Child criminals in tsarist Russia: what has led to the liberalization of
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net
The abolition of serfdom has created in Russia a large number of homeless children, and the children of criminals. Hungry children were going to survive, in 90% of cases of children's crimes were theft, for stealing the children sat in jail on a common basis.
However, the liberal teachers disagreed with this practice: they believed the child "empty vessel", which is still not too late to invest morality, and were convinced that in this regard children in any case should not be in prison. To prove the possibility of children's re-education through their efforts with the 1870-ies in Russia had created a large number of private colonies for juvenile offenders.
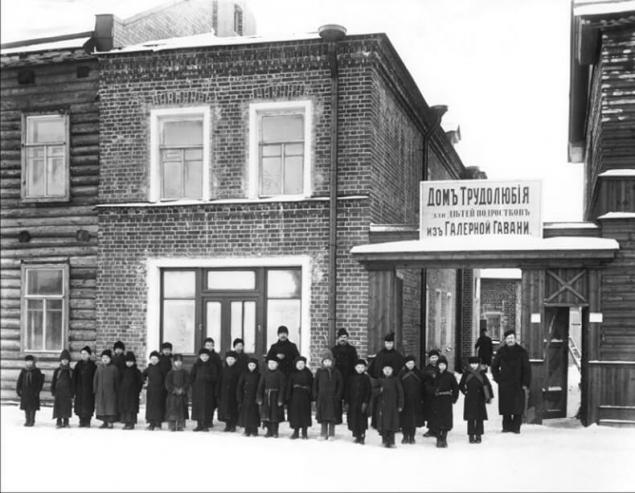

One of the best was the St. Petersburg agricultural colony was opened in October 1871 at the station of Rzhevka, and in 1913 moved to the estate of the Settlement of the Tsarskoye Selo uyezd and was designed for 200 pupils. The motto of the colony were the words of Victor Hugo: "he Who opens a school, closes the prison." Students were divided into families, each with a teacher and farm land.
The colony included a school, gymnastics, singing, reading, playing games, work in the workshops – plumbing, carpentry, wagon, shoemaking, tailoring. For good behaviour they were rewarded with books, tools for crafts, and for a good job paying 3-5 cents a day (the total amount earned was issued after release from prison). Educational results inspired the recurrence in the St. Petersburg colony was only 25%, by world standards it was an outstanding result.
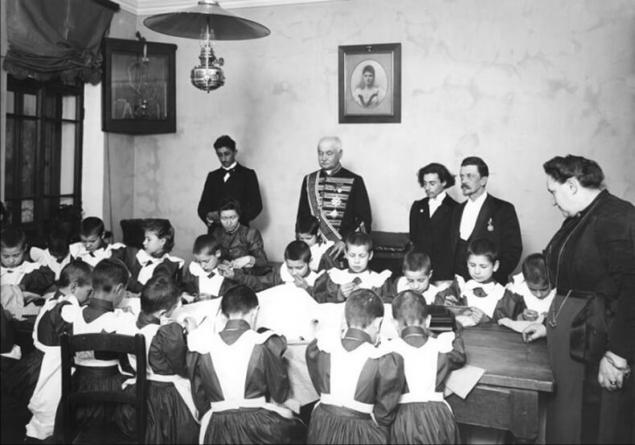
Soon I connected to this charitable organization. At the request of the ladies ' charity prison Committee in 1895, a resolution was adopted on the termination of detention not only in prisons but also in detention at the time of investigation of underage girls (they were placed in the colony, and in the absence thereof in the provinces – to the monasteries).
For several years the consequences of such liberalization pleasing to all, but in five years the situation has changed. It became clear that this system leads to a sharp increase in crime among children and adolescents, namely, juvenile delinquency was significantly ahead of the adult.
So, from 1884 to 1894 overall crime increased by 7%, and children's – 15%; from 1901 to 1910 – the General 35%, children's 112%.

Journal of the Ministry of justice noted that "if before the fear of criminal punishment, the fear to see their child dressed in a prison cloak still somewhat aroused in the common people a sense of concern for the fate of the younger generation were forced to curb evil inclinations by corrective measures, but now the parents on the question of their thieving children carefree shrug, as if talking about the normal, not the interest of their occurrence."
Many poor parents began to deliberately push their children to crime so they came "on the state-owned Costa". If caught, trouble is small; in fact still a boy in jail not go to jail, and I'll send it back for correction."
Components of success: innate, invented and acquired
What to do if you were attacked by Viper
When this became clear, the Russian system has returned to the same stringent measures against child offenders. No matter how old you are, a thief should sit in jail.
Total, let us remember:
First, the liberalization of the punishment has a positive effect, but then leads to outbreak of crime. published
Source: www.psychologos.ru/articles/view/deti-prestupniki_v_carskoy_rossii_dvoe_zn__k_chemu_privela_liberalizaciya_vop_zn_
However, the liberal teachers disagreed with this practice: they believed the child "empty vessel", which is still not too late to invest morality, and were convinced that in this regard children in any case should not be in prison. To prove the possibility of children's re-education through their efforts with the 1870-ies in Russia had created a large number of private colonies for juvenile offenders.

One of the best was the St. Petersburg agricultural colony was opened in October 1871 at the station of Rzhevka, and in 1913 moved to the estate of the Settlement of the Tsarskoye Selo uyezd and was designed for 200 pupils. The motto of the colony were the words of Victor Hugo: "he Who opens a school, closes the prison." Students were divided into families, each with a teacher and farm land.
The colony included a school, gymnastics, singing, reading, playing games, work in the workshops – plumbing, carpentry, wagon, shoemaking, tailoring. For good behaviour they were rewarded with books, tools for crafts, and for a good job paying 3-5 cents a day (the total amount earned was issued after release from prison). Educational results inspired the recurrence in the St. Petersburg colony was only 25%, by world standards it was an outstanding result.
Soon I connected to this charitable organization. At the request of the ladies ' charity prison Committee in 1895, a resolution was adopted on the termination of detention not only in prisons but also in detention at the time of investigation of underage girls (they were placed in the colony, and in the absence thereof in the provinces – to the monasteries).
For several years the consequences of such liberalization pleasing to all, but in five years the situation has changed. It became clear that this system leads to a sharp increase in crime among children and adolescents, namely, juvenile delinquency was significantly ahead of the adult.
So, from 1884 to 1894 overall crime increased by 7%, and children's – 15%; from 1901 to 1910 – the General 35%, children's 112%.

Journal of the Ministry of justice noted that "if before the fear of criminal punishment, the fear to see their child dressed in a prison cloak still somewhat aroused in the common people a sense of concern for the fate of the younger generation were forced to curb evil inclinations by corrective measures, but now the parents on the question of their thieving children carefree shrug, as if talking about the normal, not the interest of their occurrence."
Many poor parents began to deliberately push their children to crime so they came "on the state-owned Costa". If caught, trouble is small; in fact still a boy in jail not go to jail, and I'll send it back for correction."
Components of success: innate, invented and acquired
What to do if you were attacked by Viper
When this became clear, the Russian system has returned to the same stringent measures against child offenders. No matter how old you are, a thief should sit in jail.
Total, let us remember:
First, the liberalization of the punishment has a positive effect, but then leads to outbreak of crime. published
Source: www.psychologos.ru/articles/view/deti-prestupniki_v_carskoy_rossii_dvoe_zn__k_chemu_privela_liberalizaciya_vop_zn_
Tags
See also
24 frames per second or higher. For what
What can "squeeze" from usb-microscope
The woman, like a used car
Alex Kovalchuk: I'm just beginning to breathe...
Volcano Russia - a large selection of gambling entertainment, attractive preferences