The Secret Life of the Giants
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net

probe NASA Juno successfully entered orbit around Jupiter intermediate giant planet, telling that he will study after the beginning of scientific work.
According to the common joke Juno, wife of Jupiter, flies to know how he spends time with his mistresses and lovers. In fact, Juno mission does not concern relations between Jupiter and its satellites, this study is all about giant.
The main scientific objectives of Juno - get to know the structure of Jupiter. This knowledge will enable a better understanding of the structure of the planet, and learn more about the processes of formation of gas giant planets in the solar and other planetary systems. Jupiter - a unique body for our system - almost a transitional form from the planet to the brown dwarf. To become a brown dwarf Jupiter will need to find somewhere else dozen of their twins, and to reach the status of star - eight dozen. However, Jupiter - is not the kind of Earth-like planet, which is now the best studied. All under a few hundred kilometers of the helium-hydrogen gas atmosphere, Jupiter filled the sea of liquid hydrogen, the bottom of which is even more exotic stuff - metallic hydrogen. Tremendous pressure and temperature conditions formed, which just impossible to imagine in the world, you can only execute mathematical modeling or get milligrams of this material in the laboratory. How are the layers of Jupiter's interior, which processes take place there, whether there is a solid core in the center? These questions must be answered Juno.
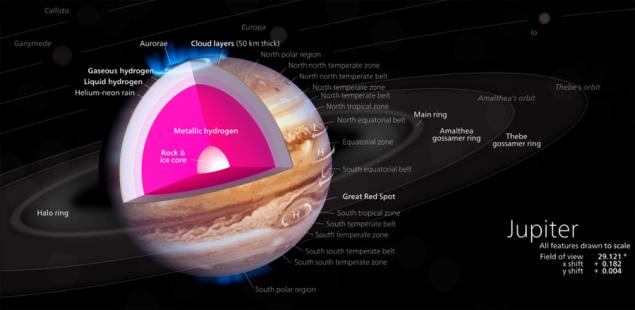
Looking to the Great Red Spot, it allows you to see not only the rich inner world of Jupiter, but also a better understanding of the processes of formation of planetary systems, and more exotic objects in the Universe: brown dwarfs
. Juno is equipped with instruments that will, in their own way to extract knowledge from the depths of Jupiter.

The outer shell of gas - the most accessible to study, so it is aimed most instruments, but the processes in the Jovian clouds should tell what's going deeper. The outer atmosphere of Jupiter will study two spectrometers: infrared and ultraviolet. For the "mass audience" has a separate camera that shoots in the visible range - its task is to delight us with beautiful fotochki until she dies from radiation
.

The infrared camera allows you to see the heat flows in the atmosphere at a depth of 70 km. To infrared data about Jupiter were full, he began to watch in advance with the help of ground-based telescopes, including the European VLT.

In the ultraviolet will be observed auroras of Jupiter. Now it is only concerned with Hubble telescope.
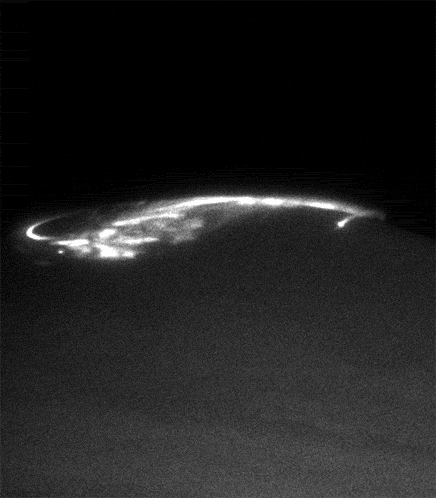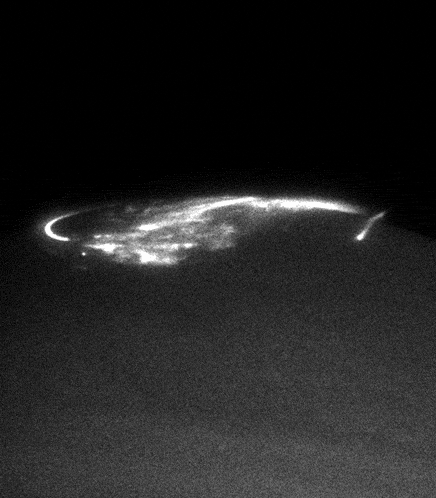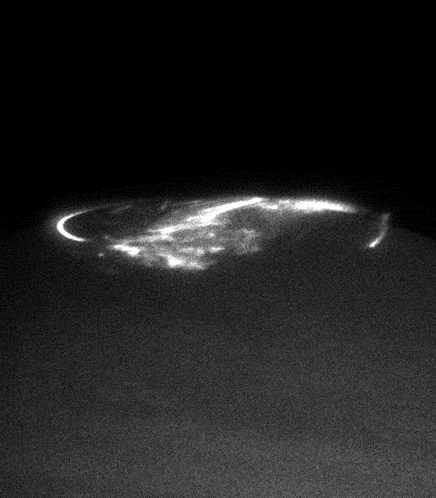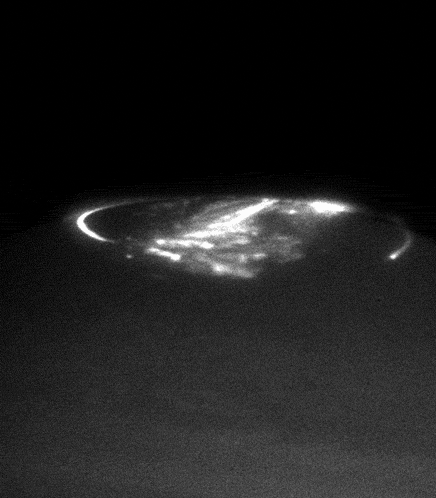
Auroras are interested scientists not only from an aesthetic point of view. Jupiter's magnetic field - the most powerful of the planets of the solar system. It is the cause of the formation of the most powerful radiation belts, and the magnetosphere's tail stretches for hundreds of millions of kilometers right up to the orbit of Saturn. The nature of its formation is hidden in the depths of Jupiter and is associated with the flow of liquid metallic hydrogen in the outer core of the giant planet, so the study of the magnetic fields and radiation belts - is another important task Juno
. For example now we know that Jupiter, as well as the Earth's geographic pole does not coincide with the magnetic, because of what the giant waving flirtatiously its radiation belts.

Unlike Earth, Jupiter has its own source of charged particles, which fills the radiation belts. We have to wait for a solar flare, to see the aurora, and Jupiter quite another major eruption in the nearest large satellite Io. And since Io always boils, then fireworks at the poles of Jupiter is not uncommon.
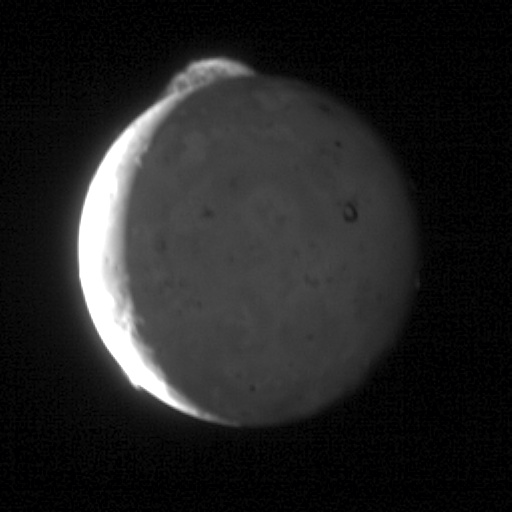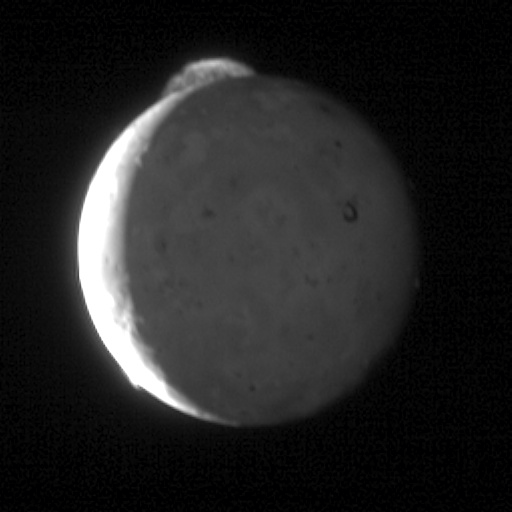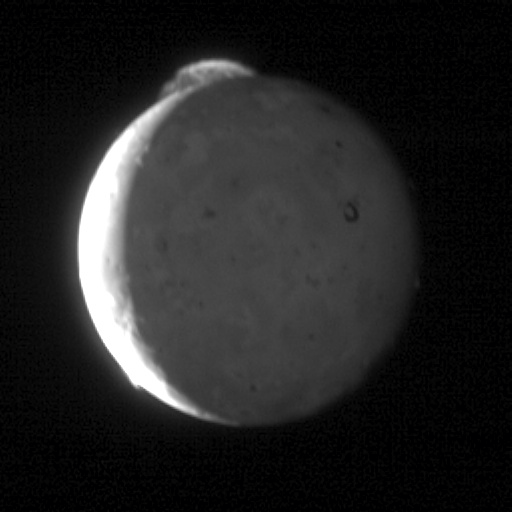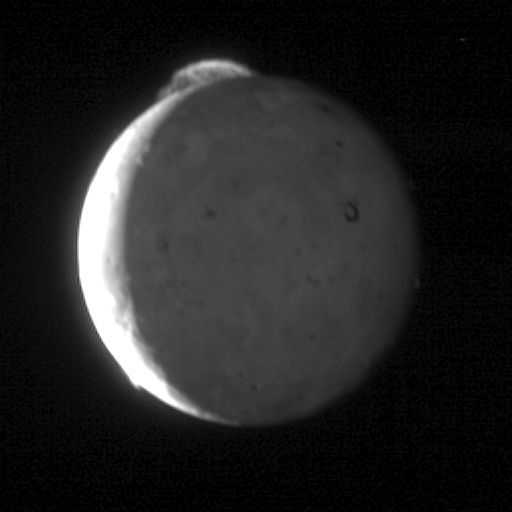
Io volcanoes spew dust and gases whose atoms are ionized by solar ultraviolet light and fill up the magnetosphere of Jupiter, becoming a big problem for spacecraft and possible future conquerors of Europe.
For the study of charged particles and plasma Juno is equipped with two sensors of low-energy and high-energy particles. A special antenna will study radio waves that are generated by auroras.
The magnetic field is mapped using a magnetometer, located on one of the "wings" of the spacecraft. This device is very sensitive to changes in the magnetic field, so he tried to make as far as possible from the electrical Juno.

To improve the accuracy of readings, a magnetometer equipped with a stellar sensors that can determine the position of the device being guided by the stars. When Juno flew past Earth, the star sensors are able to test and use both as a camcorder.

A look at the very insides Juno Jupiter's atmosphere will produce using the microwave radiometer. It will watch the heat flows to a depth of 600 km.
Finally, perhaps one of the most important studies will be carried out by recording the variations of the gravitational field of the planet. The result should be the understanding of the structure of Jupiter, distribution layers, accurate mass of its nucleus, and a more accurate understanding of its composition. Oddly enough, for these purposes will not be a separate device. The analysis will be carried out by a radio signal: non-uniformity of the gravitational field at a paltry fraction of a percent would change the spacecraft's velocity and the deviation will be determined on the Earth by the Doppler effect, which will lengthen or shorten the radio wave Juno
. The spacecraft will rotate elongated polar elliptical orbit, away to 3, 5 million square kilometers, and drawing closer to the 5 th. Km. This the first time we will be able to see Jupiter's poles, which have not yet been able to remove any probe.
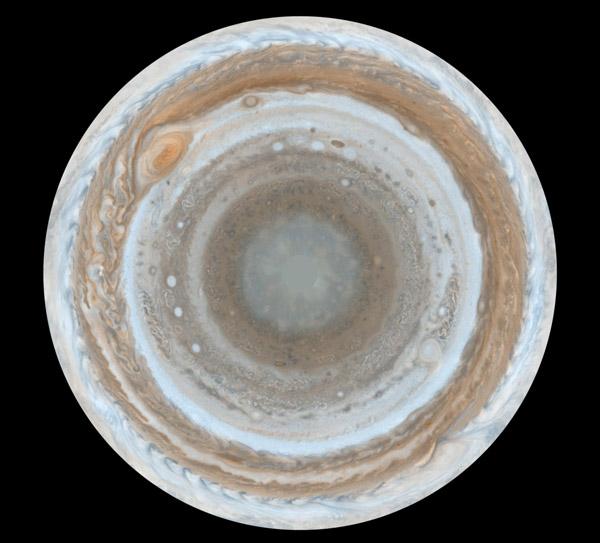

Each coil will occupy on the orbit of 14 days. This orbit is intended for research, but Juno did not immediately come to it. The work of Jupiter will start with 53, 5-day orbit, and the stage of research will begin in November 2016. Less than a year and a half, by February 2018, Juno mission is completed and the unit will be reduced in the dense layers of the atmosphere of the giant planet.
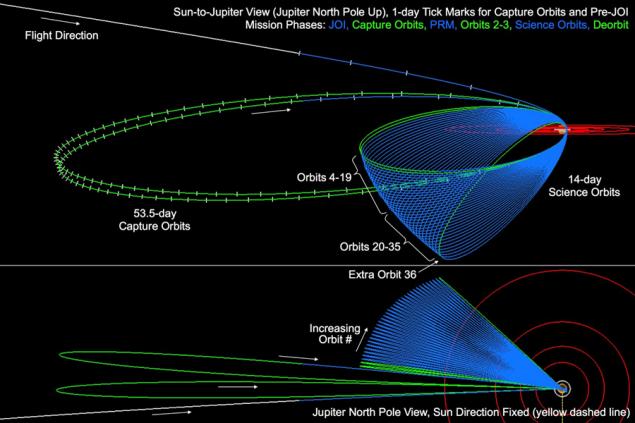
This traceless destruction apparatus is provided to avoid the risk of contamination by microorganisms terrestrial surface of Jupiter's moons, especially in Europe, where they hope to find their own lives.

If you are lucky, during the work of Juno to Jupiter to fall another large asteroid, and this event will be able to explore all the tools. As the ground-based observations, such collisions are not uncommon for Jupiter, but the Juno predecessor - Galileo probe in the 90s even luckier - he was able to observe the fall of the comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 in 1994
.

It is curious that so far in the upper atmosphere of Jupiter observed an increased content of water in those regions where there was a falling comet fragments. This discovery was made infrared telescope Herschel, and Juno also try to evaluate the water supply.
Juno is not the first researcher Jupiter, but most probes flew by and studied only span trajectories.
Almost always, a giant used to accelerate when gravity maneuvers, and only in the 90s to his unit flew NASA Galileo.
Unlike Galileo, Juno fully devote himself to the study of Jupiter, hold closer and closer inspection of the polar regions.
Follow the flight of Juno please visit whereisjuno.info, in the application for NASA Eyes or SolarWalk for iOS and Android desktops.

Source: geektimes.ru/post/278098/
Tags
See also
In NASA created a group are looking for a new scientific work for them on board the ISS
Curiosity on Mars. Tackie yes or no?
New Horizons began maneuvers to his next target
Why the discovery of "second Earth", should You care
Hawaii fabulous!
Original taken in photo magazines Korzhonova Danila
10 simple rules for women, training for result
Will we have to say goodbye to the dream of space elevators?
9 scientific evidence of the impact of kindergartens on the level of the hormone of fear