516
Weak domestic RADIATION - even you didn't know about it!
In this article I want to share my research on the topic weak radiation sources, which can be found in the daily life. I won't consider any exotic type products of uranium glass, instrument radioluminescent paint on the dial and ionization smoke detectors. We will focus on the most ordinary utensils, building materials and food, the weak and non-hazardous to health radioactivity which can be detected the simplest household dosimeter.
The theme of radiation I was interested after reading the article about the keychain Geiger. As rightly noted in the comments KbRadar, keychain is an indicator of danger, not a search device for comparing the power of the background radiation in different places.
So, I wanted to get a simple dosimeter-radiometer with the screen. I wrote in Dadzhet and ordered to review dosimeter Defender soeks. It turned out that the device has already been discontinued, and I got the last available copy. Therefore, the remainder of this article will not describe in detail this particular gadget, I will just give the results of the conducted with the help of research.
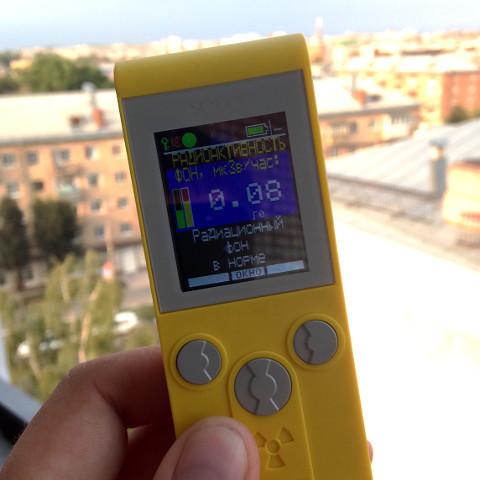

The first thing I wanted to test the accuracy of the readings. The set of household dosimeters why not put a control source (in contrast to the products of industrial and military purposes), so I started looking for a second instrument with which to compare readings. In a nearby alley there was a street clock with the display of the background radiation:

In the same place my dosimeter showed this:

So like a hundred x-rays corresponds to one sievert, the evidence almost converge.
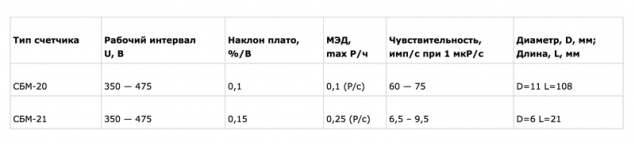
My dosimeter used good old sensor beta radiation, SBM-20 produced by Elektrokhimpribor.

This sensor is a Geiger-Muller not reagiruet to alpha and soft beta (these types of radiation cannot penetrate through a metal enclosure). However, it is ten times more sensitive than SBM-21 used in the above mentioned FOB due to its size.
Potassium-40
From this table (taken from the website of Elektrohimpribor) shows that SBM-20 will detect a minimum of 15 pulses per minute in the natural background of 15 Mr/h and SBM-21 — only 1-2 pulse. A few minutes of measurements with SBM-20 can gain enough statistics to show more or less reliable value of the weak background radiation.
One of the common naturally occurring isotope of potassium, 40K, is radioactive. Since it is chemically indistinguishable from conventional stable potassium, stable along with potassium it is involved in metabolism in living organisms and is part of many minerals. Every second in your body happens several thousand beta decay of 40K:
In addition, the c probability 12% - 40K can capture an electron and turn into 40Ar c with emission of γ quantum.
This reaction is based the potassium-argon method of nuclear geochronology.
Wood ash contains potash (potassium carbonate, K2CO3). In the photo below the meter is in the bucket with the ashes of a barbecue. The difference with the natural background of 0.12 µsv/h was worse, I had almost to bury the dosimeter to ash.
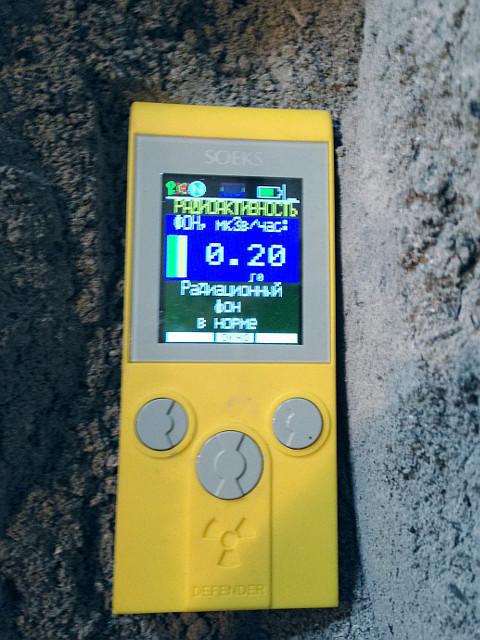

Note: If the goal is obtaining accurate numerical values of the background, the dosimeter should not be kept in the immediate vicinity of the studied subject. In my case the problem was different — to detect the mere presence of a small additional background.
Ash from burning grass contains more potash than wood, it is the differences would be noticeable. Gardeners often use ash instead of potash factory production, which is also kicking due to the presenceof the isotope 40K.
In the manufacture of crystal glass, the charge can add the same potash or potassium oxide. Therefore, you can find slightly radioactive crystal dishes. I've tried a bunch of vases and wine glasses and only inside this beer mug noticed small deviations from the background.
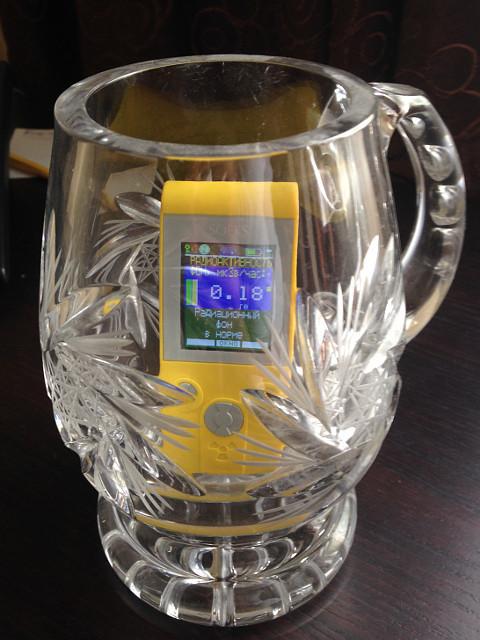

It is worth noting that the measurements of radioactivity of objects only make sense if you also measure the natural background around you and see the difference. It is evident that apart from circles background less.

Much potassium is contained in bananas. The banana is even used as a comic unit of radiation dose (see banana equivalent dose). The difference of the background inside the box with bananas and a meter away from him is very small, but still detectable.

To reliably detect such small differences of background, you have to spend a lot of time on the measurements, because the error of the SBM-20 can reach 30%. Dosimeter updates the display every ten seconds. In the process each dimension populated with green column on the left side of the screen. With each new measurement displays the average value of all previous changes and thus increases the accuracy. To indicate the accuracy of a yellow column, rising with each dimension and completely filling in two minutes — the manual says that sufficient accuracy is achieved at its maximum filling. To respond to the background change, in the logic of the instrument laid reset previous measurements when you change the background three times. In my experience never met such a substantial difference, and I can't think of anything better than just turn off and turn on the dosimeter between measurements.
To secure the presence of the difference in the background, I repeated the experience with bananas a few times. In each approach, I measured the two values of the background inside the box and in meter near. Of course, the numbers were a little pitchy, but in a box of bananas the background was always a bit higher.
Uranium and thorium
These elements are the first to remember when talking about natural sources of radiation. Natural granite may contain traces of uranium and thorium, although their number is highly dependent on the field. In the Park I stumbled across this ornamental granite cobblestone, a background surface which is twice the background a few meters near.
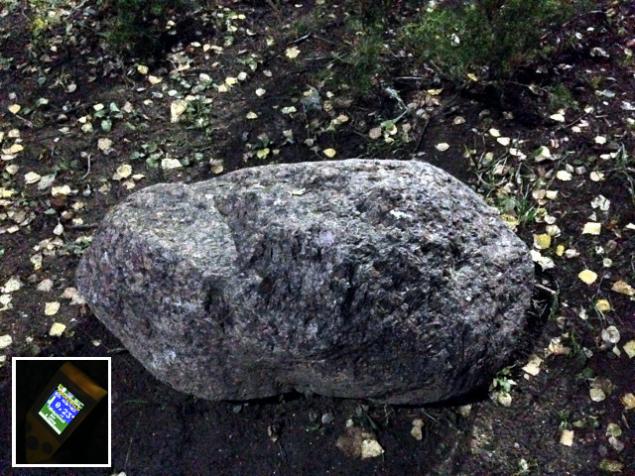

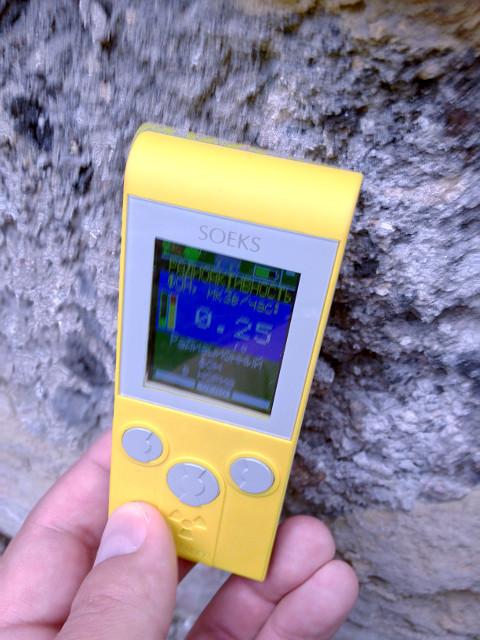
Granite tiles, reaching for the cladding of buildings and monuments can also fonit. I had to jump through many candidates until I found a twofold deviation from background, which at the time amounted to 0.12 µsv/h:

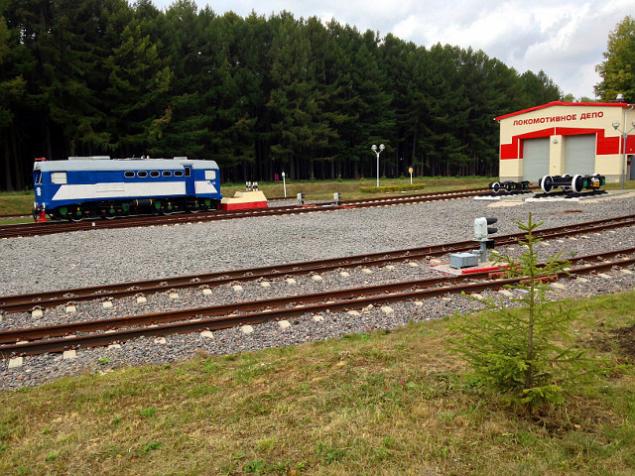
Used in the construction of crushed granite which can add to the concrete or sprinkle the road. Crushed granite is also used in railway embankments. In the photo below — the Novomoskovsk children's railway (a narrow gauge railway used for training of young railwaymen). Here the gravel good, not fonit.

Also in the construction can be used slag — a by-product of the blast furnace steel production. The Soviet vacationers was popular here such labionasal cinder blocks:

Where in the slag uranium? It is contained in coal, which is burned in blast furnace. Therefore, steel mills and thermal power plants not only increase the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, but create radioactive contamination. Living near thermal power plant can be more harmful than near nuclear power plants (until the last works in a regular mode). Some of the uranium remains in the slag from which make this cheap crushed stone and sprinkled them in the track.

Track slightly upset.

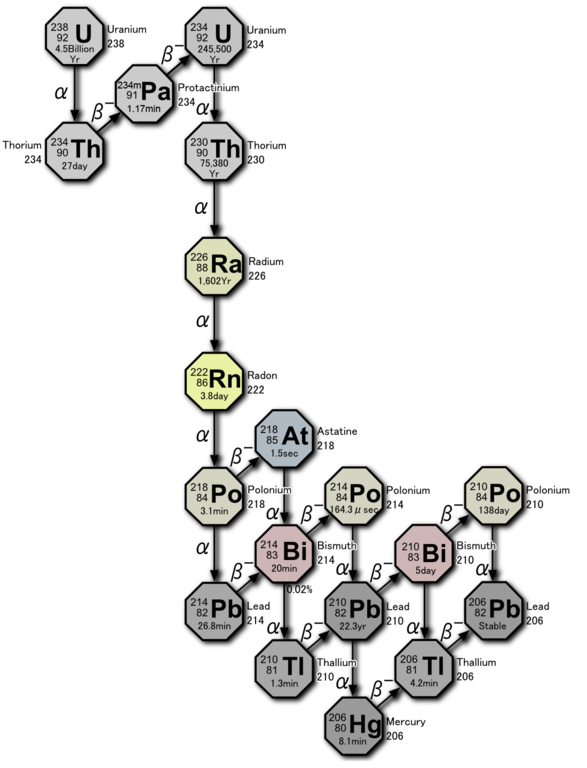
Natural isotopes of uranium and thorium emit only α-particles which can not penetrate through the meter housing. The counter responds to the β-active products of their decay (see Radioactive series).
Radon
Radon is a radioactive inert gas is seven times heavier than air. Has no stable isotopes, the longest-lived of them, 222Rn, has a half life of slightly less than four days. Natural resources of the decaying radon is continuously replenished due to α-decay of radium in the earth's crust.
Due to its inertia, atoms of radon easily leave the crystal lattice of the mineral in which they are incurred. Through cracks and pores, the gas rises to the surface and into the atmosphere and dissipating without causing any harm. Another thing is if radon goes not to the open space and in an enclosed basement of the building. If the basement is not ventilated, radon will accumulate. SBM-20 can directly detect radon because the gas is exposed to α-decay:
Occur in this decay - polonium 218Po also decays with the emission of α-particles: 218Po → 214Pb + 4He. But the core of lead 214Pb overloaded with neutrons and decay by emitting β-radiation which "sees" the SBM-20. There are other decay products (isotopes of polonium, bismuth, lead, etc.) emitting not only in α but also β-particles.
In General, for accurate measurements of radon concentrations in the air need special equipment. Domestic dosimeter can only try to detect the fact of his presence. In search of radon, I went down to the basement of the old house with a dirt floor and measured the background at the height of half a meter (it amounted to 0.12 µsv/h).
At floor level the background was only slightly higher, and I had thought that radon is not here, but noticed that the floor has a large pit about a meter in depth (boarded (once it was used to store potatoes). I suggested that a heavy gas can "drain" back through the cracks between the boards to accumulate as a Board interfere with the ventilation of the pit. At the bottom of the pits was 0.3 µsv/h.

I removed the Board, to air out the basement and repeated the measurement:

The background is noticeably decreased. Left to try to explain the result. It would seem that after ventilation changes should not be, since the dosimeter does not respond to the radon, and a subsidiary of its decay products are heavy metals. Nevertheless, the experiment showed the presence of a difference of background. The chart above shows that a large part of the produced isotopes metals living minutes and seconds, and simply do not have time to settle on the floor. Atoms decay products congenerous on even the smallest dust particles hanging in the air, making them radioactive. Ventilation allows to partially get rid of this dust.
Also a few radon can get into our homes with natural gas and artesian water. Ventilate more often, because despite the fact that α-particles do not penetrate through the skin, radon and its decay products into the lungs when breathing. There they have to be not so harmless.
Additional materials on the topic
In addition to the many references to Wikipedia articles which I put in the text above, I can recommend the following interesting materials.
Source: geektimes.ru/company/dadget/blog/262402/
The theme of radiation I was interested after reading the article about the keychain Geiger. As rightly noted in the comments KbRadar, keychain is an indicator of danger, not a search device for comparing the power of the background radiation in different places.
So, I wanted to get a simple dosimeter-radiometer with the screen. I wrote in Dadzhet and ordered to review dosimeter Defender soeks. It turned out that the device has already been discontinued, and I got the last available copy. Therefore, the remainder of this article will not describe in detail this particular gadget, I will just give the results of the conducted with the help of research.

The first thing I wanted to test the accuracy of the readings. The set of household dosimeters why not put a control source (in contrast to the products of industrial and military purposes), so I started looking for a second instrument with which to compare readings. In a nearby alley there was a street clock with the display of the background radiation:

In the same place my dosimeter showed this:

So like a hundred x-rays corresponds to one sievert, the evidence almost converge.
My dosimeter used good old sensor beta radiation, SBM-20 produced by Elektrokhimpribor.

This sensor is a Geiger-Muller not reagiruet to alpha and soft beta (these types of radiation cannot penetrate through a metal enclosure). However, it is ten times more sensitive than SBM-21 used in the above mentioned FOB due to its size.

Potassium-40
From this table (taken from the website of Elektrohimpribor) shows that SBM-20 will detect a minimum of 15 pulses per minute in the natural background of 15 Mr/h and SBM-21 — only 1-2 pulse. A few minutes of measurements with SBM-20 can gain enough statistics to show more or less reliable value of the weak background radiation.
One of the common naturally occurring isotope of potassium, 40K, is radioactive. Since it is chemically indistinguishable from conventional stable potassium, stable along with potassium it is involved in metabolism in living organisms and is part of many minerals. Every second in your body happens several thousand beta decay of 40K:
In addition, the c probability 12% - 40K can capture an electron and turn into 40Ar c with emission of γ quantum.
This reaction is based the potassium-argon method of nuclear geochronology.
Wood ash contains potash (potassium carbonate, K2CO3). In the photo below the meter is in the bucket with the ashes of a barbecue. The difference with the natural background of 0.12 µsv/h was worse, I had almost to bury the dosimeter to ash.

Note: If the goal is obtaining accurate numerical values of the background, the dosimeter should not be kept in the immediate vicinity of the studied subject. In my case the problem was different — to detect the mere presence of a small additional background.
Ash from burning grass contains more potash than wood, it is the differences would be noticeable. Gardeners often use ash instead of potash factory production, which is also kicking due to the presenceof the isotope 40K.
In the manufacture of crystal glass, the charge can add the same potash or potassium oxide. Therefore, you can find slightly radioactive crystal dishes. I've tried a bunch of vases and wine glasses and only inside this beer mug noticed small deviations from the background.

It is worth noting that the measurements of radioactivity of objects only make sense if you also measure the natural background around you and see the difference. It is evident that apart from circles background less.

Much potassium is contained in bananas. The banana is even used as a comic unit of radiation dose (see banana equivalent dose). The difference of the background inside the box with bananas and a meter away from him is very small, but still detectable.

To reliably detect such small differences of background, you have to spend a lot of time on the measurements, because the error of the SBM-20 can reach 30%. Dosimeter updates the display every ten seconds. In the process each dimension populated with green column on the left side of the screen. With each new measurement displays the average value of all previous changes and thus increases the accuracy. To indicate the accuracy of a yellow column, rising with each dimension and completely filling in two minutes — the manual says that sufficient accuracy is achieved at its maximum filling. To respond to the background change, in the logic of the instrument laid reset previous measurements when you change the background three times. In my experience never met such a substantial difference, and I can't think of anything better than just turn off and turn on the dosimeter between measurements.
To secure the presence of the difference in the background, I repeated the experience with bananas a few times. In each approach, I measured the two values of the background inside the box and in meter near. Of course, the numbers were a little pitchy, but in a box of bananas the background was always a bit higher.
Uranium and thorium
These elements are the first to remember when talking about natural sources of radiation. Natural granite may contain traces of uranium and thorium, although their number is highly dependent on the field. In the Park I stumbled across this ornamental granite cobblestone, a background surface which is twice the background a few meters near.

Granite tiles, reaching for the cladding of buildings and monuments can also fonit. I had to jump through many candidates until I found a twofold deviation from background, which at the time amounted to 0.12 µsv/h:

Used in the construction of crushed granite which can add to the concrete or sprinkle the road. Crushed granite is also used in railway embankments. In the photo below — the Novomoskovsk children's railway (a narrow gauge railway used for training of young railwaymen). Here the gravel good, not fonit.

Also in the construction can be used slag — a by-product of the blast furnace steel production. The Soviet vacationers was popular here such labionasal cinder blocks:

Where in the slag uranium? It is contained in coal, which is burned in blast furnace. Therefore, steel mills and thermal power plants not only increase the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, but create radioactive contamination. Living near thermal power plant can be more harmful than near nuclear power plants (until the last works in a regular mode). Some of the uranium remains in the slag from which make this cheap crushed stone and sprinkled them in the track.

Track slightly upset.

Natural isotopes of uranium and thorium emit only α-particles which can not penetrate through the meter housing. The counter responds to the β-active products of their decay (see Radioactive series).
Radon
Radon is a radioactive inert gas is seven times heavier than air. Has no stable isotopes, the longest-lived of them, 222Rn, has a half life of slightly less than four days. Natural resources of the decaying radon is continuously replenished due to α-decay of radium in the earth's crust.
Due to its inertia, atoms of radon easily leave the crystal lattice of the mineral in which they are incurred. Through cracks and pores, the gas rises to the surface and into the atmosphere and dissipating without causing any harm. Another thing is if radon goes not to the open space and in an enclosed basement of the building. If the basement is not ventilated, radon will accumulate. SBM-20 can directly detect radon because the gas is exposed to α-decay:
Occur in this decay - polonium 218Po also decays with the emission of α-particles: 218Po → 214Pb + 4He. But the core of lead 214Pb overloaded with neutrons and decay by emitting β-radiation which "sees" the SBM-20. There are other decay products (isotopes of polonium, bismuth, lead, etc.) emitting not only in α but also β-particles.

In General, for accurate measurements of radon concentrations in the air need special equipment. Domestic dosimeter can only try to detect the fact of his presence. In search of radon, I went down to the basement of the old house with a dirt floor and measured the background at the height of half a meter (it amounted to 0.12 µsv/h).
At floor level the background was only slightly higher, and I had thought that radon is not here, but noticed that the floor has a large pit about a meter in depth (boarded (once it was used to store potatoes). I suggested that a heavy gas can "drain" back through the cracks between the boards to accumulate as a Board interfere with the ventilation of the pit. At the bottom of the pits was 0.3 µsv/h.

I removed the Board, to air out the basement and repeated the measurement:

The background is noticeably decreased. Left to try to explain the result. It would seem that after ventilation changes should not be, since the dosimeter does not respond to the radon, and a subsidiary of its decay products are heavy metals. Nevertheless, the experiment showed the presence of a difference of background. The chart above shows that a large part of the produced isotopes metals living minutes and seconds, and simply do not have time to settle on the floor. Atoms decay products congenerous on even the smallest dust particles hanging in the air, making them radioactive. Ventilation allows to partially get rid of this dust.
Also a few radon can get into our homes with natural gas and artesian water. Ventilate more often, because despite the fact that α-particles do not penetrate through the skin, radon and its decay products into the lungs when breathing. There they have to be not so harmless.
Additional materials on the topic
In addition to the many references to Wikipedia articles which I put in the text above, I can recommend the following interesting materials.
- Article egigd — a Little about radiation
- Radiation on Lurkmore
- Test dosimeters from Popular mechanics
- An article in the journal "Chemistry — Radioactivity at home: the problem of radon
- The benefits and harms of radon
- Radiation Dose Chart on xkcd.com (there is also Russian translation). published
- P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: geektimes.ru/company/dadget/blog/262402/