of people the glucose level never falls below the normal level, it is ranging from 4.5 to 5.5 mmol / l and varies within the range of about 10-15%. Sugar fluctuations can occur in diabetics, athletes and people with severe liver disease, but it is unlikely that you. We have several mechanisms that are very effective in controlling the level of glucose in the blood and raise him almost as soon as it is reduced.

Various sources of glucose
3. The level of glucose in the blood does not depend on the share of carbohydrates in the diet (it can vary from 10 to 80% in the diet). Low starch and sugar reduces the level of glucose in the blood: we can maintain normal levels of blood glucose, despite significant fluctuations in the intake of carbohydrates and consumption of starch. This is because our liver and kidneys can synthesize glucose from amino acids (derived from proteins in the diet, or our muscles). (except if you do sports and at the same time sit on a low carbohydrate diet, in this case, the muscles will Rob the brain will develop so-called "carb flu")
4. The only way to reduce the level of glucose in the blood relatively healthy person is to do heavy physical work on an empty stomach. Hard physical labour and fasting really can drastically reduce the level of glucose in the blood and lead to loss of consciousness. Increase metabolism in the muscle cell increases the uptake of glucose from the blood, in this case muscle mass to "steal" glucose from the brain, and can lead to loss of consciousness. However, this rarely happens. Remember that no mental load was not able to burn as much glucose to reduce its level in the blood.
5. Why snacking stimulate? They are known to interfere with hormones and cause the release of insulin, cortisol, dopamine and serotonin. It's invigorating and fun, short-term boost of power. But high rise of these hormones will change the low drop, and we once again feel the nervousness, irritability and fatigue. But it's not really fatigue and not real hunger, but the result of hormonal and neurotransmitter imbalance. All of these changes (diabetes or insulin swings) is not allowed to operate and highly distracting.

Snacks cause the rise of cortisol, a stress hormone

The principle of operation of a sugar swing
Snacking is very dangerous for the brain. This habit can be compared with caffeine or abuse of breaks. The fact that snacks sweet cause the same release of dopamine. And besides they are slightly Prime, as a sweet snack causes the release of the stress hormone cortisol. This will give some strength in the short term, but will cause exhaustion in the long term. So do all drugs. Sugar cravings and increased appetite during stress reflects only an eating disorder and nothing more. Of glucose to you enough!
The satiety hormone: why willpower is powerless against leptin
10 effective exercises to relieve muscle clips
6. The brain consists mainly of fat and need fat-soluble compounds, many of which are in vegetables and berries. Don't forget to add in the diet of fats (e.g., olive oil) as fats greatly enhance the absorption of fat-soluble compounds. For example, curcumin, sideridis in the spice turmeric, has potent neuroprotective effect and is a fat-soluble compound. But that's a topic for another article.

7. Don't forget that sugar is glucose only 50%, and 50% is fructose. Excess fructose is extremely dangerous, I wrote about it. In addition, fructose directly affects the brain, in experiments with rats found that fructose with regular inclusion in the diet in large quantities, quickly led to the deterioration of connections between brain cells.published
Author: Andrey Blueskin
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.beloveshkin.com/2015/04/Nuzhen-li-sahar-dlja-mozga-pri-umstvennoj-rabote.html
25 words and phrases to avoid during public speaking
"Hard to believe": a documentary film, causing shock