548
In your house there are cosmic dust from asteroids and comets, Jupiter family
Stardust in the closet and under divanom
When you do the cleaning, the cleaner your probably gets some of the cosmic dust - the same that was once part of a comet or asteroid. Each year, the Earth gets about 40 tons of cosmic dust. While this fact may not cause doubt, there is much debate about where the dust is taken. We know that most of the descending spiral with the interplanetary dust cloud - a vast dust band around the sun. But where it appears there is this dust?
Recent studies show that about 10% of the dust comes from asteroids, but a much larger part comes from Jupiter family comets. These comets are composed of ice and dust and are traveling in an elliptical orbit around the Sun, passing close to Jupiter. Most likely, the solar system, they come because of collisions with other comets in the Kuiper Belt - a large comet belt beyond Neptune discovered.
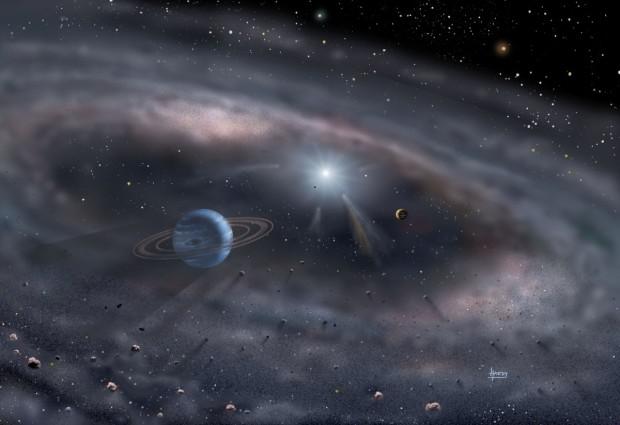

When the comet dust falls to Earth, it can cause a meteor shower, of course, if the particles are large enough. In fact, the annual Perseid meteor shower and Leonids are due to fall on a planet of dust and debris left by comet Swift-Tuttle and the Tempel-Tuttle. Dust comet moves with a huge, sometimes more than 150 million km / h. It slows the Earth's atmosphere, but the pressure on the larger particles, enough to make them burn. Smaller particles can cope with sudden changes in pressure at the entrance into the atmosphere and reach the surface.
Comets contain primordial dust, from which formed our solar system. Since they were at a great distance from the sun for most of his life, a part of the substance is in a state of deep freeze, keeping dust billions of years. Studying this dust, you can take a journey through time and learn about how water is formed and organic matter.
Of course, we will not soon will understand how the planet formed and how life could have arisen, but the study of cosmic dust helps us to make some progress on this issue.
via factroom.ru

When you do the cleaning, the cleaner your probably gets some of the cosmic dust - the same that was once part of a comet or asteroid. Each year, the Earth gets about 40 tons of cosmic dust. While this fact may not cause doubt, there is much debate about where the dust is taken. We know that most of the descending spiral with the interplanetary dust cloud - a vast dust band around the sun. But where it appears there is this dust?
Recent studies show that about 10% of the dust comes from asteroids, but a much larger part comes from Jupiter family comets. These comets are composed of ice and dust and are traveling in an elliptical orbit around the Sun, passing close to Jupiter. Most likely, the solar system, they come because of collisions with other comets in the Kuiper Belt - a large comet belt beyond Neptune discovered.

When the comet dust falls to Earth, it can cause a meteor shower, of course, if the particles are large enough. In fact, the annual Perseid meteor shower and Leonids are due to fall on a planet of dust and debris left by comet Swift-Tuttle and the Tempel-Tuttle. Dust comet moves with a huge, sometimes more than 150 million km / h. It slows the Earth's atmosphere, but the pressure on the larger particles, enough to make them burn. Smaller particles can cope with sudden changes in pressure at the entrance into the atmosphere and reach the surface.
Comets contain primordial dust, from which formed our solar system. Since they were at a great distance from the sun for most of his life, a part of the substance is in a state of deep freeze, keeping dust billions of years. Studying this dust, you can take a journey through time and learn about how water is formed and organic matter.
Of course, we will not soon will understand how the planet formed and how life could have arisen, but the study of cosmic dust helps us to make some progress on this issue.
via factroom.ru
Why did you wake up five minutes before the alarm
Tears caused by grief, tears of onion have different chemical composition