TICK-borne ENCEPHALITIS: myths and realities
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net
The first description of the disease, is very reminiscent of KE can be found in the Church records of the Scandinavian countries of VIII century. For the first time CE has been described as an independent disease in Austria in 1931 (H. Schneider,1931).
The pathogen was isolated in 1937 by Russian scientists under the leadership of L. A. Zilber. He was a member of the genus of flavivirus against which the world has still not developed any effective drug. Other cause flavivirus, e.g. yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, Dengue and West Nile that are carried by mosquitoes and Russia are for the most part exotic/imported infections.
The tick-borne encephalitis virus neurotropic, that is, affects the nervous system. It suffers from the grey matter of the brain and its membranes (meningoencephalitis), and often, but not always, involves the spinal cord. Adults suffer heavier children; one-third of survivors develop lifelong neurological damage, often with impaired mental sphere and disability. However, it should be noted that the disease develops is not at all infected. Many people carry it without symptoms.
KE distributed from Eastern Europe to the Russian Far East and Northern Japan. In Moscow and the Moscow region of tick-borne encephalitis not yet, but there is Lyme borreliosis.

Ixodes persulcatus (taiga tick) in the pose of pojelaniya — female
Viruses, as the name implies, the disease are ticks, namely Ixodes ricinus dog tick and the taiga tick Ixodes persulcatus. Dog tick carries the European subtype of TBE, whereas taiga is the source of more severe Siberian and far Eastern subtypes.

Ixodes persulcatus (taiga tick) in the pose of pojelania male
Mortality from the European subtype is low (1-2%), Siberian subtype, killed 2-3% of cases, but in the far East the mortality rate is 20 to 25% (in some years up to 40%!), partly due to selective logging only in severe cases of the disease. The far Eastern subtype can cause severe forms and in children, and, more often European, occurs in the chronic progressive form.
Registered in the world annually and 10,000 cases of TBE (who). In Russia in recent years, nearly 2,000 cases of the CE.
In nature, the main reservoir of infection, in addition to mites, are wild mammals, but, as the settlement of Siberia and the Far East and the displacement of animals from the forest areas, villages and suburbs, pokoritelya bloodsuckers become increasingly people.
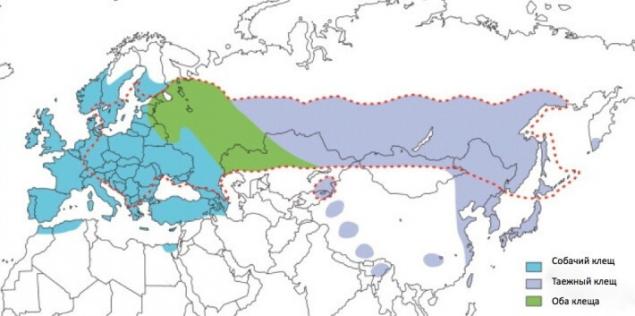
Habitats of taiga ticks and the dog. The red dashed lines delimited the distribution territory of KE.
The virus is transmitted to humans through the saliva of the tick within several minutes from the moment of suction, so a quick removal of the tick does not guarantee anything (just note that to remove the tick, however, it is necessary immediately, as soon as discovered, for the prevention of tick-borne borreliosis). Marked by rare cases of human infection by drinking raw goat and cow milk from infected animals.
Ticks become active once the temperature is set at +6°C and above, so this disease is characterized by a clear seasonality. Activities, overwintered mites out of the forest floor and placed on the grass or dwarf shrubs (usually not rising above half a meter), where waiting for pokoritelya. During this period the main thing for females of the tick to drink the blood, which is necessary for the development of numerous eggs.
Should be close to a warm-blooded animal, as it clings to the skin, hair, clothes and quietly creeps up until you find a secluded place — the person is usually under the clothing to cling to the body. People such place is often the back, armpits, groin, and domashnih wild animals — head, neck, groin.
Full for 5 — 6 days with blood, the female falls from pokoritelya on the forest floor, there lays several thousand eggs and dies.
The virus actively replicated in most ticks at a temperature of 6-25°C and ambient humidity > 85%. In hot and dry climates the virus does not survive. Therefore, in Russia the peak incidence occurs in late may — early July.
Ticks themselves become infected, prikazivati to sick animals, and, in addition, transmit the virus to their offspring transovarially (i.e., through eggs). The tick can transfer the KE as in adulthood and the stages of larvae and nymphs.
In the case of canine tick infestation most often occurs from larvae and nymphs; in the forest much more, they are barely legible in procerites, and in addition are very small, so difficult to detect on the body to suction.
As for the taiga tickin the transmission of infection much greater role played by adult ticks.
European TBE occurs usually in 2 phases:

Engorged blood female increases to the size of the beans.
The diagnosis is confirmed by serological tests with detection in the blood of a patient with neurological symptoms antibodies to the virus (TBEV-IgM + typically detected TBEV-IgG). In the initial stages virus may be detected using PCR. On brain MRI in about 20% of acute patients defined edema of the basal ganglia, thalamus and trunk, but by itself the MRI diagnosis is not installed.
As I said, specific treatment against the flavivirus does not exist. Acute forms are treated only symptomatically. In Russia often use corticosteroids, although their effectiveness in this disease not been confirmed by any studies.
But developed a very effective vaccine! In recent years, the disease practically is not registered in Austria, where vaccinated more than 86% of the population. In General, the Austrians began to apply his vaccine FSME-IMMUN® since 1976, Its efficiency reaches 95%.
Since 1991, is not less than the quality of the vaccine Encepur®, developed in Germany. In addition to foreign vaccines, we have applied the two domestic vaccine FGUP im. M. P. Chumakov and vaccine", Encevir". However, from time to time, some of the party "Encevir" spoke from circulation in connection with the exceedance of the allowable level of adverse reactions, which is probably due to inadequate clearance of the drug (marriage).
A special Commission, as we have found, not detected process errors at the factory, but the fact of the case group side effects the fact remains.
I hope the producers have learned from these scandals and now deliver high-quality vaccine.
The vaccine is grafted on the main and emergency circuits:
The basic scheme: 0, 1-2, 9-12 months for Encepur® and 0, 1-3, 5-12 months FSME-IMMUN®. Performed with subsequent re-vaccination every 3-5 years. To form immunity to the beginning of the season, the first dose is administered in the fall, second in winter.
Emergency circuit: three injections (0, 7, 21 days) for Encepur® and two injections (0, 14 day) for FSME-IMMUN®. Emergency scheme is used for unvaccinated individuals traveling to endemic foci in the spring and summer. Extra Teens were vaccinated individuals acquire immunity only for one season (he develops in 2-3 weeks), after 9-12 months they put a booster injection, and then again re-vaccination every 3-5 years. We have all registered vaccines are interchangeable in vaccination schemes.
Children: children's shape — FSME-IMMUN Junior® and Encepur children® — you can enter the 1st year of life; the Russian vaccine from 3 years.
In Russia, upon detection of the stuck tick unvaccinated persons administered intramuscularly special immunoglobulins (= gamma-globulin), i.e. ready-made antibodies to the virus, at a dose of 1.5 to 3 ml depending on age. 10 days later re-administered 6 ml. Although by itself, the prevention of immunoglobulin seems theoretically justified, and in Europe it is not recommended. The fact that so far not received evidence of the effectiveness of this method and not everything is clear with the re-introduction of the drug. In addition, there are legitimate concerns that the introduction of immunoglobulin can cause exacerbation of the disease.
So, anyway, it is better to get vaccinated!
Do not be fooled by a criminal is an inefficient means of type yodanthipirina, I often have to face in Russia, especially Novosibirsk and Tomsk — the home of the fuflomitsin. Tick — borne encephalitis- a potentially fatal disease, so don't joke with him!
Nonspecific prevention involves measures taken to prevent the suction of the tick. Remind the main rules:
1) tick season try not to visit without the need of places of the greatest congestion of ticks (forest habitats with tall grass, bushes). Hiking trails should stay. For recreation, Parking or overnight camping in the woods preferable dry pine woods with sandy soil or areas devoid of herbaceous vegetation, where ticks are extremely rare.
2) Use insect repellents with DEET at least 25 — 30% (less concentrated is not particularly effective) or means that for pyrethroids with acaricide (permethrin and alpha-permethrin) type Gardeks extreme®, which paralyze the legs of the tick. There are very effective combinations of acaricide-repellent products containing DEET and PYRETHROID at the same time. Spray these funds not only on exposed areas of the body, but also on shoes and clothes. Especially thick treat places where the mite can move with the clothes on the body (ankle, waist).
3) Going out in the woods, dress right! Wear light-colored clothes, which are easy to see bloodsucker. The so-called encefaliti khaki without acaricidal impregnation absolutely no good. Tuck pant legs into your socks, drop sleeves, hide your hair under a hat, sewn better under the hood. In recent years appeared in the sale and special costumes of the "Biotop", with sewn knitted obstacles-traps and fabric impregnated with synthetic that for pyrethroids, preserving the tick effect to 50 washings. These suits can be recommended to people working in the woods and hunters, hunters and other lovers of forest walks.
4) Regularly inspect your clothes and satellites in the woods. Remember that it is important to remove the tick with clothes or skin until he sucked. For one third of cases the suction of the tick remains undetected, especially if the vectors were the larva (nymph).
5) Upon returning home, thoroughly inspect the body. Because some areas of the body inaccessible to self-should enlist the help of relatives to explore the back and scalp.
6) Because the larval forms of ticks are very small, they can not see the clothes. To avoid suction in the house should wash the clothes in hot water.
7) Upon detection of the stuck tick, it must be removed immediately. To remove the tick, you can nail a pair of tweezers or thread, tying it around the head of the parasite. In practice, not deeply stuck tick is easy to remove just nails, grasping it as close to the skin. The tick is removed raskazivali-vykruchivatsya movements. Avoid crushing the tick! The wound can be treated with any disinfectant (chlorhexidine, povidone iodine, alcohol, etc.). If the wound is left mouthparts of a tick, remove it as a splinter. Important: do not go to this clinic! The sooner a tick is removed the less likely to catch Lyme disease. The remote tick is recommended to take (alive) to the laboratory of your hospital for infectious diseases for study by PCR on TBE and Lyme borreliosis (however, such laboratories are only in big cities).
Also read: ATTENTION! What to do if bitten by a tick
Learn how to safely and quickly remove ticks
REMEMBER: if within a month after the tick bite you have feel a sudden change in health, said increasing the temperature or increasing the red spot — you should immediately contact a doctor!published
Author: botalex
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: botalex.livejournal.com/134513.html
The pathogen was isolated in 1937 by Russian scientists under the leadership of L. A. Zilber. He was a member of the genus of flavivirus against which the world has still not developed any effective drug. Other cause flavivirus, e.g. yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, Dengue and West Nile that are carried by mosquitoes and Russia are for the most part exotic/imported infections.
The tick-borne encephalitis virus neurotropic, that is, affects the nervous system. It suffers from the grey matter of the brain and its membranes (meningoencephalitis), and often, but not always, involves the spinal cord. Adults suffer heavier children; one-third of survivors develop lifelong neurological damage, often with impaired mental sphere and disability. However, it should be noted that the disease develops is not at all infected. Many people carry it without symptoms.
KE distributed from Eastern Europe to the Russian Far East and Northern Japan. In Moscow and the Moscow region of tick-borne encephalitis not yet, but there is Lyme borreliosis.

Ixodes persulcatus (taiga tick) in the pose of pojelaniya — female
Viruses, as the name implies, the disease are ticks, namely Ixodes ricinus dog tick and the taiga tick Ixodes persulcatus. Dog tick carries the European subtype of TBE, whereas taiga is the source of more severe Siberian and far Eastern subtypes.

Ixodes persulcatus (taiga tick) in the pose of pojelania male
Mortality from the European subtype is low (1-2%), Siberian subtype, killed 2-3% of cases, but in the far East the mortality rate is 20 to 25% (in some years up to 40%!), partly due to selective logging only in severe cases of the disease. The far Eastern subtype can cause severe forms and in children, and, more often European, occurs in the chronic progressive form.
Registered in the world annually and 10,000 cases of TBE (who). In Russia in recent years, nearly 2,000 cases of the CE.
In nature, the main reservoir of infection, in addition to mites, are wild mammals, but, as the settlement of Siberia and the Far East and the displacement of animals from the forest areas, villages and suburbs, pokoritelya bloodsuckers become increasingly people.

Habitats of taiga ticks and the dog. The red dashed lines delimited the distribution territory of KE.
The virus is transmitted to humans through the saliva of the tick within several minutes from the moment of suction, so a quick removal of the tick does not guarantee anything (just note that to remove the tick, however, it is necessary immediately, as soon as discovered, for the prevention of tick-borne borreliosis). Marked by rare cases of human infection by drinking raw goat and cow milk from infected animals.
Ticks become active once the temperature is set at +6°C and above, so this disease is characterized by a clear seasonality. Activities, overwintered mites out of the forest floor and placed on the grass or dwarf shrubs (usually not rising above half a meter), where waiting for pokoritelya. During this period the main thing for females of the tick to drink the blood, which is necessary for the development of numerous eggs.
Should be close to a warm-blooded animal, as it clings to the skin, hair, clothes and quietly creeps up until you find a secluded place — the person is usually under the clothing to cling to the body. People such place is often the back, armpits, groin, and domashnih wild animals — head, neck, groin.
Full for 5 — 6 days with blood, the female falls from pokoritelya on the forest floor, there lays several thousand eggs and dies.
The virus actively replicated in most ticks at a temperature of 6-25°C and ambient humidity > 85%. In hot and dry climates the virus does not survive. Therefore, in Russia the peak incidence occurs in late may — early July.
Ticks themselves become infected, prikazivati to sick animals, and, in addition, transmit the virus to their offspring transovarially (i.e., through eggs). The tick can transfer the KE as in adulthood and the stages of larvae and nymphs.
In the case of canine tick infestation most often occurs from larvae and nymphs; in the forest much more, they are barely legible in procerites, and in addition are very small, so difficult to detect on the body to suction.
As for the taiga tickin the transmission of infection much greater role played by adult ticks.
European TBE occurs usually in 2 phases:
- The first flu-like phase develops within 1-2 weeks after the tick bite and lasts like the flu for about a week.
- But after a few days it's second phase with brain damage (from mild meningitis to severe encephalitis spinal paralysis).

Engorged blood female increases to the size of the beans.
The diagnosis is confirmed by serological tests with detection in the blood of a patient with neurological symptoms antibodies to the virus (TBEV-IgM + typically detected TBEV-IgG). In the initial stages virus may be detected using PCR. On brain MRI in about 20% of acute patients defined edema of the basal ganglia, thalamus and trunk, but by itself the MRI diagnosis is not installed.
As I said, specific treatment against the flavivirus does not exist. Acute forms are treated only symptomatically. In Russia often use corticosteroids, although their effectiveness in this disease not been confirmed by any studies.
But developed a very effective vaccine! In recent years, the disease practically is not registered in Austria, where vaccinated more than 86% of the population. In General, the Austrians began to apply his vaccine FSME-IMMUN® since 1976, Its efficiency reaches 95%.
Since 1991, is not less than the quality of the vaccine Encepur®, developed in Germany. In addition to foreign vaccines, we have applied the two domestic vaccine FGUP im. M. P. Chumakov and vaccine", Encevir". However, from time to time, some of the party "Encevir" spoke from circulation in connection with the exceedance of the allowable level of adverse reactions, which is probably due to inadequate clearance of the drug (marriage).
A special Commission, as we have found, not detected process errors at the factory, but the fact of the case group side effects the fact remains.
I hope the producers have learned from these scandals and now deliver high-quality vaccine.
The vaccine is grafted on the main and emergency circuits:
The basic scheme: 0, 1-2, 9-12 months for Encepur® and 0, 1-3, 5-12 months FSME-IMMUN®. Performed with subsequent re-vaccination every 3-5 years. To form immunity to the beginning of the season, the first dose is administered in the fall, second in winter.
Emergency circuit: three injections (0, 7, 21 days) for Encepur® and two injections (0, 14 day) for FSME-IMMUN®. Emergency scheme is used for unvaccinated individuals traveling to endemic foci in the spring and summer. Extra Teens were vaccinated individuals acquire immunity only for one season (he develops in 2-3 weeks), after 9-12 months they put a booster injection, and then again re-vaccination every 3-5 years. We have all registered vaccines are interchangeable in vaccination schemes.
Children: children's shape — FSME-IMMUN Junior® and Encepur children® — you can enter the 1st year of life; the Russian vaccine from 3 years.
In Russia, upon detection of the stuck tick unvaccinated persons administered intramuscularly special immunoglobulins (= gamma-globulin), i.e. ready-made antibodies to the virus, at a dose of 1.5 to 3 ml depending on age. 10 days later re-administered 6 ml. Although by itself, the prevention of immunoglobulin seems theoretically justified, and in Europe it is not recommended. The fact that so far not received evidence of the effectiveness of this method and not everything is clear with the re-introduction of the drug. In addition, there are legitimate concerns that the introduction of immunoglobulin can cause exacerbation of the disease.
So, anyway, it is better to get vaccinated!
Do not be fooled by a criminal is an inefficient means of type yodanthipirina, I often have to face in Russia, especially Novosibirsk and Tomsk — the home of the fuflomitsin. Tick — borne encephalitis- a potentially fatal disease, so don't joke with him!
Nonspecific prevention involves measures taken to prevent the suction of the tick. Remind the main rules:
1) tick season try not to visit without the need of places of the greatest congestion of ticks (forest habitats with tall grass, bushes). Hiking trails should stay. For recreation, Parking or overnight camping in the woods preferable dry pine woods with sandy soil or areas devoid of herbaceous vegetation, where ticks are extremely rare.
2) Use insect repellents with DEET at least 25 — 30% (less concentrated is not particularly effective) or means that for pyrethroids with acaricide (permethrin and alpha-permethrin) type Gardeks extreme®, which paralyze the legs of the tick. There are very effective combinations of acaricide-repellent products containing DEET and PYRETHROID at the same time. Spray these funds not only on exposed areas of the body, but also on shoes and clothes. Especially thick treat places where the mite can move with the clothes on the body (ankle, waist).
3) Going out in the woods, dress right! Wear light-colored clothes, which are easy to see bloodsucker. The so-called encefaliti khaki without acaricidal impregnation absolutely no good. Tuck pant legs into your socks, drop sleeves, hide your hair under a hat, sewn better under the hood. In recent years appeared in the sale and special costumes of the "Biotop", with sewn knitted obstacles-traps and fabric impregnated with synthetic that for pyrethroids, preserving the tick effect to 50 washings. These suits can be recommended to people working in the woods and hunters, hunters and other lovers of forest walks.
4) Regularly inspect your clothes and satellites in the woods. Remember that it is important to remove the tick with clothes or skin until he sucked. For one third of cases the suction of the tick remains undetected, especially if the vectors were the larva (nymph).
5) Upon returning home, thoroughly inspect the body. Because some areas of the body inaccessible to self-should enlist the help of relatives to explore the back and scalp.
6) Because the larval forms of ticks are very small, they can not see the clothes. To avoid suction in the house should wash the clothes in hot water.
7) Upon detection of the stuck tick, it must be removed immediately. To remove the tick, you can nail a pair of tweezers or thread, tying it around the head of the parasite. In practice, not deeply stuck tick is easy to remove just nails, grasping it as close to the skin. The tick is removed raskazivali-vykruchivatsya movements. Avoid crushing the tick! The wound can be treated with any disinfectant (chlorhexidine, povidone iodine, alcohol, etc.). If the wound is left mouthparts of a tick, remove it as a splinter. Important: do not go to this clinic! The sooner a tick is removed the less likely to catch Lyme disease. The remote tick is recommended to take (alive) to the laboratory of your hospital for infectious diseases for study by PCR on TBE and Lyme borreliosis (however, such laboratories are only in big cities).
Also read: ATTENTION! What to do if bitten by a tick
Learn how to safely and quickly remove ticks
REMEMBER: if within a month after the tick bite you have feel a sudden change in health, said increasing the temperature or increasing the red spot — you should immediately contact a doctor!published
Author: botalex
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: botalex.livejournal.com/134513.html
Tags
See also
How to protect yourself from ticks
7 myths about tick bites: information that will save your health!
If pets like to sleep in your bed, pay attention to it!
How to distinguish an insect from a serious illness? Determine with the naked eye.
13 most "terrible" parasites of the planet (15 photos)
9 tips that may one day save your life

















