2253
Moscow trolley (25 pics + text)
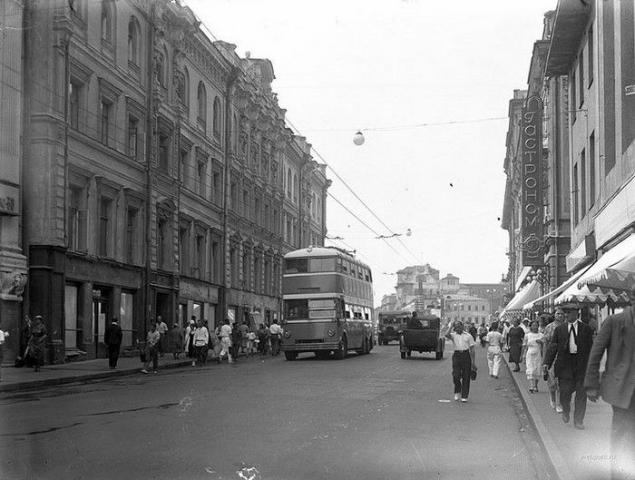

YATB-3 on Gorkogo (Tver). Photos of the 1930s. The first trolleybus was established in 1882 in Germany, Werner von Siemens. Experienced line was built in Insterburg (now - Chernyahovsk Kaliningrad region). The first regular trolleybus line was opened on the outskirts of Berlin Galenzee April 29, 1882.
1882. Germany.
Contact wires are close enough, and strong winds from a short circuit occurs. The first trolley had rods; used for current collection truck, which is either rolls freely on the wire due to the tension of the cable, or had its own electric motor and moved ahead with it trolley. Later were invented rod with wheel, and later moving current collectors.
One of the first English trolleybuses in Leeds. 1911.
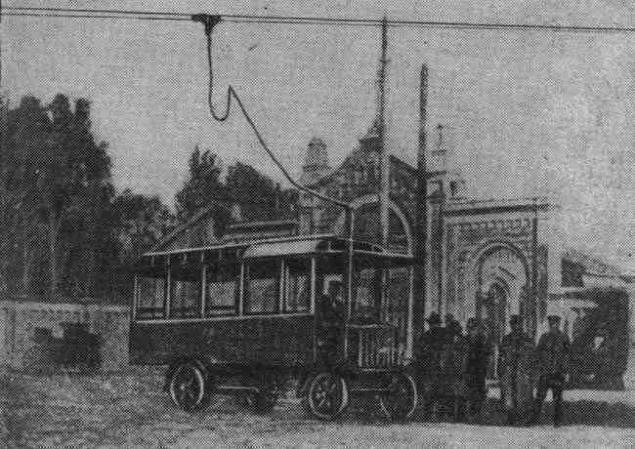

On the line in Czechoslovakia. Photos of 1900s.
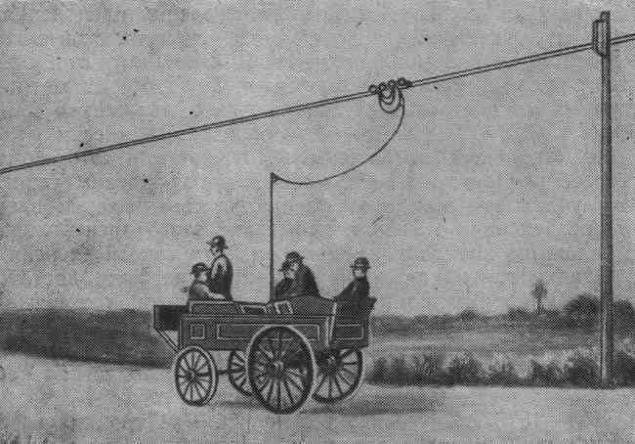
In 1902 the magazine "Car" published an article about the trial "car driven by electric power obtained from the wires along the way, but not walking on the tracks, and in the usual way." The machine is intended for transportation of goods. It happened March 26, 1902, and that day may well be regarded as the birthday of domestic trolley. Cartwright part was made by the Peter Frese, and the engine's electrical and were developed by Count Schulenburg SI.
Judging by the description, it was pyatidesyatipudovy crew who worked on the line voltage of 110 volts and a current of 7 amps. With crew wires connect the cable, and at its end was a special trolley to slide on the wire when driving crew. On tests "car easily evaded the forward direction, back up and turned." But then the idea of development has not received and Trolleytruck forgotten thirty years.

The first trolleybus company Frese & Co. 1903 St. Petersburg.
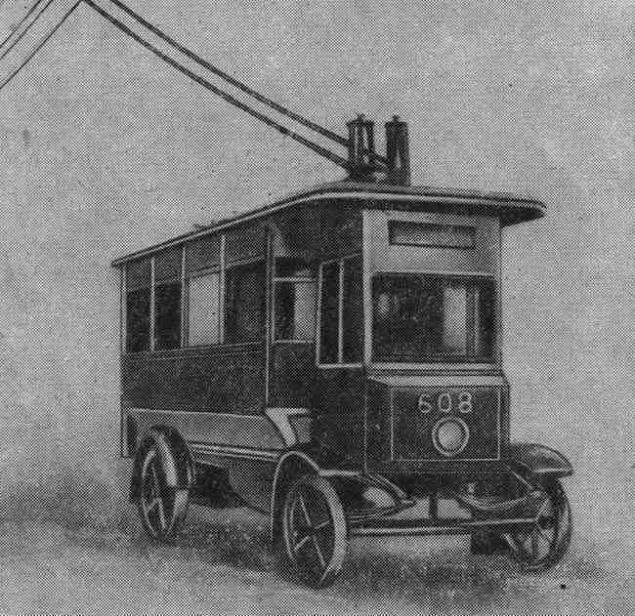
And in Moscow trolley was first introduced in 1933. The movement of the first route, while "single-track" from Tverskaya Zastava (Belosrusskaya) to the village of All Saints (now near the metro station "Falcon") opened November 15, 1933. In Moscow, the idea of building a trolleybus line was first proposed in 1924, but its implementation started only 9 years later. In December 1932 domestic factories was entrusted the design and construction of the first two experienced Soviet trolleybuses. In the summer of 1933 at the Yaroslavl automobile plant project developed by the Research Institute of the automotive industry, began production of the chassis (on the basis of the bus I-6). In October, they were sent to Automobile them. Stalin (VMS now AMO ZIL), where they have established a body made here. By November 1, 1933, two newly issued trolley, which received index "LC" (Lazar Kaganovich), was towed from the factory ZIS "Dinamo", where they installed electrical equipment (tokosёm produced by rollers). On the territory of the plant held the first technical testing machines.
The first Soviet trolleybus had a wooden frame with a metal shell, the body length of 9 m, a width of 2 to 3 m and a weight of 8, 5 tons. It could reach a maximum speed of 50 km / h. Inside, there were 37 seats (seats were soft), mirrors, nickel-plated handrails, nets for luggage; under the seats installed elektropechki. Doors open manually: front - driver, rear - conductor. Machinery painted in dark blue (top had creamy yellow stripe at the bottom - bright yellow stroke). On the front part of the body attached shiny metal shield with the inscription "From the workers, engineers and employees Gos.avtozavoda them. Stalin, the plant "Dinamo", Yaroslavl Automobile, NATI. " In October 1933 along the Leningrad highway from Tverskaya Zastava District to the bridge of the railway in the Intercession-Streshnevo mounted single-track trolley line. November 5 tests this trolleybus present secretary MK VKP (b) Khrushchev, and November 6 through an official trip to the acceptance committee consisting of the chairman of the Moscow Soviet Nikolai Bulganin, engineers, technicians and workers to produce trolleybuses. From 7 to 15 November drivers were driving practice on a single machine.
Regular movement of a single trolley began at 11 am November 15, 1933 The next day, determined the time of his work - from 7 am to 24 hours. The average speed was 36 km / h, the entire line of machine overcame 30 minutes. So opened the first in Moscow and the USSR trolleybus line.
Mass production of the same trolley was established three years later in Yaroslavl.
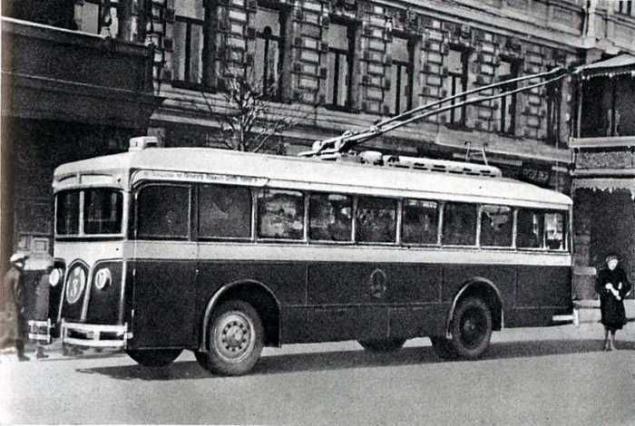

Moscow's first trolleybus, 1933
"A two-storey trolley enjoys great success among the Muscovites. Lovers ride "higher" too much. The second floor is always overcrowded adults and children. Some citizen, apparently, desperate to take place on the second floor, climbed the stairs to the roof of the trolleybus.
- Where are you getting, citizen? - I cried. - Go! For you have not done a three-storey trolley. Citizen looked at me with pleading eyes and said in despair: - What should I do? The second floor is full, and the roof free. I can not leave Moscow without making high-altitude travel by trolley. I had to take up the whistle ».
From the newspaper "Moscow freighter" from 7 November 1939.
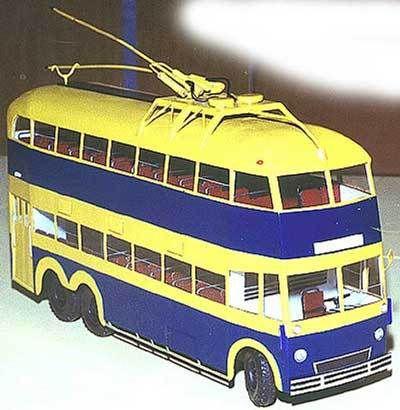

YATB-3.
In 1935, the English company English Electric Company was purchased by one storey trolley. "By order of Khrushchev in England ordered and will arrive in the near future two-storey modern trolley type - wrote" Working Moscow "January 8, 1937. - It has a metal body, triaxial chassis, 74 Seats, weighs 8500 kg. Quiet operation basic units of English cars, the rear axle, engine, motor-compressor current collectors, as well as soft start and stop - the result of careful design and perfect installation. "
"Muscovites with amazement staring at a huge trolley. Almost all the passengers tried to get to the second floor. The driver responds well Kubrick friend about this bus, - the newspaper "Moscow freighter" September 3, 1937 - a remarkable machine. The controls are very easy and manageable. We thought that because of the cumbersome machine will not be stable, but our fears were unnecessary ».

Trolleybus was delivered by sea to Leningrad and its transportation to Moscow resulted in the whole saga! Due to the huge double-decker trolley railroad categorically refused to accept it for transportation. From Leningrad to the Kalinin (Tver) being dragged in tow on the highway (how it was in 1937, this highway, it is not necessary to explain). Only 29 June 1937 dvuhetazhnik arrived in Kalinin. Here the car was loaded on a barge and taken in early July in the capital, in the second trolleybus park, where the preparation for the test. During her become identified curious details. It turned out that, despite the huge size, "foreigner" is not so roomy! Due to the high center of gravity of the passengers on the first floor is strictly forbidden to be in motion. With an impressive height of the body (4, 58 m) ceiling height on the first and second floors of 1, 78 and 1, 76 m, respectively, so that the stand on the first floor was also very difficult to even a man of medium height. Trolleybus had only one door for boarding and alighting of passengers - back. Neither the forecourt or the front door he did not have.
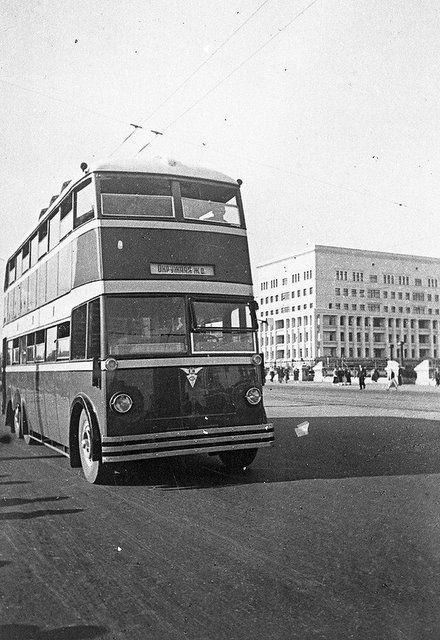

The specifics of public transport in London had nothing to do with Moscow. In the English capital city traffic even during peak hours did not know what a crowded salon. A small number of passengers it is possible to manage one door. In the 30 years in Moscow, even in non-peak times buses, trolleybuses and trams often just went to pieces.
In this double-decker trolley flaws do not end there. It turned out that the contact network Moscow trolley is not suitable for operation of imported machinery - it was required to raise a meter.
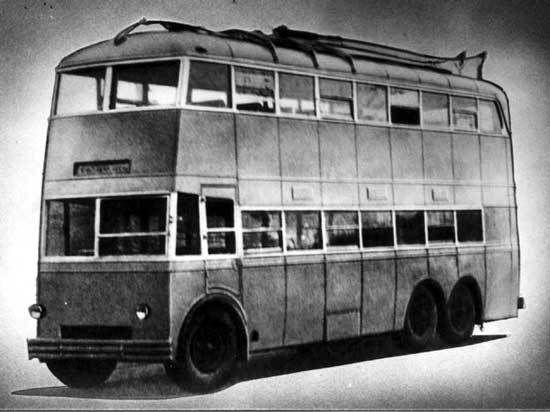

YATB-3.
As a "testing ground" were chosen the main thoroughfare of the pre-war Moscow - Gorky Street and the Leningrad highway. Contact network raised. In September, started trial operation, which lasted about a month. In October "dvuhetazhnik" was towed to the Yaroslavl Automobile Plant, who was in the prewar years the main supplier of trolleybuses in the USSR. Here it was dismantled, examined carefully and actually copied. Soviet equivalent of the English trolley was designated YATB-3 - Yaroslavl trolley, the third model. Create a complete analog "Englishman" failed - Soviet trolley was more severe. It weighed 10 tons 7.
Double-decker trolley from Yaroslavl began to arrive in Moscow in the summer of 1938. Returned and "Englishman". In Moscow, all double-decker trolleybuses were concentrated in the first trolleybus park. Originally, they shuttled between willingly and near the North River Station. After opening VSHV in September 1939 double-decker trolley came on routes linking the country with a major exhibition center of the capital.
Faithfully translated into Russian the operating instructions for the two-storey trolley, Moscow trolleybusniki were surprised to find that it allows passengers to smoke in the cabin on the second floor! "Smoke on the second floor of a two-story trolley displeases nonsmoking passengers - wrote" Moscow freighter "February 14, 1940 - Office of trust" Mostrolleybus "smoking should be prohibited in the trolley».

YATB-3.
Releasing in 1938 - 1939 years. pilot batch of 10 "dvuhetazhnikov" Yaroslavl Automobile discontinued production. Usually referred to as the cause of the imminent threat of war. In fact, up until August 1941 Yaroslavl automobile plant continued to produce single-storey trolley. After that civilian production was curtailed, began production of weapons, ammunition and artillery tractors. More convincing other causes cessation of production "dvuhetazhnikov." Affected obvious unsuitability for their design work on the streets of Moscow. It did not help even the appearance of a body trolley front door. Just try to stand up inside the car, bouncing over the potholes with a ceiling height of 178 cm! But the biggest reason - even in January 1938, Khrushchev was appointed first secretary of the Communist Party of Ukraine. "Pushed" to the capital storey trolley was just a nobody.

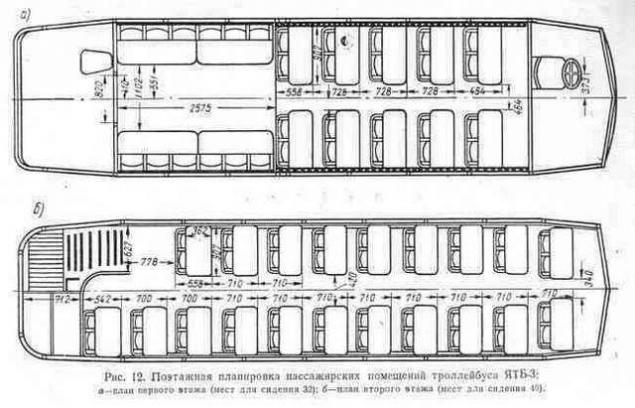
YATB-3. Lower salon.

YATB-3. Upper salon.
Neither "dvuhetazhnik" from Moscow was not evacuated. Transport by rail they can not be, and tow tractors for hundreds or thousands of miles away - all the more so since the fall of 1941, each truck was literally worth its weight in gold.
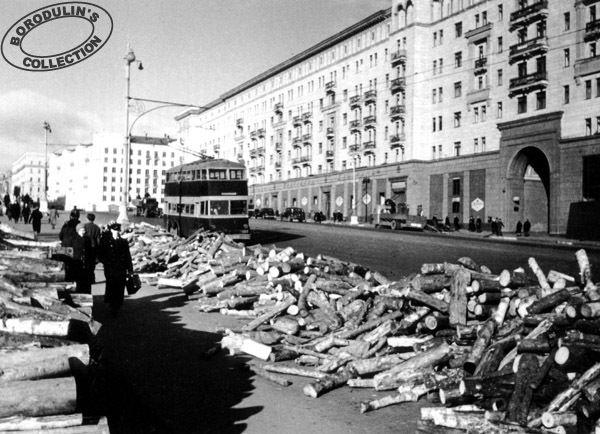

YATB-3 on Gorkogo. Fall 1941
Veterans of the first trolleybus fleet recalled that in October 1941 they were ordered as soon as Nazi motorcyclists appear at the gates of the park, double-decker trolley pour kerosene and set on fire. For this purpose machines have been installed around the barrels of kerosene tanks with cloth and appointed a special duty. Fortunately, fascist riders at the gate of the park and have not appeared, is not short of just a few kilometers.
YATB-3.
In the postwar years, double-decker trolleybuses were excluded from the operation. Operating experience these machines shows that they are poorly suited to our regions. Newer trolley made one-story, designed for perevozku large number of passengers (mostly stoyachix). It was decided to abandon the use of double-decker articulated trolleybuses in favor of machines. But these were only in the late 50s from the factory gate "SVARZ." No instance trolley YATB-3 to the present day has not been preserved.
The last two "dvuhetazhnika" written off in 1953, although these cars had all-metal body, could serve longer. What was the reason?
At one time the run was a legend that would go Stalin from the Kremlin to the Kuntsevo dacha, and before his "Packard" was a two-storey trolley, swaying from side to side. A leader of all people thought that "dvuhetazhnik" is about to fall on its side. And Stalin ordered to eliminate such trolleys.
This banal version of the truth has nothing to do, if only because touring between the Kremlin and the Middle cottage, a tuple Stalin could never cross a double-decker trolley route.
Another version says that the double-decker trolley buses were decommissioned after a series of tilts, accompanied by a large number of victims. The author even met with several "witnesses" of such disasters. However, when they called the scene, it became clear - nothing like this could not be there because trolleybus lines in these locations are not suitable for motion double-decker cars. By the way, in the archives and found no evidence of overturning "dvuhetazhnikov." This is largely due to the fact that they operated in strict accordance with the instructions. Conductors were not allowed congestion machines, carefully monitor the content of the second floor.

YATB-3.
But the most plausible reason, it seems to me, is as follows: for normal use double-decker trolleybuses were required to raise the contact network of one meter. It is this meter, and destroyed them! After all, in Moscow there was no line, which would be fully serviced "dvuhetazhnikami." And they operated in parallel with the conventional, one-story trolley. But if the two-storey trolley went well under the raised contact network, about one-story trolley do not. "Working on a simple" yatebeshke "under a raised contact system - it does not even work, and things anguish, - told the author of this article (Mikhail Yegorov - d1) is one of the veterans of the Moscow trolley. - On these lines almost normal trolley firmly attached to the wire, as the tram to the rails! To stop - do not drive! Stop the car - do not go round! And the bar were more likely to fly wires. From passengers continuous complaints. Khrushchev gave to steer a car - and certainly no double-decker trolley we would not have appeared! »
So, having got to the line with a raised trolley line, trolley floor almost completely deprived of one of its most important qualities - maneuverability. By the beginning of the Great Patriotic War in Moscow was 11 "dvuhetazhnikov." A conventional single-storey cars - 572 units! How many drivers and passengers of the Moscow daily trolley double-decker trolley mothers and their hapless "godfather» ?!
At London's transport such problems did not arise - everything trolleybuses were bunk.
However, specialists from Moscow after the war tried to increase the maneuverability of single-storey machines due to installation of the elongated rod current collectors. This experiment was a complete failure - when moving trolley with elongated bars at the ends of their occurring vibrations that break rods with wires. By the way, for this reason, it is impossible to increase the length of the rod trolley greater than that which they have today. So at the Moscow transport were only two ways: either all trolley buses and trams will be one-story, or, as in London - bunk. There is no third. Moscow, as is known, has taken the first path.
Well, it's not even a trolley, but would still I decided to show you here is an interesting vehicle:

German bus-trailer.
In 1959 in Moscow there were two German bus Do54 and one two-storey passenger trailer to the towing vehicle DS-6, which only some have been built in the GDR 7 pieces. The total length of the trailer to the towing vehicle was 14800 mm, of which he had a trailer 112200 mm. On the ground floor of the trailer was provided 16 seats and 43 standing places, the second - 40 seats and 3 standing. The first floor was connected to a second two 9-step ladders. Interior height of the first floor - 180 cm, the second - 171 cm. The diesel engine tractor power of 120 hp allow this design to reach speeds of 50 km / h. Initially, the trailer with two double-decker buses went from number 111 to the metro station "October" to MSU, and then all three cars were sent to the route of the Sverdlov Square to Vnukovo Airport. Travel these machines until 1964.

The first Soviet Trolleytruck began to appear in the 30-ies. the last century. These were the handicraft converted passenger cars YATB. Use these trucks for their own needs trolleybus depot.
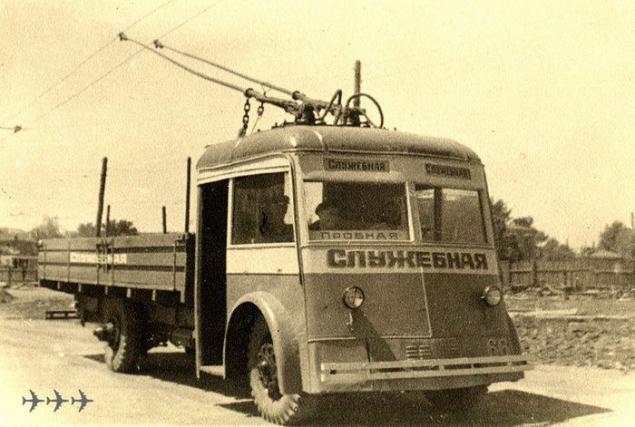

Gradually the scope of these machines began to grow and operators are thinking about using the "horned" in those places where there was no contact network. Particularly acute this problem has become the shortage of fuel during the war.
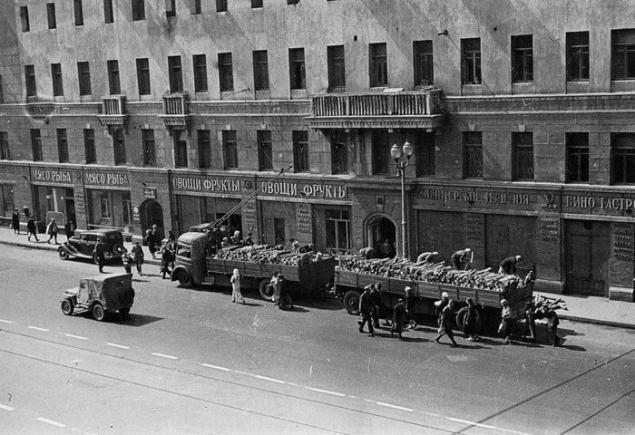

Trolleytruck on Gorkogo. Photo 1941