732
10 misconceptions about modern world
Science does not stand still, and occasionally rejects things that previously seemed to us quite ochevidnymi
From ancient times, people wanted to know about his home planet as much as possible. Today we think that we know enough about it. The problem is that it just seems to us. Here are some widespread misconceptions about the Earth, and the phenomena that occur in it.
1. Everest moved to the side, rather than vverh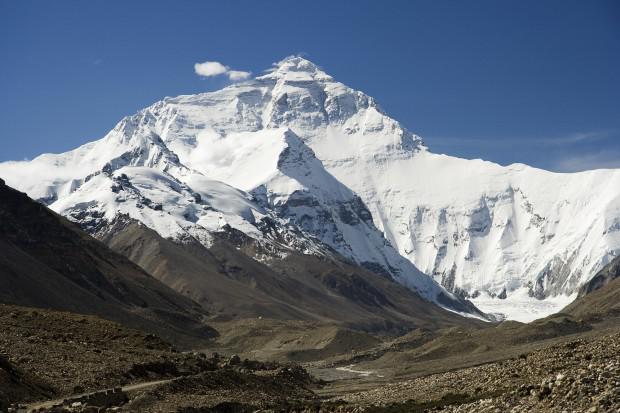
Fifty million years ago, the Indian subcontinent has decided that he does not like to coexist with the equator. And he went to the north. Eventually he crashed into Asia, with the result that emerged Himalayas, and with them, and Everest. Today, his height is about 9 km away. But since the collision of the Indian subcontinent and Asia is still ongoing, Everest must also continually grow, right? No, not so, scientists say, carefully controlling the height of the mountain. Giorgio Poretta, a professor at the University of Trieste in 1995, learned that Everest is not actually increased by any significant amount. The best instruments for the measurement simply increased the accuracy of the measurement of height. Instead, says Poretta, due to the ongoing continental collision of India and Asia, Mount Everest is moving northeast at a speed of 42 mm per year. So if you decided to climb this mountain, you go up by about the same height, which in 1953 climbed by Sir Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay. However, your ascent will take almost 3 meters to the north-east of the place where it was made the first ascent.

2. Mauna Loa - the highest mountain in mire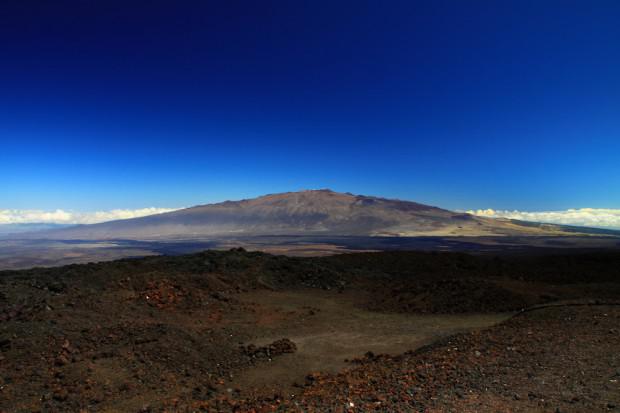
Above it was about Everest. So, Mount Everest, is, in fact, is not the highest mountain on Earth. Mount Mauna Loa (which means "Long Mountain") is part of the Hawaiian Islands. And it does not look as high as Mount Everest, but only because most of it is under water, and we can see only the top of it. The height of the mountain, from the top to the bottom, is just over 10 km 2, making it much higher than Everest. In addition, the mountain has a lot of other differences from Everest. About half of the Hawaiian Islands - part of Mauna Loa. This is not just a mountain, it's a volcano, or rather, a lot of volcanoes, which are called "shields" as they are wide and really resemble shields. "Shields" on Mauna Loa appear when lava erupts from the depths of the planet at a very high speed. Molten rock flows from Mauna Loa is very fast, and she did not have enough time to harden. The eruptions on Mauna Loa were frequent a million years ago. Even now the volcano is still active. But that's not all. The tremendous weight of the Mauna Loa "selling" the ocean floor at a depth of 8 km. Taking into account this fact, the height of the volcano will be more than 17 km, making it the highest mountain on the planet today.
3. Tornado nevidimy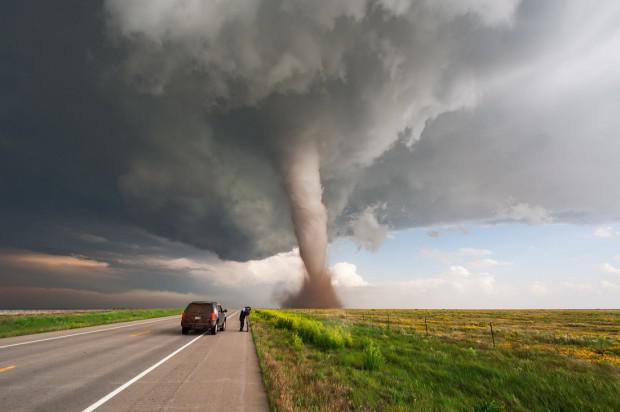
Everybody was running for cover when they see that they are approaching tornado. But how is it that we see a tornado? After all, air is invisible, after all. Well, from a technical point of view, what we see is actually a cloud of water droplets, and sometimes out of the mud and debris. This cloud is formed within an invisible funnel moving air, which is the tornado. Tornadoes generally occur in the so-called "super cells," areas of the storm with very strong rotating updrafts. Nobody knows exactly what causes emerged from the cell funnel reach down to the ground. There is speculation that this might be due to the temperature difference at the boundaries of adjacent downcomer. Water vapor is typically condensed inside the rotating air funnel, and the funnel descends. However, tornadoes can inflict destruction on the ground long before the funnel fully formed.
4. Clouds weigh tonny
What could be more beautiful than the fluffy white clouds floating in the blue sky? Such clouds, we usually think that they are light, like a mist. However, the cloud is actually very heavy. Cumulus clouds are medium in size is made up of water droplets and can weigh 500 tonnes. A float in the sky a huge behemoth maybe because the atmosphere around him even harder. This is easy to forget, but we and cumulus clouds are in the lowest layers of the atmosphere. Air molecules have a certain weight and pressure of the air can be up to 1 kg per square centimeter, or 17 tons. And it's a lot of pressure for the average person in the growth of 168 cm and weight 70 kg. We are not pushing this weight just because the air is not only outside, but also inside our bodies. In addition, the air is also possible to apply the law of Archimedes. The force that pushes up the cloud is equivalent to the mass of the air, displacing the cloud. All this is very close to the Earth's surface, so that multi-ton cumulus clouds float above us for the same reason that cruise ship floats on the water surface.
5. On Earth, there are magnetic tornado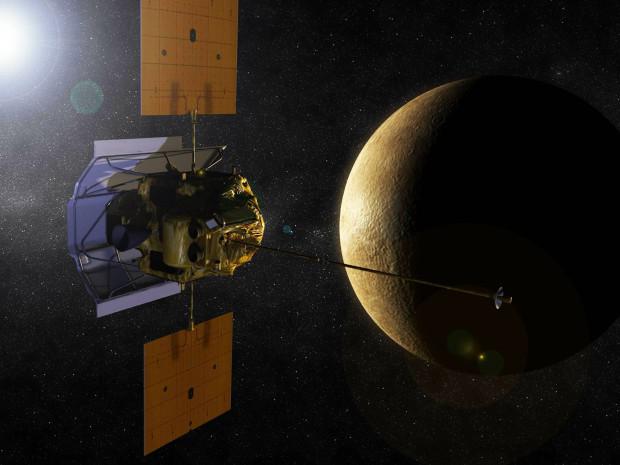
NASA experts were surprised when their automatic interplanetary station "Messenger" sent to Mercury, found in the planet's magnetic field twisted "tornado", a length of 800 km. These effects movement of magnetic fluxes, or "plasmoid", formed at the points where the magnetic field of Mercury faces the magnetic field of the sun. Scientists believe that it is because of this phenomenon is such a thin atmosphere of Mercury. These magnetic tornadoes direct solar wind (ie a plasma that came from the Sun) down to the surface of Mercury, where she particles with an electric charge, decomposed gases that are tied up in the rocks.
Scientists have long known that the magnetic fields of the Earth and the Sun are related. It is because they occur so-called "northern lights." But what the scientists did not know before the opening to the Mercury, so it is that the bond magnetic fields are so close. On Earth has its own magnetic tornadoes, but they do not worry about the cost. Despite the fact that the magnetic phenomena on the planet occur every 8 minutes, the atmosphere of our planet's thick enough, and it protects us from deadly radiation.
6. Rock obitaemy
Have you ever be in the desert, or in a deep cave, and to feel that you were not alone? It did not. Perhaps rocks have eyes and ears, but the tiny life-forms called endolithic rock called home. Endolithic are extremophiles, which means that they are very fond of extreme conditions. They are found in the bowels of the Earth for nearly three-kilometer depth. Most of them survive due to food and water, falling down through cracks in the earth, but some of them literally eat rock and release acid, which allows them to get themselves even more stone snacks. When it comes to how deep in the depths of life may be a limiting factor is the temperature. The heat spreads from the center of the planet, and at a depth of 5 km under the surface temperature may rise to 125 ° C. Researchers have not been able to learn, live there something to even greater depths, but the study of extremophiles shows that they at the above temperature problems begin with breeding. So the depth of 5 km in fact may be the limit for them.
7. Switzerland daily rises and falls almost 25 sm
Land not only provides food for some forms of life, she is also a bit elastic. That is why the volcano Mauna Loa could going into the ocean floor as deep. This flexibility also means that the Moon and the Sun can affect the surface of the planet, although this effect is not as strong as in the sea. In the case of the Earth's surface is no banks, which can measure the ebb and flow, but certain parts of the crust rise, and then very slowly and almost imperceptibly fall.
But this is only observed in the Great Plains, and in other places where there are huge mountain ranges and volcanoes, to prevent this, do not you? Not really. Compared with the Moon or the Sun, even insignificant Alps. In fact, very precise measurements have shown that Switzerland during the "earth tides' daily rise and fall of 25 cm.
8. Cyclones can tantsevat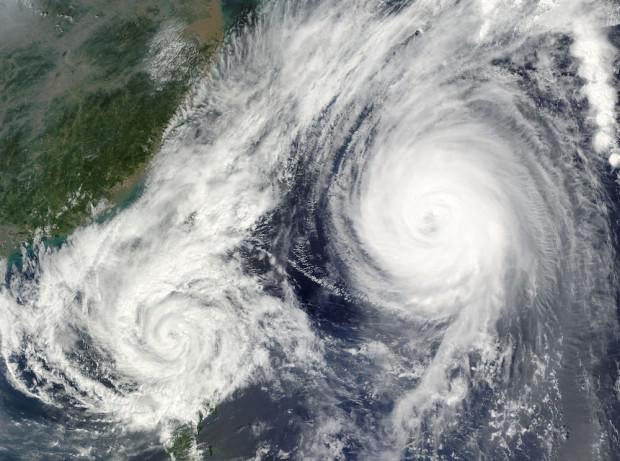
Tornadoes are sometimes called cyclones, but technically cyclones - a low pressure area with winds in a spiral, with the spiral rotates in the northern hemisphere, counterclockwise in the southern hemisphere clockwise. Zyklon could be a hurricane, or any other type of low-pressure system with the corresponding direction of the wind. Sakuho Fujiwara was a Japanese meteorologist who managed to find out that when two cyclones are close enough to each other, they begin to "dance" around some common center. This "Fujiwara effect" is observed only in the event that there are cyclones, approximately equal strength. Otherwise, the weak will be consumed by a cyclone stronger. The most expensive and the most devastating example of this world saw in 2012, the year. Most hurricanes in the Caribbean and the Atlantic Ocean in the end meet with westerly winds, which displace them out of North America. Hurricane "Sandy" for a while is what is happening. But suddenly, he changed course and returned to the US and Canada as superstorms, and it happened because of what turned out to be close to another low-pressure system. Winds in this system have already begun to weaken, and the storm, which came from the Caribbean, was ready to die down. But as it turned a number of "Sandy" was much larger, the two storms merged into one, and it happened in the worst place that one could think of - on the bank.
9. Large earthquakes occur medlenno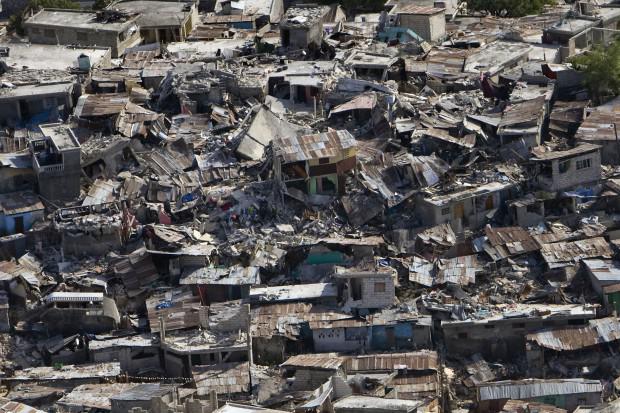
An earthquake occurs when rocks start to move along faults. The faults are different. A fault may be a small crack in the earth's crust, and then an earthquake will also be small. Either fault line may be located at the junction of two tectonic plates. Moving plate has tremendous energy, and when they move, then the results can be catastrophic.
Many large earthquakes are preceded by seismic tremors, but scientists were surprised when they learned that the rocks can move relative to each other even without any shocks. They were able to find out after the deployment of highly sensitive seismic equipment along the San Andreas fault in California (where the Pacific and North American tectonic plates slide past each other), and along the Alpine Fault in New Zealand (where the Pacific plate slides along the Australian continental plate ). At the Alpine Fault in the past few large earthquakes, but in its central part has always been unusually quiet. Scientists have begun to closely monitor this part, believing that it could accumulate energy reserves that could cause a catastrophe of apocalyptic proportions. Instead, they found "a seismic tremor," a series of small earthquakes, each of which lasted about 30 minutes. Something similar has been fixed, and along the San Andreas fault, though here the scientists are not quite sure what it is "tremor." This may be the accumulation of stress before the next earthquake, or it may be small discharges accumulated energy, which will help reduce the intensity of future large earthquakes, which happen when the fault zone will start the movement again.
10. Next supervolcano eruption probably will not Yelloustoune
Yellowstone Park is replete with geysers, hot springs and boiling mud pots. Some of these funny things there arose in the early 21st century. At the same time, archaeologists realized that in nature there is such a thing as supervolcanoes, and that Yellowstone Volcano among them number one. Since everyone was wondering when he finally explodes. However, this is unlikely to happen soon. Recent studies have shown that in a volcano, of course, a lot of magma, but it was not in the eruptive form, ie can not be ejaculated. Because in the history of mankind has not been super-eruption, no one really knows what kind of signs they are associated with, and where to find them. Before the main eruption may be many earthquakes or any other natural disaster. On the other hand, conventional volcanoes sometimes wake up unexpectedly. It is quite possible that the supervolcano may do the same.
Much more interesting candidate for a super-eruption of the Chilean volcano can be Laguna del Mole, although it currently does not erupted, and there are no warning signs. He simply inflated annually by 24-28 cm, and no one knows why this is happening.
via factroom.ru

From ancient times, people wanted to know about his home planet as much as possible. Today we think that we know enough about it. The problem is that it just seems to us. Here are some widespread misconceptions about the Earth, and the phenomena that occur in it.
1. Everest moved to the side, rather than vverh

Fifty million years ago, the Indian subcontinent has decided that he does not like to coexist with the equator. And he went to the north. Eventually he crashed into Asia, with the result that emerged Himalayas, and with them, and Everest. Today, his height is about 9 km away. But since the collision of the Indian subcontinent and Asia is still ongoing, Everest must also continually grow, right? No, not so, scientists say, carefully controlling the height of the mountain. Giorgio Poretta, a professor at the University of Trieste in 1995, learned that Everest is not actually increased by any significant amount. The best instruments for the measurement simply increased the accuracy of the measurement of height. Instead, says Poretta, due to the ongoing continental collision of India and Asia, Mount Everest is moving northeast at a speed of 42 mm per year. So if you decided to climb this mountain, you go up by about the same height, which in 1953 climbed by Sir Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay. However, your ascent will take almost 3 meters to the north-east of the place where it was made the first ascent.

2. Mauna Loa - the highest mountain in mire

Above it was about Everest. So, Mount Everest, is, in fact, is not the highest mountain on Earth. Mount Mauna Loa (which means "Long Mountain") is part of the Hawaiian Islands. And it does not look as high as Mount Everest, but only because most of it is under water, and we can see only the top of it. The height of the mountain, from the top to the bottom, is just over 10 km 2, making it much higher than Everest. In addition, the mountain has a lot of other differences from Everest. About half of the Hawaiian Islands - part of Mauna Loa. This is not just a mountain, it's a volcano, or rather, a lot of volcanoes, which are called "shields" as they are wide and really resemble shields. "Shields" on Mauna Loa appear when lava erupts from the depths of the planet at a very high speed. Molten rock flows from Mauna Loa is very fast, and she did not have enough time to harden. The eruptions on Mauna Loa were frequent a million years ago. Even now the volcano is still active. But that's not all. The tremendous weight of the Mauna Loa "selling" the ocean floor at a depth of 8 km. Taking into account this fact, the height of the volcano will be more than 17 km, making it the highest mountain on the planet today.
3. Tornado nevidimy

Everybody was running for cover when they see that they are approaching tornado. But how is it that we see a tornado? After all, air is invisible, after all. Well, from a technical point of view, what we see is actually a cloud of water droplets, and sometimes out of the mud and debris. This cloud is formed within an invisible funnel moving air, which is the tornado. Tornadoes generally occur in the so-called "super cells," areas of the storm with very strong rotating updrafts. Nobody knows exactly what causes emerged from the cell funnel reach down to the ground. There is speculation that this might be due to the temperature difference at the boundaries of adjacent downcomer. Water vapor is typically condensed inside the rotating air funnel, and the funnel descends. However, tornadoes can inflict destruction on the ground long before the funnel fully formed.
4. Clouds weigh tonny

What could be more beautiful than the fluffy white clouds floating in the blue sky? Such clouds, we usually think that they are light, like a mist. However, the cloud is actually very heavy. Cumulus clouds are medium in size is made up of water droplets and can weigh 500 tonnes. A float in the sky a huge behemoth maybe because the atmosphere around him even harder. This is easy to forget, but we and cumulus clouds are in the lowest layers of the atmosphere. Air molecules have a certain weight and pressure of the air can be up to 1 kg per square centimeter, or 17 tons. And it's a lot of pressure for the average person in the growth of 168 cm and weight 70 kg. We are not pushing this weight just because the air is not only outside, but also inside our bodies. In addition, the air is also possible to apply the law of Archimedes. The force that pushes up the cloud is equivalent to the mass of the air, displacing the cloud. All this is very close to the Earth's surface, so that multi-ton cumulus clouds float above us for the same reason that cruise ship floats on the water surface.
5. On Earth, there are magnetic tornado

NASA experts were surprised when their automatic interplanetary station "Messenger" sent to Mercury, found in the planet's magnetic field twisted "tornado", a length of 800 km. These effects movement of magnetic fluxes, or "plasmoid", formed at the points where the magnetic field of Mercury faces the magnetic field of the sun. Scientists believe that it is because of this phenomenon is such a thin atmosphere of Mercury. These magnetic tornadoes direct solar wind (ie a plasma that came from the Sun) down to the surface of Mercury, where she particles with an electric charge, decomposed gases that are tied up in the rocks.
Scientists have long known that the magnetic fields of the Earth and the Sun are related. It is because they occur so-called "northern lights." But what the scientists did not know before the opening to the Mercury, so it is that the bond magnetic fields are so close. On Earth has its own magnetic tornadoes, but they do not worry about the cost. Despite the fact that the magnetic phenomena on the planet occur every 8 minutes, the atmosphere of our planet's thick enough, and it protects us from deadly radiation.
6. Rock obitaemy

Have you ever be in the desert, or in a deep cave, and to feel that you were not alone? It did not. Perhaps rocks have eyes and ears, but the tiny life-forms called endolithic rock called home. Endolithic are extremophiles, which means that they are very fond of extreme conditions. They are found in the bowels of the Earth for nearly three-kilometer depth. Most of them survive due to food and water, falling down through cracks in the earth, but some of them literally eat rock and release acid, which allows them to get themselves even more stone snacks. When it comes to how deep in the depths of life may be a limiting factor is the temperature. The heat spreads from the center of the planet, and at a depth of 5 km under the surface temperature may rise to 125 ° C. Researchers have not been able to learn, live there something to even greater depths, but the study of extremophiles shows that they at the above temperature problems begin with breeding. So the depth of 5 km in fact may be the limit for them.
7. Switzerland daily rises and falls almost 25 sm

Land not only provides food for some forms of life, she is also a bit elastic. That is why the volcano Mauna Loa could going into the ocean floor as deep. This flexibility also means that the Moon and the Sun can affect the surface of the planet, although this effect is not as strong as in the sea. In the case of the Earth's surface is no banks, which can measure the ebb and flow, but certain parts of the crust rise, and then very slowly and almost imperceptibly fall.
But this is only observed in the Great Plains, and in other places where there are huge mountain ranges and volcanoes, to prevent this, do not you? Not really. Compared with the Moon or the Sun, even insignificant Alps. In fact, very precise measurements have shown that Switzerland during the "earth tides' daily rise and fall of 25 cm.
8. Cyclones can tantsevat

Tornadoes are sometimes called cyclones, but technically cyclones - a low pressure area with winds in a spiral, with the spiral rotates in the northern hemisphere, counterclockwise in the southern hemisphere clockwise. Zyklon could be a hurricane, or any other type of low-pressure system with the corresponding direction of the wind. Sakuho Fujiwara was a Japanese meteorologist who managed to find out that when two cyclones are close enough to each other, they begin to "dance" around some common center. This "Fujiwara effect" is observed only in the event that there are cyclones, approximately equal strength. Otherwise, the weak will be consumed by a cyclone stronger. The most expensive and the most devastating example of this world saw in 2012, the year. Most hurricanes in the Caribbean and the Atlantic Ocean in the end meet with westerly winds, which displace them out of North America. Hurricane "Sandy" for a while is what is happening. But suddenly, he changed course and returned to the US and Canada as superstorms, and it happened because of what turned out to be close to another low-pressure system. Winds in this system have already begun to weaken, and the storm, which came from the Caribbean, was ready to die down. But as it turned a number of "Sandy" was much larger, the two storms merged into one, and it happened in the worst place that one could think of - on the bank.
9. Large earthquakes occur medlenno

An earthquake occurs when rocks start to move along faults. The faults are different. A fault may be a small crack in the earth's crust, and then an earthquake will also be small. Either fault line may be located at the junction of two tectonic plates. Moving plate has tremendous energy, and when they move, then the results can be catastrophic.
Many large earthquakes are preceded by seismic tremors, but scientists were surprised when they learned that the rocks can move relative to each other even without any shocks. They were able to find out after the deployment of highly sensitive seismic equipment along the San Andreas fault in California (where the Pacific and North American tectonic plates slide past each other), and along the Alpine Fault in New Zealand (where the Pacific plate slides along the Australian continental plate ). At the Alpine Fault in the past few large earthquakes, but in its central part has always been unusually quiet. Scientists have begun to closely monitor this part, believing that it could accumulate energy reserves that could cause a catastrophe of apocalyptic proportions. Instead, they found "a seismic tremor," a series of small earthquakes, each of which lasted about 30 minutes. Something similar has been fixed, and along the San Andreas fault, though here the scientists are not quite sure what it is "tremor." This may be the accumulation of stress before the next earthquake, or it may be small discharges accumulated energy, which will help reduce the intensity of future large earthquakes, which happen when the fault zone will start the movement again.
10. Next supervolcano eruption probably will not Yelloustoune

Yellowstone Park is replete with geysers, hot springs and boiling mud pots. Some of these funny things there arose in the early 21st century. At the same time, archaeologists realized that in nature there is such a thing as supervolcanoes, and that Yellowstone Volcano among them number one. Since everyone was wondering when he finally explodes. However, this is unlikely to happen soon. Recent studies have shown that in a volcano, of course, a lot of magma, but it was not in the eruptive form, ie can not be ejaculated. Because in the history of mankind has not been super-eruption, no one really knows what kind of signs they are associated with, and where to find them. Before the main eruption may be many earthquakes or any other natural disaster. On the other hand, conventional volcanoes sometimes wake up unexpectedly. It is quite possible that the supervolcano may do the same.
Much more interesting candidate for a super-eruption of the Chilean volcano can be Laguna del Mole, although it currently does not erupted, and there are no warning signs. He simply inflated annually by 24-28 cm, and no one knows why this is happening.
via factroom.ru