686
Technics - youth! Part two.
So ladies and gentlemen, thank you for the positive feedback from the first literacy!
The epigraph. "... The American experts verdict: Mi-24 helicopter is not. Although outwardly similar to the Mi-24 helicopter and is used as a helicopter, from a technical point of view - it is a hybrid. He can not take off from the "Piglet" and hover in the air. His visual disproportionately large pylons are actually wings. »...
psycho83
We continue our story. Start here.
"Wings, legs and tails»
If we dealt with tails in the previous section, but now we were "the wings and legs».
Today we look at these seemingly unrelated questions: why helicopters are different types of chassis, which is better, well, the most important question of why the helicopter wings? Hopefully at the end of our educational program you will understand why all these issues are interlinked. Will consider the example of the classic helicopter, no "hybrids»)).
10 photos + video.

Let's start the tradition of the corner).
To begin to find out what kinds of ups allowed on the helicopter (for example, the Mi-8, because it is easiest to find the illustration).
Flight Manual Mi-8 allows the following:
- A vertical take-off, ie, vertical climb without forward speed;
- Take off in the helicopter without the influence of 'air cushion' that vertical climb of not less than 10 m height of the obstacles and accelerate to desired forward speed is the zone of influence 'air cushion';
- Take off in the helicopter using the influence of the "air cushion", in which a runaway acceleration or part of the (early) acceleration is carried out in the area of influence of the "air cushion" at a height of not less than 1, 0-1, 5 m from the ground to the wheels of the chassis;
- Take off from short run, that is, run (acceleration) of the helicopter on the runway -posadochnoy band up to speed not exceeding 40 km / h, the separation of the helicopter off the ground and a further acceleration while climbing.
I think everything here is clear and understandable painted, but the question arises: why do so many species?
The fact that it depends on not only the external factors.
The first two take-off is used when the take-off weight and other conditions allow you to do, or if there are obstacles to the site and perform takeoff other way is impossible.
Posted in [mergetime] 1395337784 [/ mergetime]
The third kind of take-off weight is used when still quite noticeable, and requires additional force, and that creates a "theft».
Ie the power required to hover the helicopter close to the ground, is slightly less than the capacity, the need to hover at an altitude, due to the influence of the earth, or, as some say, due to the "air cushion". Effect "air cushion" the greater the closer to the rotor surface. In practice, it can be assumed that the helicopter hovering near the ground, where the distance from the rotor to the ground is equal to its diameter, the influence of "air cushion" so small as to be negligible. At the same distance from the rotor to the ground equal to its radius, increased lift at constant engine power will be about 10-15%.
Posted in [mergetime] 1395337835 [/ mergetime]
Well, kind of off the fourth with a short run, or take off on an aircraft. Running at maximum loading of the helicopter. How did you know this a variety of take-offs is only possible if the helicopter wheeled chassis.
And why others are helicopter skids? Quite simply, the power supply allows it to produce helicopters take off from the weight limit. Usually a chassis used in light helicopters. Also the chassis is less expensive and needs less maintenance, which is also important.

There are even more rare variants chassis - floats

or directly the helicopter fuselage (in this case, if at all possible to use the term - the chassis), in this case example - gidrovertolet Mi-14.

Moving to another sensitive issue - the wings of the helicopter.

Oddly wing helicopter only need two cases. This creation of lift in flight and use as a wing pylon i.e. the place where you can post attachments. And all !!!
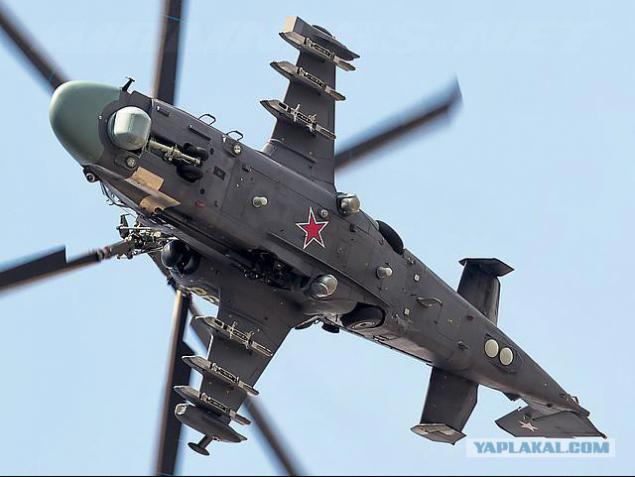

The presence of the wing does not deprive the helicopter and its properties does not make a helicopter flight. In some cases (at the time of takeoff Helicopter) Wing prevents take-off, because creates additional resistance to flow from the rotor. When working on the ground and at low speeds the helicopter wing is in the stream of HB and sleek inductive flow from the rotor top, t. E. Under negative angles of attack. Thus arising on the wing (and also on the fuselage) resistance force is negative lift. For single-rotor helicopter hovering the force of 2-2, 5% of the gravity of the helicopter.
The maximum value of the lift coefficient of the wing have single-rotor helicopters up to 1, 1-1, 15, and the critical angle of attack - 20-22 °. Wing significantly improves the aerodynamic qualities of the helicopter.
Wing helicopters normally set at an angle of 13-15 ° and more with the longitudinal axis of the helicopter. This ensures that the work of the wing on the cruising speed at the most appropriate angle of attack close to the most advantageous.
As the flight speed V is gradually emerging from the wing jet NV, for some values of the flight speed and angle of attack of the wing lift force becomes positive. Next, the lift increases in proportion to the velocity head (if not taken into account to reduce the angle of attack of the wing due to the increasing inclination of the helicopter forward). At high speed flight the wing substantially unloads rotor, giving up to 25% of its traction at a speed of 300km / h.
Here's it is boring, gray, homespun truth).

But to use it as a pylon - look at the picture, imagine where it's positioned on the helicopter ...

And furious supporters cruise samoletovertoletov. Did you know that the wings flap no helicopters and other mechanization? And if a large aerodynamic effect creates a wing if it hang the entire arsenal? Think gentlemen, think ...

Source:
The epigraph. "... The American experts verdict: Mi-24 helicopter is not. Although outwardly similar to the Mi-24 helicopter and is used as a helicopter, from a technical point of view - it is a hybrid. He can not take off from the "Piglet" and hover in the air. His visual disproportionately large pylons are actually wings. »...
psycho83
We continue our story. Start here.
"Wings, legs and tails»
If we dealt with tails in the previous section, but now we were "the wings and legs».
Today we look at these seemingly unrelated questions: why helicopters are different types of chassis, which is better, well, the most important question of why the helicopter wings? Hopefully at the end of our educational program you will understand why all these issues are interlinked. Will consider the example of the classic helicopter, no "hybrids»)).
10 photos + video.

Let's start the tradition of the corner).
To begin to find out what kinds of ups allowed on the helicopter (for example, the Mi-8, because it is easiest to find the illustration).
Flight Manual Mi-8 allows the following:
- A vertical take-off, ie, vertical climb without forward speed;
- Take off in the helicopter without the influence of 'air cushion' that vertical climb of not less than 10 m height of the obstacles and accelerate to desired forward speed is the zone of influence 'air cushion';
- Take off in the helicopter using the influence of the "air cushion", in which a runaway acceleration or part of the (early) acceleration is carried out in the area of influence of the "air cushion" at a height of not less than 1, 0-1, 5 m from the ground to the wheels of the chassis;
- Take off from short run, that is, run (acceleration) of the helicopter on the runway -posadochnoy band up to speed not exceeding 40 km / h, the separation of the helicopter off the ground and a further acceleration while climbing.
I think everything here is clear and understandable painted, but the question arises: why do so many species?
The fact that it depends on not only the external factors.
The first two take-off is used when the take-off weight and other conditions allow you to do, or if there are obstacles to the site and perform takeoff other way is impossible.
Posted in [mergetime] 1395337784 [/ mergetime]
The third kind of take-off weight is used when still quite noticeable, and requires additional force, and that creates a "theft».
Ie the power required to hover the helicopter close to the ground, is slightly less than the capacity, the need to hover at an altitude, due to the influence of the earth, or, as some say, due to the "air cushion". Effect "air cushion" the greater the closer to the rotor surface. In practice, it can be assumed that the helicopter hovering near the ground, where the distance from the rotor to the ground is equal to its diameter, the influence of "air cushion" so small as to be negligible. At the same distance from the rotor to the ground equal to its radius, increased lift at constant engine power will be about 10-15%.
Posted in [mergetime] 1395337835 [/ mergetime]
Well, kind of off the fourth with a short run, or take off on an aircraft. Running at maximum loading of the helicopter. How did you know this a variety of take-offs is only possible if the helicopter wheeled chassis.
And why others are helicopter skids? Quite simply, the power supply allows it to produce helicopters take off from the weight limit. Usually a chassis used in light helicopters. Also the chassis is less expensive and needs less maintenance, which is also important.

There are even more rare variants chassis - floats

or directly the helicopter fuselage (in this case, if at all possible to use the term - the chassis), in this case example - gidrovertolet Mi-14.

Moving to another sensitive issue - the wings of the helicopter.

Oddly wing helicopter only need two cases. This creation of lift in flight and use as a wing pylon i.e. the place where you can post attachments. And all !!!

The presence of the wing does not deprive the helicopter and its properties does not make a helicopter flight. In some cases (at the time of takeoff Helicopter) Wing prevents take-off, because creates additional resistance to flow from the rotor. When working on the ground and at low speeds the helicopter wing is in the stream of HB and sleek inductive flow from the rotor top, t. E. Under negative angles of attack. Thus arising on the wing (and also on the fuselage) resistance force is negative lift. For single-rotor helicopter hovering the force of 2-2, 5% of the gravity of the helicopter.
The maximum value of the lift coefficient of the wing have single-rotor helicopters up to 1, 1-1, 15, and the critical angle of attack - 20-22 °. Wing significantly improves the aerodynamic qualities of the helicopter.
Wing helicopters normally set at an angle of 13-15 ° and more with the longitudinal axis of the helicopter. This ensures that the work of the wing on the cruising speed at the most appropriate angle of attack close to the most advantageous.
As the flight speed V is gradually emerging from the wing jet NV, for some values of the flight speed and angle of attack of the wing lift force becomes positive. Next, the lift increases in proportion to the velocity head (if not taken into account to reduce the angle of attack of the wing due to the increasing inclination of the helicopter forward). At high speed flight the wing substantially unloads rotor, giving up to 25% of its traction at a speed of 300km / h.
Here's it is boring, gray, homespun truth).

But to use it as a pylon - look at the picture, imagine where it's positioned on the helicopter ...

And furious supporters cruise samoletovertoletov. Did you know that the wings flap no helicopters and other mechanization? And if a large aerodynamic effect creates a wing if it hang the entire arsenal? Think gentlemen, think ...

Source: