Francis McGlone: Slowly and gently — what we all need
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net
Our skin: the largest organ of the human body, protecting us from the outside world. The skin surface is densely populated by nerve endings of different types that signal the brain about the temperature, pressure, pain, itch and touch.
We know a lot about the skin, but as it turns out, it still remains Terra Incognita. Recently, scientists have discovered another type of nerve fibers that register only slow and gentle touch and poglazhivanieI send them to the brain, and we have a pleasant feeling. They in turn serve as reward and encouragement of physical contact between people, providing the basis for forming and maintaining social ties and attachment.
It turns out that such strokes are processed primarily in the emotional regions of the brain and not touch. Physical touch can convey more emotional information than speech.
Francis McGlone, Professor of cognitive neuropsychology at the University of Liverpool John Moors, has long studied the pain receptors in the skin. He also worked in the research division of Unilever, where his work helped me to understand what happens to us when we use cosmetic products.In the last few years he and colleagues study these types of nerve fibers that respond to touch.

It is believed that the sense of smell is the most ancient and basic in our brain, but your research says otherwise.
I think that the sense of touch can be a major feeling. During the evolution of this sense is well preserved, and for good reason. A good example is the study of worms-nematodes, which showed that if the worm develops in isolation, without touch other hearts, it never reaches its normal size, and its development is inhibited.
Another example: before 1921, the scientists distinguish two kinds of locusts: the one that lives alone and one that strays into pack. It turned out that this same insect. Tactile stimulation, which the insect gets in the pack, drastically changes his lifestyle. Scientists have even made solitary locusts into gregarious, stroking her legs for two hours. It increases the level of serotonin in the brain of the insect and change its behavior.
The human embryo first develops the sense of touch, we must ask ourselves – why?
Why some people don't like it when touch them?
We are all "victims" of our genes and environment, and the debate about their role in human development today are based on a solid scientific basis, particularly in the field of epigenetics. Research Michael's Mini showed that the licking and combing in rats to determine the development of young pups. Those that get this in abundance, socially stable, resistant to stress and less aggressive. Rats, which are not stirred is the opposite. We assume that this maternal affection – a touch, scratching, and licking play a critical role in social development and protection from stress in adult life.
An important question is whether our newborns and infants today, the same affection and touch as before? The pressure of society and the desire to possess material things leads, among other things, to the fact that many couples place their children increasingly early age in gardens and nurseries where children can't get a tactile feel for his developing brain sufficiently.
Inset: the Policy of Ceausescu in Romania in the second half of the 20th century, aimed at creating "human capital" forced people to give birth to as many children as possible. This led to the fact that parents, unable to feed children, gave them into state orphanages. By 1989, they contained about 170,000 children 12-15 children had one caregiver, and even in the best conditions, the children did not get enough attention and care. This cruel natural experiment showed, among other things, that the lack of affection during the critical period of development leads to huge negative changes in a person's life.
This may explain why one likes the touch, but not to others. Our research group considers autism as a result of underdevelopment of the system of tactile sensations, and this is confirmed by the observations that some autistic children can not tolerate the most gentle of touches, while others, on the contrary, show an abnormal interest in touching. It was not developed among them, either in the womb or after birth. We all are in different places of the autism spectrum — depending on how much our mothers loved or didn't love to touch and to touch us in childhood. It is likely that massage therapy can help the person to love the touch of others.
You said about development in the womb?
From about the fifth month the fetus is covered with a special human hair, lanugo, which usually disappear before birth, but sometimes after a few months. Our interest arose from clinical observations. It turned out that sometimes, these hair have an adult in the same places that have the fruit: for the back and shoulders – women with anorexia, aversion to food. We hypothesized that one function of these hairs in the womb to feel the massaging motion of the amniotic fluid, and to develop the nervous system through nerve endings in the skin.
There is a hypothesis that tactile sensations allow the brain of the foetus to understand that he has a body. We think this is an important and critical stage in the socialization of the developing brain. After all, the key symptom of anorexia is the lack of understanding of their own body. Such patients often react negatively to a gentle touch – just those that are served by the tactile nerves. We assume that when the system of these nerves does not develop normally, we get anorexia in women and autism in men.

Temple Grandin
Based on this, what could be the idea of a possible therapy of autism?
Temple Grandin, the famous autistic, in conversation with me confirmed that she hated it when her mother touched. When she was in College, she studied animal behavior, she noticed that when the cows come into the yard massacre, they calmed down, they find themselves in the narrow space special gate.
These gates are called "cow press", make narrow, to put pressure on the flanks of the cow. Temple made his own press to calm down. I guess a lot of pressure on Boca soothes very sensitive nerve endings on her skin. Therapists thought it was interesting, and they began to try to hug autistic children. The kids hated it, and the physicians did not pay attention to what temple Grandin squeezed his body itself and not someone else.
Now we applied for a grant to study how emotional touch can help at-risk children (siblings of children diagnosed with autism) and will use the method of functional spectroscopy in the near infrared region. Early diagnosis of abnormal development of the tactile sensation can help create a therapy for these children, because the main problem is late diagnosis, usually at the age of two years. We miss the critical period, the brain is not receiving something at the right time, is still developing, but something did not return.
Returning to the Tempo Grandin. Can we get as much benefit from touching themselves, as from the touch of other people?
This is a very interesting question, and honestly, I don't know the answer. Concern as to whether autistic people are more likely than children without autism? If they calm down, stroking themselves? We know that the nerve endings responsible for gentle touch, not found on the skin, devoid of hair on the palms and soles of the feet. Therefore, when we touch her arms, fingers and palm, we touch skin, where there are no such nerves skin where they are. I have an idea of an experiment – I noticed that when I touch myself, I feel sensations in touch, but not on the hand!
Oxytocin. About him many now say that it is almost a love drug, even use sprays to raise the level of this hormone. Your research shows that stroking work better?
Oxytocin is known for its role in maternal behavior, but it also serves the courtship. Gentle touch reduces blood pressure and calms the heart rate, decrease the production of the stress hormone cortisol and increase the level of oxytocin, the "love hormone". Artificially increasing it by means of a spray is unlikely to give the full effect created by a gentle stroking, which, in addition, and spur the production of endorphins that cause a pleasant feeling of relaxation.
You used for research robots. Tell us about it.
We studied these nerve fibres with the help of microneurography.
Insert: Microneurography – neurophysiological method for the visualization and recording of events happening in the nerve fibers. The person is administered the finest needle into the nerve, for example, in the hand, it doesn't hurt that "listens" what is happening in the nerve.
Needed to remove the "human factor" of the strokes, and be able to clearly control their characteristics – speed and pressure, so we created a robotic arm.
Today we are so in love in all sorts of gadgets. You see the future of massage parlors, where robots look people?
I think that the popularity of massage is one of the examples that people felt that touch is so important and enjoyable. Although not all types of massage uses gentle touch, energetic and even painful it types probably stimulate other types of nerves in the muscles. In any case, the massage increases the production of opioids in the brain and creates a pleasant feeling. Already there are devices which massage your back and very relaxing. The company Philips, for example, designed the costumes, which is a built-in vibrators.
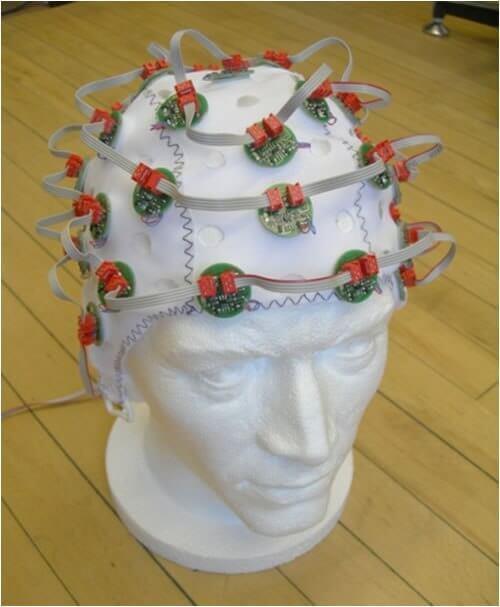

I developed vibrotactile massage helmet (pictured), who pats his head, and this is one of the most pleasant places for a massage.
How to make people more and more often touch each other?
I think "game" is a key factor in the history of social touching, especially infants and children it is necessary to give enough nurturing touch, and secondly, encourage them to create tactile contact through games and to build appropriate social relationships. Interesting about the finding, reported by a group of psychologists from Emory University at the annual conference of the Society for Neuroscience in Washington in November 2014.
They found in mice another group of nerve fibers that are responsible for tactile sensations, which finally formed only in the period of youth! These nerve fibres are obtained, processed touch in a few rough relationships between teenagers, it can be concluded that there must be another group of nerves responsible for other stages of development. The story quickly unfolds as we predicted, in terms of what this type of nerves there are a number of subclasses. The same picture with the nerves responsible for pain perception – we know 4-5 subclasses, and for the perception of the itch – at least two.
You mentioned a study in which scientists stroked the legs of locusts for two hours. Something similar happens with the person?
This study is interesting because evolution has kept the mechanism in which a gentle touch associated with the work of serotonin, which makes alone along social animal. To me it became curious in connection with club drug ecstasy (MDMA), because it increases the production of serotonin. The person who took ecstasy, improves tactile perception and changes behavior – it tends to hang out among people, it leads to their touches, it pulls to a real rave!
After your articles, the Newspapers came out with headlines like "scientists have discovered how to actually iron their women!" How accurately it is necessary to observe the rate of stroking, or just gentle strokes enough?
And, magic speed stroking! We all intuitively feel it – every mother knows it, and every lover, or should know, because it's an innate skill. We found that the optimal speed is between 1 and 10 centimeters per second, so usually we inform about 3-5 inches per second as the ideal. But we are all different and we should practice until we find the best approach for the person. By the way, these nerves react to static and gentle touch, although not so actively.
In accordance with the theory of mirror neurons, whether we are happy when we see one man stroking another?
Yes. My colleague, Dr. Susan Walker, presented a report on our study on the conference of the Society for Neuroscience, which has been particularly highlighted during the event. This experiment showed that when people watched short clips where people stroked different parts of other people, and then evaluated how much they think it's nice, the feeling was quite adequate. Most people liked it when you stroked his back.
Are there differences in how people of different cultures relate to each other?
Research Tiffany field showed, for example, that the French, communicating with each other, often touching each other, but Americans often touch themselves. It seems that French mothers create for their children a more socially-positive environment.
It seems that we live in a world of scarcity touches, and it is observed in many countries. If our understanding of the role of emotional and caressing touch is true, it is also fundamentally important for brain health as the Higgs boson is to particle physics. Touch is the glue that connects us all together.
We will see many more discoveries in this area in the near future. In the meantime, we should understand how we underestimate the role of social touch, as for brain development and for the development of social relations. All of us need more touching and stroking. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: mindware.ru/blog/?p=7025#.WF68QAYoB24.facebook
We know a lot about the skin, but as it turns out, it still remains Terra Incognita. Recently, scientists have discovered another type of nerve fibers that register only slow and gentle touch and poglazhivanieI send them to the brain, and we have a pleasant feeling. They in turn serve as reward and encouragement of physical contact between people, providing the basis for forming and maintaining social ties and attachment.
It turns out that such strokes are processed primarily in the emotional regions of the brain and not touch. Physical touch can convey more emotional information than speech.
Francis McGlone, Professor of cognitive neuropsychology at the University of Liverpool John Moors, has long studied the pain receptors in the skin. He also worked in the research division of Unilever, where his work helped me to understand what happens to us when we use cosmetic products.In the last few years he and colleagues study these types of nerve fibers that respond to touch.

It is believed that the sense of smell is the most ancient and basic in our brain, but your research says otherwise.
I think that the sense of touch can be a major feeling. During the evolution of this sense is well preserved, and for good reason. A good example is the study of worms-nematodes, which showed that if the worm develops in isolation, without touch other hearts, it never reaches its normal size, and its development is inhibited.
Another example: before 1921, the scientists distinguish two kinds of locusts: the one that lives alone and one that strays into pack. It turned out that this same insect. Tactile stimulation, which the insect gets in the pack, drastically changes his lifestyle. Scientists have even made solitary locusts into gregarious, stroking her legs for two hours. It increases the level of serotonin in the brain of the insect and change its behavior.
The human embryo first develops the sense of touch, we must ask ourselves – why?
Why some people don't like it when touch them?
We are all "victims" of our genes and environment, and the debate about their role in human development today are based on a solid scientific basis, particularly in the field of epigenetics. Research Michael's Mini showed that the licking and combing in rats to determine the development of young pups. Those that get this in abundance, socially stable, resistant to stress and less aggressive. Rats, which are not stirred is the opposite. We assume that this maternal affection – a touch, scratching, and licking play a critical role in social development and protection from stress in adult life.
An important question is whether our newborns and infants today, the same affection and touch as before? The pressure of society and the desire to possess material things leads, among other things, to the fact that many couples place their children increasingly early age in gardens and nurseries where children can't get a tactile feel for his developing brain sufficiently.
Inset: the Policy of Ceausescu in Romania in the second half of the 20th century, aimed at creating "human capital" forced people to give birth to as many children as possible. This led to the fact that parents, unable to feed children, gave them into state orphanages. By 1989, they contained about 170,000 children 12-15 children had one caregiver, and even in the best conditions, the children did not get enough attention and care. This cruel natural experiment showed, among other things, that the lack of affection during the critical period of development leads to huge negative changes in a person's life.
This may explain why one likes the touch, but not to others. Our research group considers autism as a result of underdevelopment of the system of tactile sensations, and this is confirmed by the observations that some autistic children can not tolerate the most gentle of touches, while others, on the contrary, show an abnormal interest in touching. It was not developed among them, either in the womb or after birth. We all are in different places of the autism spectrum — depending on how much our mothers loved or didn't love to touch and to touch us in childhood. It is likely that massage therapy can help the person to love the touch of others.
You said about development in the womb?
From about the fifth month the fetus is covered with a special human hair, lanugo, which usually disappear before birth, but sometimes after a few months. Our interest arose from clinical observations. It turned out that sometimes, these hair have an adult in the same places that have the fruit: for the back and shoulders – women with anorexia, aversion to food. We hypothesized that one function of these hairs in the womb to feel the massaging motion of the amniotic fluid, and to develop the nervous system through nerve endings in the skin.
There is a hypothesis that tactile sensations allow the brain of the foetus to understand that he has a body. We think this is an important and critical stage in the socialization of the developing brain. After all, the key symptom of anorexia is the lack of understanding of their own body. Such patients often react negatively to a gentle touch – just those that are served by the tactile nerves. We assume that when the system of these nerves does not develop normally, we get anorexia in women and autism in men.

Temple Grandin
Based on this, what could be the idea of a possible therapy of autism?
Temple Grandin, the famous autistic, in conversation with me confirmed that she hated it when her mother touched. When she was in College, she studied animal behavior, she noticed that when the cows come into the yard massacre, they calmed down, they find themselves in the narrow space special gate.
These gates are called "cow press", make narrow, to put pressure on the flanks of the cow. Temple made his own press to calm down. I guess a lot of pressure on Boca soothes very sensitive nerve endings on her skin. Therapists thought it was interesting, and they began to try to hug autistic children. The kids hated it, and the physicians did not pay attention to what temple Grandin squeezed his body itself and not someone else.
Now we applied for a grant to study how emotional touch can help at-risk children (siblings of children diagnosed with autism) and will use the method of functional spectroscopy in the near infrared region. Early diagnosis of abnormal development of the tactile sensation can help create a therapy for these children, because the main problem is late diagnosis, usually at the age of two years. We miss the critical period, the brain is not receiving something at the right time, is still developing, but something did not return.
Returning to the Tempo Grandin. Can we get as much benefit from touching themselves, as from the touch of other people?
This is a very interesting question, and honestly, I don't know the answer. Concern as to whether autistic people are more likely than children without autism? If they calm down, stroking themselves? We know that the nerve endings responsible for gentle touch, not found on the skin, devoid of hair on the palms and soles of the feet. Therefore, when we touch her arms, fingers and palm, we touch skin, where there are no such nerves skin where they are. I have an idea of an experiment – I noticed that when I touch myself, I feel sensations in touch, but not on the hand!
Oxytocin. About him many now say that it is almost a love drug, even use sprays to raise the level of this hormone. Your research shows that stroking work better?
Oxytocin is known for its role in maternal behavior, but it also serves the courtship. Gentle touch reduces blood pressure and calms the heart rate, decrease the production of the stress hormone cortisol and increase the level of oxytocin, the "love hormone". Artificially increasing it by means of a spray is unlikely to give the full effect created by a gentle stroking, which, in addition, and spur the production of endorphins that cause a pleasant feeling of relaxation.
You used for research robots. Tell us about it.
We studied these nerve fibres with the help of microneurography.
Insert: Microneurography – neurophysiological method for the visualization and recording of events happening in the nerve fibers. The person is administered the finest needle into the nerve, for example, in the hand, it doesn't hurt that "listens" what is happening in the nerve.
Needed to remove the "human factor" of the strokes, and be able to clearly control their characteristics – speed and pressure, so we created a robotic arm.
Today we are so in love in all sorts of gadgets. You see the future of massage parlors, where robots look people?
I think that the popularity of massage is one of the examples that people felt that touch is so important and enjoyable. Although not all types of massage uses gentle touch, energetic and even painful it types probably stimulate other types of nerves in the muscles. In any case, the massage increases the production of opioids in the brain and creates a pleasant feeling. Already there are devices which massage your back and very relaxing. The company Philips, for example, designed the costumes, which is a built-in vibrators.

I developed vibrotactile massage helmet (pictured), who pats his head, and this is one of the most pleasant places for a massage.
How to make people more and more often touch each other?
I think "game" is a key factor in the history of social touching, especially infants and children it is necessary to give enough nurturing touch, and secondly, encourage them to create tactile contact through games and to build appropriate social relationships. Interesting about the finding, reported by a group of psychologists from Emory University at the annual conference of the Society for Neuroscience in Washington in November 2014.
They found in mice another group of nerve fibers that are responsible for tactile sensations, which finally formed only in the period of youth! These nerve fibres are obtained, processed touch in a few rough relationships between teenagers, it can be concluded that there must be another group of nerves responsible for other stages of development. The story quickly unfolds as we predicted, in terms of what this type of nerves there are a number of subclasses. The same picture with the nerves responsible for pain perception – we know 4-5 subclasses, and for the perception of the itch – at least two.
You mentioned a study in which scientists stroked the legs of locusts for two hours. Something similar happens with the person?
This study is interesting because evolution has kept the mechanism in which a gentle touch associated with the work of serotonin, which makes alone along social animal. To me it became curious in connection with club drug ecstasy (MDMA), because it increases the production of serotonin. The person who took ecstasy, improves tactile perception and changes behavior – it tends to hang out among people, it leads to their touches, it pulls to a real rave!
After your articles, the Newspapers came out with headlines like "scientists have discovered how to actually iron their women!" How accurately it is necessary to observe the rate of stroking, or just gentle strokes enough?
And, magic speed stroking! We all intuitively feel it – every mother knows it, and every lover, or should know, because it's an innate skill. We found that the optimal speed is between 1 and 10 centimeters per second, so usually we inform about 3-5 inches per second as the ideal. But we are all different and we should practice until we find the best approach for the person. By the way, these nerves react to static and gentle touch, although not so actively.
In accordance with the theory of mirror neurons, whether we are happy when we see one man stroking another?
Yes. My colleague, Dr. Susan Walker, presented a report on our study on the conference of the Society for Neuroscience, which has been particularly highlighted during the event. This experiment showed that when people watched short clips where people stroked different parts of other people, and then evaluated how much they think it's nice, the feeling was quite adequate. Most people liked it when you stroked his back.
Are there differences in how people of different cultures relate to each other?
Research Tiffany field showed, for example, that the French, communicating with each other, often touching each other, but Americans often touch themselves. It seems that French mothers create for their children a more socially-positive environment.
It seems that we live in a world of scarcity touches, and it is observed in many countries. If our understanding of the role of emotional and caressing touch is true, it is also fundamentally important for brain health as the Higgs boson is to particle physics. Touch is the glue that connects us all together.
We will see many more discoveries in this area in the near future. In the meantime, we should understand how we underestimate the role of social touch, as for brain development and for the development of social relations. All of us need more touching and stroking. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: mindware.ru/blog/?p=7025#.WF68QAYoB24.facebook
Tags
See also
Rules of Life of Freddie Mercury
"Every day I wonder what is the most worthy of the people - alone ..."
Diet affecting autism: what we have and gives a chance to succeed
What should we build a bike?
14 ways to wash the dishes from Nagar
What should we build a spacesuit? Interview with the man who makes the space is not so far away
Life is better than we know what we really need.
That's what we sell under the guise of noble fish
DEAD DOCTORS DO NOT LIE
20 photos that hugs - that is what we all want so