716
Curiosity at the bottom
22 pictures + text
Finally, share the results of research NASA Curiosity December and half of January. And the purpose of the drilling is also defined. The basic summary of news: almost all the minerals, which are now surrounded by the rover, formed with the participation of water. That is, in fact, it is at the bottom of the former ancient Martian pond.

Just two meters Curiosity drove to the moment experienced in his brush. Since then, this week, he sent so many things that amaze, surprise or confound that fit sentence, "You shall not boil a pot." But he goes on right now, and it's Mars, so "keep the pot».
Everything in order.
About a month ago Curiosity has entered a new type of surface of Mars, which is characterized by high thermal inertia. This means that it is slowly heated up and cools more slowly, indicating a high density of the rock. (Read more about the geology of the crater Gale)

Then the landscape changed, and went under the wheels of the rover's massive stone slab, covered with wide cracks:
Even then, for its resemblance to a place called the pond Yellowknifle Bay (Bay of Yellowknife, in the town in Canada).

An analysis of climate station onboard REMS showed that soil temperature readings really changed:

Specially marked the result of 120 hydrochloric when the rover approached the surface of the third type of Glenelg, which will be studied later. The site, called Shaler, attracts attention with its unusual layered structure:

The lower flat part - the "bottom" of the Gulf - girded low threshold that their material is different from the bottom:

Curiosity began to study the "floor" and "Threshold»:

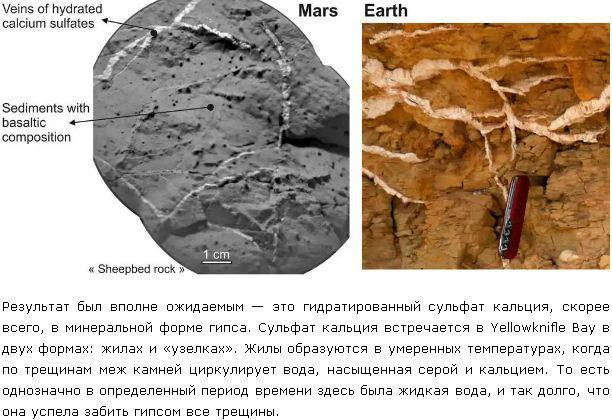
Immediately it was observed characteristic white veins that permeated virtually all the cracks in the valley. White arrows indicate the conductors, black - small mineral concretions. Geologists known veins similar to Earth, but Mars has been carefully analyzed:

Besides gypsum plaster still lived there "nodules»:
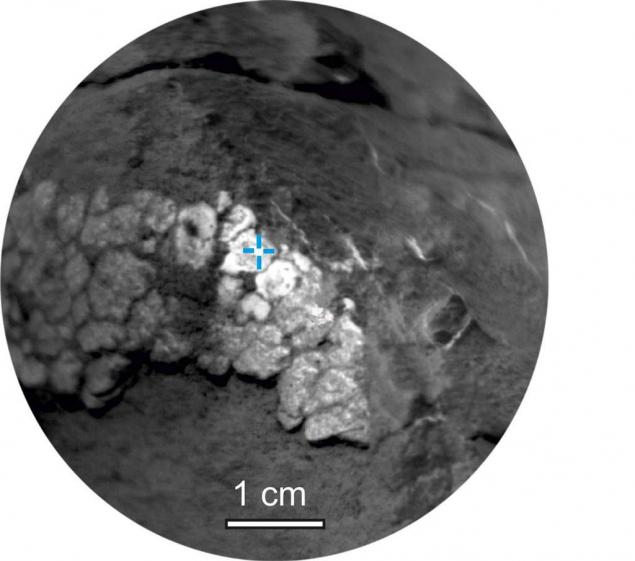
Results of spectral analysis of one core (Crest) and "knots» (Rapitan) NASA share with the public:

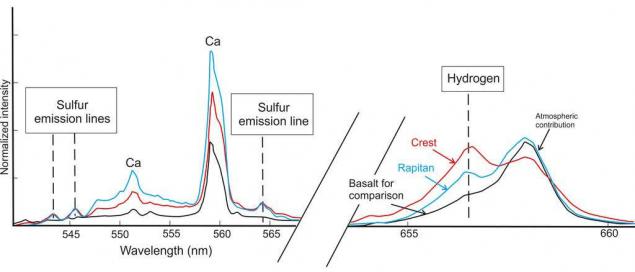
Because gypsum - is a mineral that binds water, there must be an increase of the hydrogen concentration in the soil. That is an interesting side must change the results of the readings DAN. They have not yet released, but is determined by the hydrogen and using ChemCam:
At the bottom of the balls were found. Generally balls on Mars - not the deficit. Opporutnity found two totally different types of structure, material and the origin of the balls. Now Curiosity began to complete his collection:

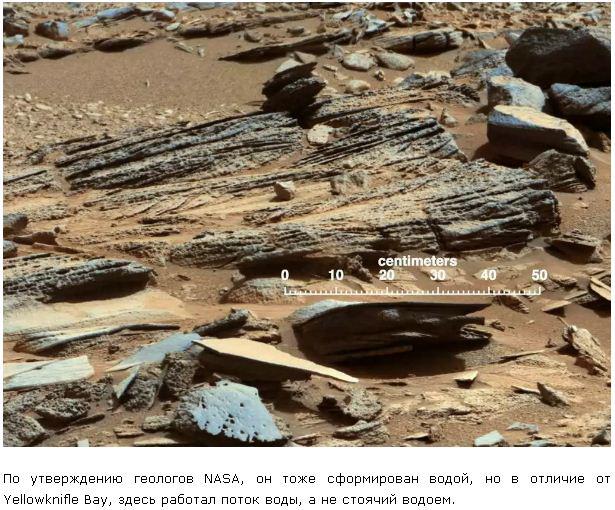
Stone "threshold" is also formed with the participation of water, but in completely different conditions. This cemented sandstone, mixed with larger grains of different minerals. One such 2mm granules, most likely quartz, journalists dubbed "Mars Flower".

Curiosity was selected several times to the "threshold", but for serious study took just now:

Generally, he chose a surprisingly rich place to explore. "Threshold" was not simple. As seen in the photos the overall plan, it cuts through the longitudinal crack:
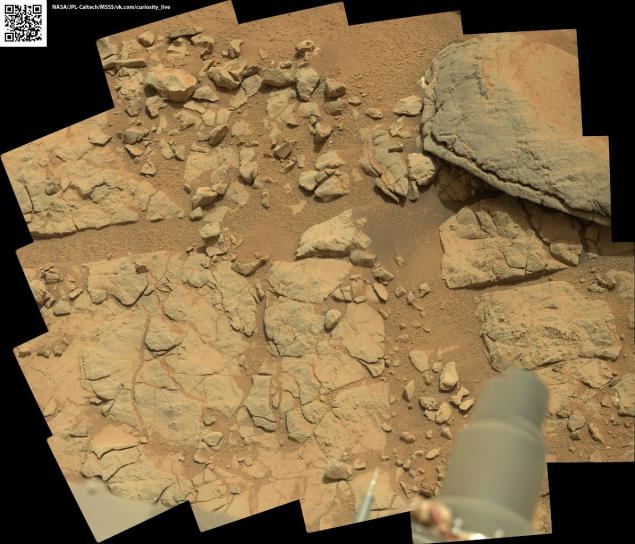

Just yesterday, the rover looked into it and found that it is not simple, but with "stuffing»:


However, the most interesting was found earlier:
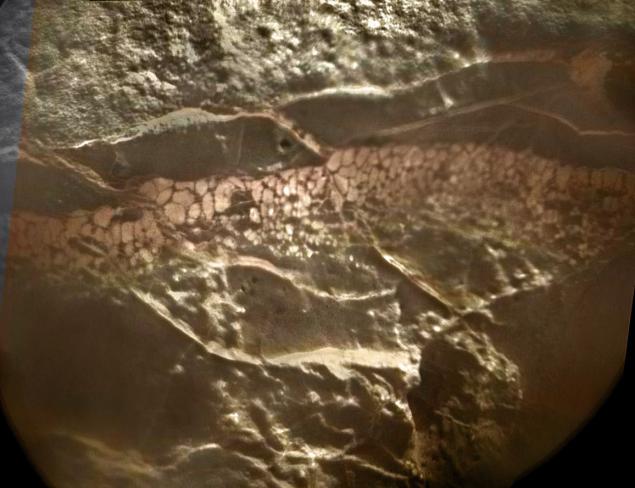
This is the most natural fossilized mud on Mars. Zoom (wide side of the picture about 7-10 cm) suggests that nothing but fine mineral particles with water could not form such sag. NASA describes this breed as «siltstone» - «petrified mud," though the term is used in geology "alevrity⇗."

The day before yesterday, when NASA has not yet been told about the results of research, the news «Curiosity found fossilized mud on Mars" was worthy of tabloid front pages, but even that faded when she came the next batch of pictures:
This mosaic of photographs ChemCam, which brings out the texture, reminiscent penoplast⇗. The photograph of mast cells, this layer is not as expressive:

Now, finally, about where the Suriosity will drill.
The place name "John Klein," is at the "bottom". I thought they choose sandstone security reasons, but they preferred the place more promising from a scientific perspective.
More land can be viewed on panorama in GigaPan⇗.

Now a small output.
Yes, there was water on Mars, it was a lot, and it is not short-term sporadic floods generated by meteorites and volcanoes. Flows formed gravel, accumulating "mud" and precipitated solutes at the bottom. But these facts are no novelty. Opportunity found the same thing, except, perhaps, only pebbles. A gypsum and other minerals, water formed, has in its piggy. The fact that all traces of water that flowed on Mars in the period of the Hesperides. When the planet raged powerful volcanic eruptions, and their emissions are filled with air and water compounds of sulfur and chlorine. But it is not yet clear what role was played by the most fatal for possible Martian life. Either sulfuric acid, perchlorates, or themselves eruption. It is known fact that two recent Great extinction on Earth 250 million. And 65 million. Years ago, linked to two powerful eruptions in Sibiri⇗ and Indii⇗. So if there was life before, it did not survive its doomsday. Therefore, the "dirt" and plaster do not promise a sign of life. The most delicious - ahead.
("Pink" picture calibrated NASA. They write "handled as it would look in the world»)
© Habra
Source:
Finally, share the results of research NASA Curiosity December and half of January. And the purpose of the drilling is also defined. The basic summary of news: almost all the minerals, which are now surrounded by the rover, formed with the participation of water. That is, in fact, it is at the bottom of the former ancient Martian pond.

Just two meters Curiosity drove to the moment experienced in his brush. Since then, this week, he sent so many things that amaze, surprise or confound that fit sentence, "You shall not boil a pot." But he goes on right now, and it's Mars, so "keep the pot».
Everything in order.
About a month ago Curiosity has entered a new type of surface of Mars, which is characterized by high thermal inertia. This means that it is slowly heated up and cools more slowly, indicating a high density of the rock. (Read more about the geology of the crater Gale)

Then the landscape changed, and went under the wheels of the rover's massive stone slab, covered with wide cracks:
Even then, for its resemblance to a place called the pond Yellowknifle Bay (Bay of Yellowknife, in the town in Canada).

An analysis of climate station onboard REMS showed that soil temperature readings really changed:

Specially marked the result of 120 hydrochloric when the rover approached the surface of the third type of Glenelg, which will be studied later. The site, called Shaler, attracts attention with its unusual layered structure:

The lower flat part - the "bottom" of the Gulf - girded low threshold that their material is different from the bottom:

Curiosity began to study the "floor" and "Threshold»:

Immediately it was observed characteristic white veins that permeated virtually all the cracks in the valley. White arrows indicate the conductors, black - small mineral concretions. Geologists known veins similar to Earth, but Mars has been carefully analyzed:

Besides gypsum plaster still lived there "nodules»:

Results of spectral analysis of one core (Crest) and "knots» (Rapitan) NASA share with the public:

Because gypsum - is a mineral that binds water, there must be an increase of the hydrogen concentration in the soil. That is an interesting side must change the results of the readings DAN. They have not yet released, but is determined by the hydrogen and using ChemCam:

At the bottom of the balls were found. Generally balls on Mars - not the deficit. Opporutnity found two totally different types of structure, material and the origin of the balls. Now Curiosity began to complete his collection:

Stone "threshold" is also formed with the participation of water, but in completely different conditions. This cemented sandstone, mixed with larger grains of different minerals. One such 2mm granules, most likely quartz, journalists dubbed "Mars Flower".

Curiosity was selected several times to the "threshold", but for serious study took just now:

Generally, he chose a surprisingly rich place to explore. "Threshold" was not simple. As seen in the photos the overall plan, it cuts through the longitudinal crack:

Just yesterday, the rover looked into it and found that it is not simple, but with "stuffing»:


However, the most interesting was found earlier:
This is the most natural fossilized mud on Mars. Zoom (wide side of the picture about 7-10 cm) suggests that nothing but fine mineral particles with water could not form such sag. NASA describes this breed as «siltstone» - «petrified mud," though the term is used in geology "alevrity⇗."

The day before yesterday, when NASA has not yet been told about the results of research, the news «Curiosity found fossilized mud on Mars" was worthy of tabloid front pages, but even that faded when she came the next batch of pictures:

This mosaic of photographs ChemCam, which brings out the texture, reminiscent penoplast⇗. The photograph of mast cells, this layer is not as expressive:

Now, finally, about where the Suriosity will drill.
The place name "John Klein," is at the "bottom". I thought they choose sandstone security reasons, but they preferred the place more promising from a scientific perspective.
More land can be viewed on panorama in GigaPan⇗.

Now a small output.
Yes, there was water on Mars, it was a lot, and it is not short-term sporadic floods generated by meteorites and volcanoes. Flows formed gravel, accumulating "mud" and precipitated solutes at the bottom. But these facts are no novelty. Opportunity found the same thing, except, perhaps, only pebbles. A gypsum and other minerals, water formed, has in its piggy. The fact that all traces of water that flowed on Mars in the period of the Hesperides. When the planet raged powerful volcanic eruptions, and their emissions are filled with air and water compounds of sulfur and chlorine. But it is not yet clear what role was played by the most fatal for possible Martian life. Either sulfuric acid, perchlorates, or themselves eruption. It is known fact that two recent Great extinction on Earth 250 million. And 65 million. Years ago, linked to two powerful eruptions in Sibiri⇗ and Indii⇗. So if there was life before, it did not survive its doomsday. Therefore, the "dirt" and plaster do not promise a sign of life. The most delicious - ahead.
("Pink" picture calibrated NASA. They write "handled as it would look in the world»)
© Habra

Source: