Tatiana Chernigovskaya, It's not me — my brain
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net
And my eye isn't that dark?.. The darkest...
How not dark, I guess
myself always on the lady of clubs.
N. V. Gogol "The Government Inspector"

It's not me, it's my brain. This is, like, the twenty-first century answer to the question nineteenth. To us this innovation (not the night be commemorated word) even flew across the ocean, but will fly...
Strictly speaking, the movement in this direction — when the wine for unorthodox actions, and even for the entire life scenario rests on a different kind of physiological or even anatomical features has been observed before. But with the advent of the new Millennium it came to almost completely remove the responsibility from the individual and to give it a "acid", in particular genomic DNA, twisted into a spiral that no court will deal...
The sorrows of young Werther, Turgenev young ladies, extra people, rahmatovich and Frankenstein, and Hannibal ball of decterov with silent lambs — everything, everything is now reduced to four letters — A, G, T and C — the text of the sentence. Comfortable, but embarrassing and dangerous.
Prophetically decades ago, it caught Joseph Brodsky: "... take the top telepaths, Buddhists, spiritualists, drugs, Freudians, neurologists, psychopaths... Soul tied a big veil. Will unite us in a continuous spiral. Stuck in the socket with ethyl morality. It will release from the verb".
The brain in the world and the world in the brainthe Topic of this article goes beyond the traditional anthropological debates about human nature and affects fundamental principles of the functioning of the most complex of all complex systems, neural networks.

We are talking about the degree of personal independence from a physiological (if not physical-chemical) processes, deterministic behavior properties of the brain and even genetics when you can't avoid the question of free will as the network itself (could it behave differently?), and of the subject. The latter is fundamental to any discussion about the specifics of the person and his differences from "zombie" or other virtual or real systems that claim to possess human abilities.
Probably most people will agree that a distinguishing feature of man is the consciousness. The case for small: there is no consensus on the definition of what exactly it is... the Term consciousness is used in at least two different aspects:
1) as a characteristic of any of the properties of living beings,
2) how the presence of certain levels and States of consciousness.
There are actually a lot of different meanings that are invested in this project:
• Consciousness has any sense and react to external stimuli creature. Then you need to recognize that they have fish, shrimp, etc.
• Not in a dream or in a coma. How then, in this sense, to determine the condition of in sleep, in hypnosis, etc.?
• Awareness: we are conscious, we are aware that are aware. How then to be with young children? With a highly developed, but not speaking creatures?
• So What is it called when asked to imagine what the world terms other consciousness — for example, a bat with its echolocation, or octopus. Virtual imaginable alien creatures a little more than incomprehensible to us in this sense than any earthly animal.
In modern science there is a very wide range of types of attitude to the problem of consciousness and its natural-scientific study — from osmoregulatory when the most complicated and radical to understand the issues simply do (and this is true for most experimentally working scientists), to postulating the irreducibility of these parallel "worlds" and appeal not to generally look for neurophysiological correlates of consciousness (if it is not within the scientific paradigm, or, at least, it is natural-scientific unit).
Some hope for a way out of this situation inspires the development of cognitivist approaches, are multidisciplinary by definition. For example, the radical cognitivist (as he calls himself) Victor allakhverdov is in opposition to the irrationalism and noncognitivism, to look at man from the standpoint of the synthetic theory of evolution, to behaviorism and psychoanalysis and argues that "the recognition of the irreducibility of knowledge to the behavior, focus on the description of the processes of information processing, the understanding of the role of the subjective constructs in the description of the world, emphasis on problems of balance between the conscious and the unconscious" gives hope for a breakthrough and a deadlock. He also claims thatconsciousness is lagging structure, as the brain carries out independent checks, choosing correct, in his view, hypotheses of different variants, including incorrect.
Subjective reality, qualia, or phenomenal consciousness — perhaps the most important theme in these discussions. This also highlights the biggest modern neuroscientist Gerald Edelman.
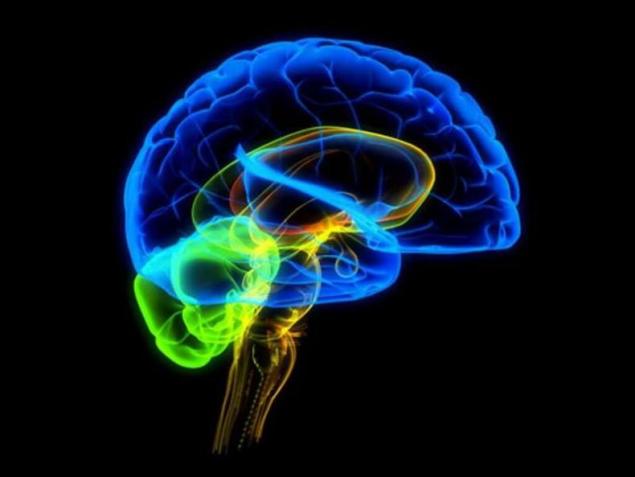
The Central problem of consciousness — how subjective experiences arise from physical phenomena. It is written and continues to write a lot of articles and books. We see only what we know. Images and ideas — not a copy and not even the amount of physical signals arriving at our receptors. They build our brains. In other words, what is seen, heard and perceived, to have different kinds of animals and all of them from us, not because of different ranges of vision, hearing, smell, etc., and because all creatures your brain that processes sensory signals, forming a subjective (!) images. Not only in different species but also among different individuals within one species, different qualia. It should be noted that the presence of subjective reality is not detected behavioral methods, therefore, experimental testing requires special mental development.
In connection with the above, you need to get used to make major amendments to individual, ethnic, religious, professional and other cultural differences, to build a neural network and the subjective worlds of different people. The pivotal importance of cross-cultural (as it is now called) the nature of thinking described by Nikolai Marr, Israel Frank-Kamenetskii, Freidenberg, Olga, Pavel Gurevich, Mikhail Steblin-Kamensky...
The brain is not the sum of billions of neurons and their connections and such, plus the sum of individual experiences that have shaped this tool — our brain — and set it up.
Perception is an active process of knowledge extraction and construction of the world. Different living systems do it differently, extracting from the world the desired characteristics (e.g., magnetic field or polarized light) and building-specific model of the world. It is the presence of the subjective world and the subject itself distinguishes man from the cyborg. Yet. The advantage of man consists in the possession of liberum arbitrium — free will, the ability to voluntary and conscious choice and consent taken by the decision — voluntarius consensus.
All cognitive processes are receiving and processing information according to certain rules and algorithms. In the brain there are mental representations, providing contact with the world. This hypothesis of a high degree of abstraction, the underlying picture of the world that cannot be verified empirically, because "objective", "real" picture of the world just yet, or it knows only the Creator. The addition of the opinions of a statistically acceptable number of people adds nothing, as they all have a similar brain. As Kant says, "reason does not derive its laws (a priori) from nature but prescribes them to her".
Unable to evade a dangerous question: why formal thinking applicable to the real world? Why do we accept as an axiom that is well-organized in the framework of our algorithms construction — true? True in the framework of our thinking.
Here we face a paradox: the brain is in the world, and the world is in the brain. Search of subjective experience in the physical world (i.e. the quality and intensity of sensory stimuli) is absurd: it is not there, as it is built in the brain, in some, additional space of the brain. Who look for mental representations? Who interpretered?
It would seem that the obvious answer is "me", but... as if from another dimension, from another space, from the inside of the brain, not as a physical object and mental entity. And because the brain is (with someone) dialogue... And who says ("don't go there"...)? Would have said — right and left hemisphere, how would two different personalities. But now the picture has become much more varied, and the brain — much "naselenie".
It seems that the texts reads the neural network itself, the neural networkthat we caught or that you are... one Consolation is that it was caught and the world. Or she is the world. And its shape, density, grace netting, flexibility and resilience are alive, and we can knit your patterns, not obeying the templates given to us a priori — sustainability.
Can we brain trust? Potential the ability to deliver personality is not only about sensory and semantic information, but also inadequate assessment of the affiliation of the sensations this subject well known of the mental disease. Research Vilayanur Ramachandran show that "belief consciousness" can destroy them, therefore, arbitrary ways, conscious of the impact even such extreme and abnormal sensations there.
The question that remains is not going anywhere: our brain — the implementation of the "set of all sets not members of themselves" Bertrand Russell or a self-contained masterpiece in a recursive relationship with allowed him the person in whose body it is placed? And what is posted? What from the world that we perceive and which is adapted, belongs to him, and what causes our brain? This means that the question of the separation of subject and object remains Central.
It was long ago realized the largest minds, such as Alexei Ukhtomsky, the outstanding Russian scientist ahead of his time almost a century and believed that neither of the subject nor of the object that we are not spectators, but participants, and even what our nature is doing, that is, it is as if there is independently of us. In this connection, you need to remember Alexander Piatigorsky and Merab Mamardashvili, and Vladimir Zinchenko, who was said by that being and consciousness are a continuum, and that thinking and existence are the same.
A situation where the object of study is not independent of the observer, physics experienced a long time ago, when began to be developed quantum theory and the confused world of Schrodinger's cat. Such scenes that violate all the usual ideas about space and time, as is commonly thought, inhabited the quantum world, in which everything depends on the presence of the observer. In the macrocosm of these phenomena, until recently, were not observed. But it is in physics, and the Sciences that study living systems, the role of the observer — role of the brain — not to underestimate. So, analytic philosophy — the same player on the field, as neurophysiology and cognitive psychology.
Strictly speaking, now neuroscience and philosophy of mind well without each other cost, one can even say they even interfere, as mutually forced each other to look. Hope to build a bridge between them, designed to overcome the failure, until quite illusory: the current status of research can still be described as Where-it-happens studies, as any the most sophisticated technique gives only the answer to the question of which brain area is active or passive during the activities, whereas I would like to not "address," and an explanation.
In the discussion of the autonomy of the brain, raised in the articles by Ernst Nagel, David Dubrovsky insists that a person can "operate on their own a class of their neural systems, that is, to control them", and it follows that the internal hard determinism are not obvious.
The brain — the Creator or the mirror?In 1922, long before the emergence of cognitive science, Semyon Frank wrote:
"Social science the methodological peculiarity that in it the subject of knowledge in a way coincides with its object. The ant researcher is not the participant of the nest, bacteriologist belongs to another group of phenomena, than study the world of microorganisms, the same social scientist he is, consciously or unconsciously, citizen, that is, member of study society".
Remember in this regard and his brilliant predecessors. "Great Kant taught us that time, space and causality in all its regularities and possibilities all its forms are in our consciousness quite independently of the objects that they are and make their contents — wrote Arthur Schopenhauer, or, in other words, it is equally possible to come, proceeding from the subject or from the object; therefore, they can with equal right be called as methods of the contemplation of the subject, and the properties of the object, since the latter is an object (in Kant: the phenomenon), that is, a performance."
We know that a baby born now are genetically not very different from the one born at the beginning of our biological history. Know which line it was a dead end, and which has led to the emergence of modern humans and different racial and ethnic groups. Despite the ambiguity of the relationship to the discussion of whether continues or has already ended biological evolution of man, should indicate to the emergence of data showing that the human brain is still under the influence of adaptive evolutionary processes (e.g., microcephalin — gene that regulates the volume of the brain — continues to evolve adaptive).
Opening Rizzolatti Giacomo and Michael Arbib mirror neurons and mirror systems in General gives a completely new data on the emergence of language and reflection as the Foundation of human consciousness. The mirror system of the brain Carteret external information — actions by another creature, not necessarily of the same kind, but with a clear system of coordinates and the interpreted behavior. They are almost in all parts of the human brain and are activated in particular in anticipation of action, with the empathy of emotion or the memory of them, etc. It shows the basis on which developed the brain, ready to build models of consciousness and also for social learning and appropriate behavior in society. The lack of capacity observed in extreme forms of autism and schizophrenia, leads to the loss of a person from society with the most severe existential consequences.
It is extremely important that the formation of these systems are reliable mechanisms of self-identification that is broken when the mental pathology of schizophrenia and is also associated with the functioning of mirror systems.
So, very difficult organized by the human brain — a mirror for the world, or himself forms the world? It is important to the world or only to the individual himself to ensure the viability? Why do we repeat it? To duplicate that yourself or the world? To learn how the brain works or what are the laws of the world as a whole? And unless we can duplicate what is organized more complicated than we even can imagine? To create the model to verify the correctness of the hypotheses? — Yes, but, for example, training an artificial neural network, we know not how the brain operates, and how learning takes place! Just as in teaching primates human sign language, we find out just to what extent they can complete their education — no more.
It is now clear that the processes of memory operation (write, read, search) in the human and the computer differ a lot. The basis for the organization of computer memory is the addressing — location information in memory. Various types of contents search (keys, sets, signs, etc.) provided by the system address references. Human memory also has a large set of keys that allows you to quickly read information. However, even if we get comparable results, we have no confidence that the processes themselves were the same!
For example, now there are robots that can compensate for movement disorders by continuously remodel itself depending on the situation. Does it follow that the robot now has consciousness and subjective reality? The freedom to make decisions about yourself?
Studies of Konstantin Anokhin give us specific information about what high degree of difficulty of the processes of memory worked by nature for animals standing on different levels of the evolutionary ladder, and the most successful moves are fixed genetically. Man is incomparably more degrees of freedom of the selection algorithms as fixation and reading information that increases the level of difficulty. The brain is commonly modeled as a classical physical system, which by definition is computing. However, it is clear that this is not so, and therefore, in the future, when such approaches are possible for modeling are likely to come under a different scientific paradigm (cf. the hypothesis of John Eccles that describe functions of some of brain structures necessary involvement of quantum concepts).
We denote the properties of mental processes, which, in our opinion, make the computer metaphor is completely irrelevant, looking back before that to Roger Penrose, who wrote that consciousness cannot be reduced to the calculation, as living brain is endowed with the ability to understand. What is the understanding? Not fixing and correlating with something that is understanding — not an idle question, primarily with respect to other types of intelligence, not the human type. According to Penrose, the brain really works like a computer, but this computer is so unimaginable complexity that its simulation is not under the power of scientific understanding.
The brain is the design of soft and hard links and includes the top-down algorithms, bottom-up procedure of teaching and non-computed layers. This gives us reason to believe that at least in the foreseeable time it will not lend themselves to adequate modelling.
So the irrelevance of the computer metaphor in its current form is determined by the following properties of human consciousness:
Extraordinary the role of context, and hence the possibility of multiple interpretations of messages and events in General. This alone is enough so the world was reflected in a distorting mirror (in the theory of communication talking about communication holes or failures, not least for this reason). It should be recalled in this regard, biosemiotics and theoretical biology Jacob Ukskula with his idea Umwelt's — worlds, separate for each creature and almost impervious to others: "Everything has it's own Umwelt adapted to its specific needs" (each creature your world, adapted to its existence) — only high organisation of consciousness gives the chance to consider the worlds of other people.
— Redundancy and the possibility of many paths to find the same. The use of different algorithms at different times without obvious reasons. And finding that was not looking (in passing). As wandering by and large (and almost his) house — what you might find... Space familiar only partially, and not very bright. Stumble and not go by there... it's Hard to go on the same route several times, except that this route is trivial and automatic. Actually, if a person persistently uses the same route on the mental operations, it says its epileptogenicity (when Slippers should be only a parallel). And the opposite: if each time to try a new route, then there is clearly not without schizoid. And it can not only lead to unproductive search (behavior), but also to discoveries, as it included low-frequency associative processes.
The surprise and unpredictability of the matched objects or procedures: the more rare and "foreign" objects, the more effective can be a creative process (this explains the continuity of the "norm" when the line between madness, schizotypal consciousness and genius is determined by the external coordinates — adaptation to society). Is it possible, by the way, computer simulation of hallucinations when the brain begins to replace sensory input to their simulation? Because the brain sees, hears and feels that "willing and able", and not what is in the "objective" world.
— Vagueness, inaccuracy, approximation of descriptions does not reduce the effectiveness of the search in the memory and algorithm behavior (something that is usually associated with hemispheric type of consciousness). Couldn't agree more: what a man, hard to the computer and Vice versa.
— Neprijatnosti Aristotelian type of thinking and even the artificiality of his brain, because this type of logic a person should be specially trained to use. Plurality of types of thinking, determined by the culture and the task (everyday, scientific, and religious thinking used in the game, see the work of cross-cultural psychologists Claude Levi-Strauss, Alexander Luria, Michael D. Cole, Peeter Tulviste, etc.). Note that this multiplicity is provided by the brain, in particular the characteristics of its hemispherical functional organization.
— Humor and laughter, "carnival" — properties of the human psyche which acts as a "tickling of the heart", when it is possible to lose the fear and conscience, and the "tickling of the mind", when you can violate the laws of reason, common sense and etiquette. The psyche needs to rest. If your computer can simulate a sense of humor? All he can require of the algorithm, or script, or permutations. Is this a way to generate funny, that is unexpected? Rather no than Yes, but if so, something simple and therefore not very funny or — bust unlikely options — redaktirovanie. It's all about dose and context. The laws are ridiculous, the same as the laws of poetry, from an unexpected angle, analogy, unusual starting point.

Yes, the chess supercomputer Deep Blue defeated Kasparov in chess, and humanity was shocked. Soon woke up: it's just a game, based on the search options (i.e. not the whole intellect), and besides, with incomparable amounts of memory opponents (even incorrectly), and besides, "atskanotaju" artificial intelligence on a particular player... Experts say that to write a program a high-level backgammon games, for example, is incomparably more complicated: the bone Lord bone... the Case that is.
However, another world chess champion Vladimir Kramnik said that chess is too complex for the computer, since the number of possible combinations represents a number with 28 zeros; as the algorithm of human thinking is that we can choose the direction of the calculations, and not to try all combinations, then we have a chance to score. Which is a relief. Although not for long as we already see.
Race at the speed we lost long ago: the speed of electronic circuits is already millions of times greater than the rate of excitation of neurons in the brain, wherein the electronic circuit demonstrate the high accuracy of synchronization and processing instructions that are in any way not characteristic of neurons.
What? — And anything. Not yet seen nor Pascal, nor Leonardo, nor Shopengauera. And will not be visible ever in these zeros with ones, because nobody has yet made any breakthrough in science and philosophy, not to mention the art, with a particularly well-oiled calculating machine "Felix". Fashion designers of intellectual processes have long recognized that to create even the semblance of human intelligence need to "repeat" not only "left-brain Felix" and "right brain" Henri Bergson or does not fit into any framework of Mozart and Pushkin. And this is — no, never... what makes us human, no Abyssinians with the Sumerians in their accounts will not lay...
Back to the questions posed at the beginning — how we relate to determinism in our thinking and behavior neuronal mechanisms providing the functioning of the neural network in our brain? Is there still progress in the correlation and explanation of the data of neuroscience and subjective experience, phenomenal consciousness, mental phenomena of high rank?
I'm afraid that there'll be more questions than answers, but the mere awareness of these problems as really existing must be, I hope, a signal for increasing attention — as do the philosophers, and — especially — experimental work in the neuroscience researchers.
According to the best-known form of the theorem of Kurt gödel, published in 1931 in Konigsberg, formal system powerful enough to combine the wording of the claims of arithmetic and logic cannot be both complete and consistent. This, in particular, it follows that the intuition and understanding cannot be reduced to any set of rules. This theorem gödel was the beginning of an important stage of development of the philosophy of consciousness, and Penrose through decades verdict: awareness and understanding as the basis of human intelligence are the result of neurophysiological processes, but they cannot be explained in physical, mathematical, and other scientific terms and impossible to model by computational means.
The AI know that until we are able to simulate "leopolitano" computing brain activity, while inside the brain operates something like an "analog computer" that provides almost all the "propolene", intuitive processes, non-trivial moves and Association — based creative breakthroughs, and therefore, the life of civilization and cultural evolution. Penrose believes that to find at least some explanation of the phenomenon of consciousness, we have to go beyond the limits of known science. It is very likely. And yet the answers to our questions we should seek with the help of scientific methods — even if the nature of these future methods of science, we have a vague idea.

Now, however, new evidence that higher and that of human mental functions it is possible to study the neurophysiological and find corresponding patterns of activity (we are not looking for more loci, and are looking for more of a "melody", since most of the neuronal processes is like a jazz session, which involves temporarily joined structures of the brain). For example, it is known that the hippocampus and frontal cortex form a personal memory and the ability to move it in time to host the event. Moreover, it was shown that the hippocampus is responsible not only for the past (memories), but for the future or possible (imagination).
Finally, continuing the conversation about determinism behavior brain processes: should we take into account individual characteristics of the brain, analyzing, for example, socially significant event? It is known that there are people impulsive, risk-averse, acting instantly, almost without thinking about whether it is necessary to commit this act, or is it better to stop and think, and then make the decision. And there is careful and slow. Tomographic studies show the presence of inhibitory mechanisms in the brain, activated for a few milliseconds before the decision (inferior frontal cortex, which sends braking signal in the subthalamic nucleus of the midbrain, which stops the movement, and the area located in front of the supplementary motor cortex that is responsible for whether action is made or not). If the network works correctly? How variable individual mechanisms?
Discouraged experimental evidence that the brain "makes a decision" in about a few seconds before the person realizes it. MRI may show that a person is going to lie or his decision will be incorrect. It is extremely important in this context to think how arbitrary, subject to the will, are our actions. If we assume that consciousness is primarily awareness, we again encounter a huge gap between the well studied psychophysiology perception and in fact not studied awareness. It seems to be on this path, we would have to help introspection, but, as he wrote Nobel prize winner Francis Crick, the last years of his life dealing with the problem of consciousness, introspection is deceiving us at every step.
Doubt in the very existence of freedom of will, directly related to the problem of awareness occurred repeatedly, starting with the famous experiment of Benjamin Libet, and then Simon Fisher, Daniel Wegner and Mark Hallate. Some researchers and writing: the idea that our conscious thoughts generate actions, obeying, thus, free will is wrong, and believing in it is like really to believe that the rabbit and sitting until the right moment in the magician's top hat.
Hulett, for example, based on the analysis of a large number of specially constructed experiments inclined to think that free will in its purest form the result of introspection.
In other words, I would have commented, the brain in parallel with the touch sensations gives rise to a sense of Agency, that is literally "jerking us around"... not only that, the brain sends us a signal about the "free decision" a few before the (motor, for example) of the signal, and that we are misleading even when it seems to be triggered introspection... we Have to recognize that the brain is our consciousness to some information about its activities...
In this respect, we cannot bypass the question of selfhood (ipseity), which is defined as transparency of the body, or the unity of spiritual and physical in man. The soul is the form of the body, wrote Aristotle, and after him, Thomas Aquinas. However, the attitude to this very different, not only different philosophers and psychologists, but in the different religions: from complete denial of self in Buddhism (Mahayana) to the interpretation of it as a fault (and hence the formation as a result of experience) the way it is understood Luther. Self is not a thing in itself, but a function, and it is not always included (like reflection). This means that there is a gap between what happens and our awareness of this and evaluation is not always present.
Do not forget about the so-called Minimal Self (primary motor skills and understanding of the structure of your body) and Extended Self (the awareness of themselves as individuals, with all contexts), and also about the special status of the brain, the so-called Default Mode — the state of "dormancy", when there is, in particular, the perception important for the subject of signals.
I tend to believe that shown in neurophysiological experiments, the proactive brain consciousness puts into question the existence of freedom of will, except that the Minimal Self and does not affect the Extended Self. The difference between man and other biological kinds, from computers and "zombie" that is in the possession of liberum arbitrium — free Will, the ability to voluntarily and knowingly. "The act of will and action of the body, — says Schopenhauer, is not objectively known by two different States, United by the bond of causality; they are not among themselves in regard to causes and actions, no, they are one and the same, but only this two completely different ways — once quite directly and once in contemplation for the mind. The action of the body is nothing but the objectified, that is entered into the contemplation, the act of will." And then — "my body and my will are one and the same".
Free will and the future of humanityso understanding and recognition of Agency is not only philosophical, but also quite existential value. Yes, it might be absent from the neural network itself, and the brain fools us down and even takes too much upon himself. But not the person taking informed decisions, for which it is responsible! Robot and zombies are not liable, the other thing is homo sapiens. Otherwise the whole human civilization is a mockery. This began to reflect not in the twenty-first century.
"The will is a rational movement, commanding a sense of attraction. No matter what direction she went, she always has her companion mind in some way following on her heels", — wrote the Abbot Bernard of Clairvaux (1090-1153) in his work "De Gratia et libero arbitrio" ("On grace and free will").
It will take a little time, and the brain mapping will be able to tell us, for example, on the potential danger of a person for society, and it presents the society with a complex legal and cultural issues, including on the freedom of the will and the measure of personal responsibility for their actions.
The United States is actively discussing plans to use brain scans in legal proceedings to check the veracity of the testimony, and no one doubts that sooner or later it will happen (as has become the practice DNA analysis), but it's just another version of the lie detector, but the assessment of the brain as a possible "culprit" potential of crimes will change the whole system of jurisprudence, if not the whole human culture.
In General, the future promises to be boring... posted
Author: Tatiana Chernigovskaya
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! ©
Source: //www.strana-oz.ru/2013/1/eto-ne-ya---eto-moy-mozg
How not dark, I guess
myself always on the lady of clubs.
N. V. Gogol "The Government Inspector"

It's not me, it's my brain. This is, like, the twenty-first century answer to the question nineteenth. To us this innovation (not the night be commemorated word) even flew across the ocean, but will fly...
Strictly speaking, the movement in this direction — when the wine for unorthodox actions, and even for the entire life scenario rests on a different kind of physiological or even anatomical features has been observed before. But with the advent of the new Millennium it came to almost completely remove the responsibility from the individual and to give it a "acid", in particular genomic DNA, twisted into a spiral that no court will deal...
The sorrows of young Werther, Turgenev young ladies, extra people, rahmatovich and Frankenstein, and Hannibal ball of decterov with silent lambs — everything, everything is now reduced to four letters — A, G, T and C — the text of the sentence. Comfortable, but embarrassing and dangerous.
Prophetically decades ago, it caught Joseph Brodsky: "... take the top telepaths, Buddhists, spiritualists, drugs, Freudians, neurologists, psychopaths... Soul tied a big veil. Will unite us in a continuous spiral. Stuck in the socket with ethyl morality. It will release from the verb".
The brain in the world and the world in the brainthe Topic of this article goes beyond the traditional anthropological debates about human nature and affects fundamental principles of the functioning of the most complex of all complex systems, neural networks.

We are talking about the degree of personal independence from a physiological (if not physical-chemical) processes, deterministic behavior properties of the brain and even genetics when you can't avoid the question of free will as the network itself (could it behave differently?), and of the subject. The latter is fundamental to any discussion about the specifics of the person and his differences from "zombie" or other virtual or real systems that claim to possess human abilities.
Probably most people will agree that a distinguishing feature of man is the consciousness. The case for small: there is no consensus on the definition of what exactly it is... the Term consciousness is used in at least two different aspects:
1) as a characteristic of any of the properties of living beings,
2) how the presence of certain levels and States of consciousness.
There are actually a lot of different meanings that are invested in this project:
• Consciousness has any sense and react to external stimuli creature. Then you need to recognize that they have fish, shrimp, etc.
• Not in a dream or in a coma. How then, in this sense, to determine the condition of in sleep, in hypnosis, etc.?
• Awareness: we are conscious, we are aware that are aware. How then to be with young children? With a highly developed, but not speaking creatures?
• So What is it called when asked to imagine what the world terms other consciousness — for example, a bat with its echolocation, or octopus. Virtual imaginable alien creatures a little more than incomprehensible to us in this sense than any earthly animal.
In modern science there is a very wide range of types of attitude to the problem of consciousness and its natural-scientific study — from osmoregulatory when the most complicated and radical to understand the issues simply do (and this is true for most experimentally working scientists), to postulating the irreducibility of these parallel "worlds" and appeal not to generally look for neurophysiological correlates of consciousness (if it is not within the scientific paradigm, or, at least, it is natural-scientific unit).
Some hope for a way out of this situation inspires the development of cognitivist approaches, are multidisciplinary by definition. For example, the radical cognitivist (as he calls himself) Victor allakhverdov is in opposition to the irrationalism and noncognitivism, to look at man from the standpoint of the synthetic theory of evolution, to behaviorism and psychoanalysis and argues that "the recognition of the irreducibility of knowledge to the behavior, focus on the description of the processes of information processing, the understanding of the role of the subjective constructs in the description of the world, emphasis on problems of balance between the conscious and the unconscious" gives hope for a breakthrough and a deadlock. He also claims thatconsciousness is lagging structure, as the brain carries out independent checks, choosing correct, in his view, hypotheses of different variants, including incorrect.
Subjective reality, qualia, or phenomenal consciousness — perhaps the most important theme in these discussions. This also highlights the biggest modern neuroscientist Gerald Edelman.

The Central problem of consciousness — how subjective experiences arise from physical phenomena. It is written and continues to write a lot of articles and books. We see only what we know. Images and ideas — not a copy and not even the amount of physical signals arriving at our receptors. They build our brains. In other words, what is seen, heard and perceived, to have different kinds of animals and all of them from us, not because of different ranges of vision, hearing, smell, etc., and because all creatures your brain that processes sensory signals, forming a subjective (!) images. Not only in different species but also among different individuals within one species, different qualia. It should be noted that the presence of subjective reality is not detected behavioral methods, therefore, experimental testing requires special mental development.
In connection with the above, you need to get used to make major amendments to individual, ethnic, religious, professional and other cultural differences, to build a neural network and the subjective worlds of different people. The pivotal importance of cross-cultural (as it is now called) the nature of thinking described by Nikolai Marr, Israel Frank-Kamenetskii, Freidenberg, Olga, Pavel Gurevich, Mikhail Steblin-Kamensky...
The brain is not the sum of billions of neurons and their connections and such, plus the sum of individual experiences that have shaped this tool — our brain — and set it up.
Perception is an active process of knowledge extraction and construction of the world. Different living systems do it differently, extracting from the world the desired characteristics (e.g., magnetic field or polarized light) and building-specific model of the world. It is the presence of the subjective world and the subject itself distinguishes man from the cyborg. Yet. The advantage of man consists in the possession of liberum arbitrium — free will, the ability to voluntary and conscious choice and consent taken by the decision — voluntarius consensus.
All cognitive processes are receiving and processing information according to certain rules and algorithms. In the brain there are mental representations, providing contact with the world. This hypothesis of a high degree of abstraction, the underlying picture of the world that cannot be verified empirically, because "objective", "real" picture of the world just yet, or it knows only the Creator. The addition of the opinions of a statistically acceptable number of people adds nothing, as they all have a similar brain. As Kant says, "reason does not derive its laws (a priori) from nature but prescribes them to her".
Unable to evade a dangerous question: why formal thinking applicable to the real world? Why do we accept as an axiom that is well-organized in the framework of our algorithms construction — true? True in the framework of our thinking.
Here we face a paradox: the brain is in the world, and the world is in the brain. Search of subjective experience in the physical world (i.e. the quality and intensity of sensory stimuli) is absurd: it is not there, as it is built in the brain, in some, additional space of the brain. Who look for mental representations? Who interpretered?
It would seem that the obvious answer is "me", but... as if from another dimension, from another space, from the inside of the brain, not as a physical object and mental entity. And because the brain is (with someone) dialogue... And who says ("don't go there"...)? Would have said — right and left hemisphere, how would two different personalities. But now the picture has become much more varied, and the brain — much "naselenie".
It seems that the texts reads the neural network itself, the neural networkthat we caught or that you are... one Consolation is that it was caught and the world. Or she is the world. And its shape, density, grace netting, flexibility and resilience are alive, and we can knit your patterns, not obeying the templates given to us a priori — sustainability.
Can we brain trust? Potential the ability to deliver personality is not only about sensory and semantic information, but also inadequate assessment of the affiliation of the sensations this subject well known of the mental disease. Research Vilayanur Ramachandran show that "belief consciousness" can destroy them, therefore, arbitrary ways, conscious of the impact even such extreme and abnormal sensations there.
The question that remains is not going anywhere: our brain — the implementation of the "set of all sets not members of themselves" Bertrand Russell or a self-contained masterpiece in a recursive relationship with allowed him the person in whose body it is placed? And what is posted? What from the world that we perceive and which is adapted, belongs to him, and what causes our brain? This means that the question of the separation of subject and object remains Central.
It was long ago realized the largest minds, such as Alexei Ukhtomsky, the outstanding Russian scientist ahead of his time almost a century and believed that neither of the subject nor of the object that we are not spectators, but participants, and even what our nature is doing, that is, it is as if there is independently of us. In this connection, you need to remember Alexander Piatigorsky and Merab Mamardashvili, and Vladimir Zinchenko, who was said by that being and consciousness are a continuum, and that thinking and existence are the same.
A situation where the object of study is not independent of the observer, physics experienced a long time ago, when began to be developed quantum theory and the confused world of Schrodinger's cat. Such scenes that violate all the usual ideas about space and time, as is commonly thought, inhabited the quantum world, in which everything depends on the presence of the observer. In the macrocosm of these phenomena, until recently, were not observed. But it is in physics, and the Sciences that study living systems, the role of the observer — role of the brain — not to underestimate. So, analytic philosophy — the same player on the field, as neurophysiology and cognitive psychology.
Strictly speaking, now neuroscience and philosophy of mind well without each other cost, one can even say they even interfere, as mutually forced each other to look. Hope to build a bridge between them, designed to overcome the failure, until quite illusory: the current status of research can still be described as Where-it-happens studies, as any the most sophisticated technique gives only the answer to the question of which brain area is active or passive during the activities, whereas I would like to not "address," and an explanation.
In the discussion of the autonomy of the brain, raised in the articles by Ernst Nagel, David Dubrovsky insists that a person can "operate on their own a class of their neural systems, that is, to control them", and it follows that the internal hard determinism are not obvious.

The brain — the Creator or the mirror?In 1922, long before the emergence of cognitive science, Semyon Frank wrote:
"Social science the methodological peculiarity that in it the subject of knowledge in a way coincides with its object. The ant researcher is not the participant of the nest, bacteriologist belongs to another group of phenomena, than study the world of microorganisms, the same social scientist he is, consciously or unconsciously, citizen, that is, member of study society".
Remember in this regard and his brilliant predecessors. "Great Kant taught us that time, space and causality in all its regularities and possibilities all its forms are in our consciousness quite independently of the objects that they are and make their contents — wrote Arthur Schopenhauer, or, in other words, it is equally possible to come, proceeding from the subject or from the object; therefore, they can with equal right be called as methods of the contemplation of the subject, and the properties of the object, since the latter is an object (in Kant: the phenomenon), that is, a performance."
We know that a baby born now are genetically not very different from the one born at the beginning of our biological history. Know which line it was a dead end, and which has led to the emergence of modern humans and different racial and ethnic groups. Despite the ambiguity of the relationship to the discussion of whether continues or has already ended biological evolution of man, should indicate to the emergence of data showing that the human brain is still under the influence of adaptive evolutionary processes (e.g., microcephalin — gene that regulates the volume of the brain — continues to evolve adaptive).
Opening Rizzolatti Giacomo and Michael Arbib mirror neurons and mirror systems in General gives a completely new data on the emergence of language and reflection as the Foundation of human consciousness. The mirror system of the brain Carteret external information — actions by another creature, not necessarily of the same kind, but with a clear system of coordinates and the interpreted behavior. They are almost in all parts of the human brain and are activated in particular in anticipation of action, with the empathy of emotion or the memory of them, etc. It shows the basis on which developed the brain, ready to build models of consciousness and also for social learning and appropriate behavior in society. The lack of capacity observed in extreme forms of autism and schizophrenia, leads to the loss of a person from society with the most severe existential consequences.
It is extremely important that the formation of these systems are reliable mechanisms of self-identification that is broken when the mental pathology of schizophrenia and is also associated with the functioning of mirror systems.
So, very difficult organized by the human brain — a mirror for the world, or himself forms the world? It is important to the world or only to the individual himself to ensure the viability? Why do we repeat it? To duplicate that yourself or the world? To learn how the brain works or what are the laws of the world as a whole? And unless we can duplicate what is organized more complicated than we even can imagine? To create the model to verify the correctness of the hypotheses? — Yes, but, for example, training an artificial neural network, we know not how the brain operates, and how learning takes place! Just as in teaching primates human sign language, we find out just to what extent they can complete their education — no more.
It is now clear that the processes of memory operation (write, read, search) in the human and the computer differ a lot. The basis for the organization of computer memory is the addressing — location information in memory. Various types of contents search (keys, sets, signs, etc.) provided by the system address references. Human memory also has a large set of keys that allows you to quickly read information. However, even if we get comparable results, we have no confidence that the processes themselves were the same!
For example, now there are robots that can compensate for movement disorders by continuously remodel itself depending on the situation. Does it follow that the robot now has consciousness and subjective reality? The freedom to make decisions about yourself?
Studies of Konstantin Anokhin give us specific information about what high degree of difficulty of the processes of memory worked by nature for animals standing on different levels of the evolutionary ladder, and the most successful moves are fixed genetically. Man is incomparably more degrees of freedom of the selection algorithms as fixation and reading information that increases the level of difficulty. The brain is commonly modeled as a classical physical system, which by definition is computing. However, it is clear that this is not so, and therefore, in the future, when such approaches are possible for modeling are likely to come under a different scientific paradigm (cf. the hypothesis of John Eccles that describe functions of some of brain structures necessary involvement of quantum concepts).
We denote the properties of mental processes, which, in our opinion, make the computer metaphor is completely irrelevant, looking back before that to Roger Penrose, who wrote that consciousness cannot be reduced to the calculation, as living brain is endowed with the ability to understand. What is the understanding? Not fixing and correlating with something that is understanding — not an idle question, primarily with respect to other types of intelligence, not the human type. According to Penrose, the brain really works like a computer, but this computer is so unimaginable complexity that its simulation is not under the power of scientific understanding.
The brain is the design of soft and hard links and includes the top-down algorithms, bottom-up procedure of teaching and non-computed layers. This gives us reason to believe that at least in the foreseeable time it will not lend themselves to adequate modelling.
So the irrelevance of the computer metaphor in its current form is determined by the following properties of human consciousness:
Extraordinary the role of context, and hence the possibility of multiple interpretations of messages and events in General. This alone is enough so the world was reflected in a distorting mirror (in the theory of communication talking about communication holes or failures, not least for this reason). It should be recalled in this regard, biosemiotics and theoretical biology Jacob Ukskula with his idea Umwelt's — worlds, separate for each creature and almost impervious to others: "Everything has it's own Umwelt adapted to its specific needs" (each creature your world, adapted to its existence) — only high organisation of consciousness gives the chance to consider the worlds of other people.
— Redundancy and the possibility of many paths to find the same. The use of different algorithms at different times without obvious reasons. And finding that was not looking (in passing). As wandering by and large (and almost his) house — what you might find... Space familiar only partially, and not very bright. Stumble and not go by there... it's Hard to go on the same route several times, except that this route is trivial and automatic. Actually, if a person persistently uses the same route on the mental operations, it says its epileptogenicity (when Slippers should be only a parallel). And the opposite: if each time to try a new route, then there is clearly not without schizoid. And it can not only lead to unproductive search (behavior), but also to discoveries, as it included low-frequency associative processes.
The surprise and unpredictability of the matched objects or procedures: the more rare and "foreign" objects, the more effective can be a creative process (this explains the continuity of the "norm" when the line between madness, schizotypal consciousness and genius is determined by the external coordinates — adaptation to society). Is it possible, by the way, computer simulation of hallucinations when the brain begins to replace sensory input to their simulation? Because the brain sees, hears and feels that "willing and able", and not what is in the "objective" world.
— Vagueness, inaccuracy, approximation of descriptions does not reduce the effectiveness of the search in the memory and algorithm behavior (something that is usually associated with hemispheric type of consciousness). Couldn't agree more: what a man, hard to the computer and Vice versa.
— Neprijatnosti Aristotelian type of thinking and even the artificiality of his brain, because this type of logic a person should be specially trained to use. Plurality of types of thinking, determined by the culture and the task (everyday, scientific, and religious thinking used in the game, see the work of cross-cultural psychologists Claude Levi-Strauss, Alexander Luria, Michael D. Cole, Peeter Tulviste, etc.). Note that this multiplicity is provided by the brain, in particular the characteristics of its hemispherical functional organization.
— Humor and laughter, "carnival" — properties of the human psyche which acts as a "tickling of the heart", when it is possible to lose the fear and conscience, and the "tickling of the mind", when you can violate the laws of reason, common sense and etiquette. The psyche needs to rest. If your computer can simulate a sense of humor? All he can require of the algorithm, or script, or permutations. Is this a way to generate funny, that is unexpected? Rather no than Yes, but if so, something simple and therefore not very funny or — bust unlikely options — redaktirovanie. It's all about dose and context. The laws are ridiculous, the same as the laws of poetry, from an unexpected angle, analogy, unusual starting point.

Yes, the chess supercomputer Deep Blue defeated Kasparov in chess, and humanity was shocked. Soon woke up: it's just a game, based on the search options (i.e. not the whole intellect), and besides, with incomparable amounts of memory opponents (even incorrectly), and besides, "atskanotaju" artificial intelligence on a particular player... Experts say that to write a program a high-level backgammon games, for example, is incomparably more complicated: the bone Lord bone... the Case that is.
However, another world chess champion Vladimir Kramnik said that chess is too complex for the computer, since the number of possible combinations represents a number with 28 zeros; as the algorithm of human thinking is that we can choose the direction of the calculations, and not to try all combinations, then we have a chance to score. Which is a relief. Although not for long as we already see.
Race at the speed we lost long ago: the speed of electronic circuits is already millions of times greater than the rate of excitation of neurons in the brain, wherein the electronic circuit demonstrate the high accuracy of synchronization and processing instructions that are in any way not characteristic of neurons.
What? — And anything. Not yet seen nor Pascal, nor Leonardo, nor Shopengauera. And will not be visible ever in these zeros with ones, because nobody has yet made any breakthrough in science and philosophy, not to mention the art, with a particularly well-oiled calculating machine "Felix". Fashion designers of intellectual processes have long recognized that to create even the semblance of human intelligence need to "repeat" not only "left-brain Felix" and "right brain" Henri Bergson or does not fit into any framework of Mozart and Pushkin. And this is — no, never... what makes us human, no Abyssinians with the Sumerians in their accounts will not lay...
Back to the questions posed at the beginning — how we relate to determinism in our thinking and behavior neuronal mechanisms providing the functioning of the neural network in our brain? Is there still progress in the correlation and explanation of the data of neuroscience and subjective experience, phenomenal consciousness, mental phenomena of high rank?
I'm afraid that there'll be more questions than answers, but the mere awareness of these problems as really existing must be, I hope, a signal for increasing attention — as do the philosophers, and — especially — experimental work in the neuroscience researchers.
According to the best-known form of the theorem of Kurt gödel, published in 1931 in Konigsberg, formal system powerful enough to combine the wording of the claims of arithmetic and logic cannot be both complete and consistent. This, in particular, it follows that the intuition and understanding cannot be reduced to any set of rules. This theorem gödel was the beginning of an important stage of development of the philosophy of consciousness, and Penrose through decades verdict: awareness and understanding as the basis of human intelligence are the result of neurophysiological processes, but they cannot be explained in physical, mathematical, and other scientific terms and impossible to model by computational means.
The AI know that until we are able to simulate "leopolitano" computing brain activity, while inside the brain operates something like an "analog computer" that provides almost all the "propolene", intuitive processes, non-trivial moves and Association — based creative breakthroughs, and therefore, the life of civilization and cultural evolution. Penrose believes that to find at least some explanation of the phenomenon of consciousness, we have to go beyond the limits of known science. It is very likely. And yet the answers to our questions we should seek with the help of scientific methods — even if the nature of these future methods of science, we have a vague idea.

Now, however, new evidence that higher and that of human mental functions it is possible to study the neurophysiological and find corresponding patterns of activity (we are not looking for more loci, and are looking for more of a "melody", since most of the neuronal processes is like a jazz session, which involves temporarily joined structures of the brain). For example, it is known that the hippocampus and frontal cortex form a personal memory and the ability to move it in time to host the event. Moreover, it was shown that the hippocampus is responsible not only for the past (memories), but for the future or possible (imagination).
Finally, continuing the conversation about determinism behavior brain processes: should we take into account individual characteristics of the brain, analyzing, for example, socially significant event? It is known that there are people impulsive, risk-averse, acting instantly, almost without thinking about whether it is necessary to commit this act, or is it better to stop and think, and then make the decision. And there is careful and slow. Tomographic studies show the presence of inhibitory mechanisms in the brain, activated for a few milliseconds before the decision (inferior frontal cortex, which sends braking signal in the subthalamic nucleus of the midbrain, which stops the movement, and the area located in front of the supplementary motor cortex that is responsible for whether action is made or not). If the network works correctly? How variable individual mechanisms?
Discouraged experimental evidence that the brain "makes a decision" in about a few seconds before the person realizes it. MRI may show that a person is going to lie or his decision will be incorrect. It is extremely important in this context to think how arbitrary, subject to the will, are our actions. If we assume that consciousness is primarily awareness, we again encounter a huge gap between the well studied psychophysiology perception and in fact not studied awareness. It seems to be on this path, we would have to help introspection, but, as he wrote Nobel prize winner Francis Crick, the last years of his life dealing with the problem of consciousness, introspection is deceiving us at every step.
Doubt in the very existence of freedom of will, directly related to the problem of awareness occurred repeatedly, starting with the famous experiment of Benjamin Libet, and then Simon Fisher, Daniel Wegner and Mark Hallate. Some researchers and writing: the idea that our conscious thoughts generate actions, obeying, thus, free will is wrong, and believing in it is like really to believe that the rabbit and sitting until the right moment in the magician's top hat.
Hulett, for example, based on the analysis of a large number of specially constructed experiments inclined to think that free will in its purest form the result of introspection.
In other words, I would have commented, the brain in parallel with the touch sensations gives rise to a sense of Agency, that is literally "jerking us around"... not only that, the brain sends us a signal about the "free decision" a few before the (motor, for example) of the signal, and that we are misleading even when it seems to be triggered introspection... we Have to recognize that the brain is our consciousness to some information about its activities...
In this respect, we cannot bypass the question of selfhood (ipseity), which is defined as transparency of the body, or the unity of spiritual and physical in man. The soul is the form of the body, wrote Aristotle, and after him, Thomas Aquinas. However, the attitude to this very different, not only different philosophers and psychologists, but in the different religions: from complete denial of self in Buddhism (Mahayana) to the interpretation of it as a fault (and hence the formation as a result of experience) the way it is understood Luther. Self is not a thing in itself, but a function, and it is not always included (like reflection). This means that there is a gap between what happens and our awareness of this and evaluation is not always present.
Do not forget about the so-called Minimal Self (primary motor skills and understanding of the structure of your body) and Extended Self (the awareness of themselves as individuals, with all contexts), and also about the special status of the brain, the so-called Default Mode — the state of "dormancy", when there is, in particular, the perception important for the subject of signals.
I tend to believe that shown in neurophysiological experiments, the proactive brain consciousness puts into question the existence of freedom of will, except that the Minimal Self and does not affect the Extended Self. The difference between man and other biological kinds, from computers and "zombie" that is in the possession of liberum arbitrium — free Will, the ability to voluntarily and knowingly. "The act of will and action of the body, — says Schopenhauer, is not objectively known by two different States, United by the bond of causality; they are not among themselves in regard to causes and actions, no, they are one and the same, but only this two completely different ways — once quite directly and once in contemplation for the mind. The action of the body is nothing but the objectified, that is entered into the contemplation, the act of will." And then — "my body and my will are one and the same".
Free will and the future of humanityso understanding and recognition of Agency is not only philosophical, but also quite existential value. Yes, it might be absent from the neural network itself, and the brain fools us down and even takes too much upon himself. But not the person taking informed decisions, for which it is responsible! Robot and zombies are not liable, the other thing is homo sapiens. Otherwise the whole human civilization is a mockery. This began to reflect not in the twenty-first century.
"The will is a rational movement, commanding a sense of attraction. No matter what direction she went, she always has her companion mind in some way following on her heels", — wrote the Abbot Bernard of Clairvaux (1090-1153) in his work "De Gratia et libero arbitrio" ("On grace and free will").
It will take a little time, and the brain mapping will be able to tell us, for example, on the potential danger of a person for society, and it presents the society with a complex legal and cultural issues, including on the freedom of the will and the measure of personal responsibility for their actions.
The United States is actively discussing plans to use brain scans in legal proceedings to check the veracity of the testimony, and no one doubts that sooner or later it will happen (as has become the practice DNA analysis), but it's just another version of the lie detector, but the assessment of the brain as a possible "culprit" potential of crimes will change the whole system of jurisprudence, if not the whole human culture.
In General, the future promises to be boring... posted
Author: Tatiana Chernigovskaya
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! ©
Source: //www.strana-oz.ru/2013/1/eto-ne-ya---eto-moy-mozg
Tags
See also
It is necessary to know! 12 facts about high temperature
How does Savings (13 photos)
Stunning 60 "hacks" of the brain that will make your life better
It is mine!
My Cuba.
This is my boar!
Brain tricks
Answers to strange questions that were asked at least once every
The virus of degradation and loss of humanity