Scientists from Oxford proved that fish can learn to distinguish the faces of people
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net
In an attempt to understand and appreciate the features of the process and the depth perception of you and me around the living beings, scientists at Oxford University have managed to teach Taxotidae family fish store and identify previously seen people's faces. Value experiment and its results not only in a practical component, but in the entertainment "staging". However, judge for yourself ...

Funny, but the mechanism of compensation that makes the ferocious lion like kittens get on the orders of the trainer sticks on his hind legs and jump through burning rings and working to fish. And it has allowed a group of scientists from Oxford to deliver a series of experiments, a burst of light on the long-running dispute about the nature of the ability of those around us sentient beings to face recognition.
The objectives of the experiment
There are two competing theories about how a person learns the face of others: (a) the ability to recognize is innate, and is achieved through certain parts of the cortex of the neocortex, and (b) the ability to recognize the acquiree and is formed in the process of co-existence with the object recognition.
Research Objective: To determine the ability of fish as sentient beings without the neocortex, to recognize human faces. It is worth noting that attempts to define the role of the neocortex in the human ability to recognize previously been made in experiments with pigeons. The unequivocal answer to this question, in spite of the positive results of experiments that had been received, since, on the one hand, it was proved the existence of the birds of the initial structure of the neocortex, on the other - it is difficult to completely exclude the possibility that hundreds of years of living together with a man in pigeons did not develop device that allows to recognize faces. The "counterweight" to the birds, the fish do not have the neocortex, and not in a position for the time of its existence, the possibility of direct contact with a person is unlikely to have developed over time, any specific recognition tools.
The training Bryzgunov (Toxotes chatareus) of Taxotidae family not only learned to recognize human faces, but also in order to eliminate any doubts about this, clearly showed the participants of the experiment, as well learned lessons learned.
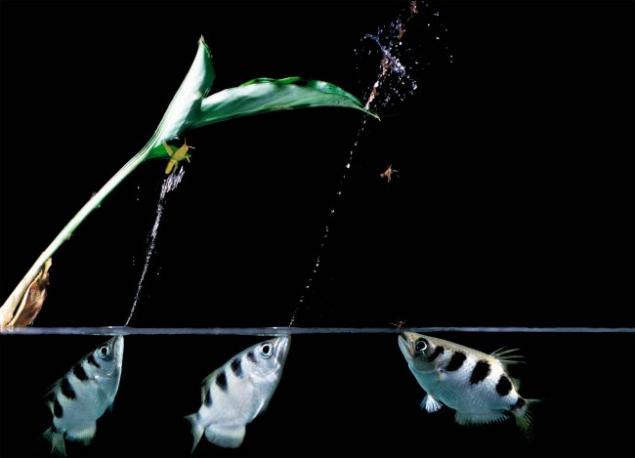
They live "wisdom" of the family Bryzgunov ray-finned fish in the fresh waters of Australia, India, Polynesia and the Philippines. A group of scientists drawn from Oxford these small fish just for its distinctive way to produce food: to fly over water extraction are amazingly accurately hit released from the mouth water spray from a distance of 1-2 meters. Fallen grasshoppers, flies and mosquitoes become easy prey, and even in "difficult" times do not leave the populations of these fish without food. It is not known which of the group of experts came up with the idea to use in experiments Bryzgunov unique abilities, but in the end the result fully confirmed the expectations.
Experiment and the results

For the experiment in the immediate vicinity of the aquarium was placed waterproof display on which the serial output color and black-and-white images of several human faces.
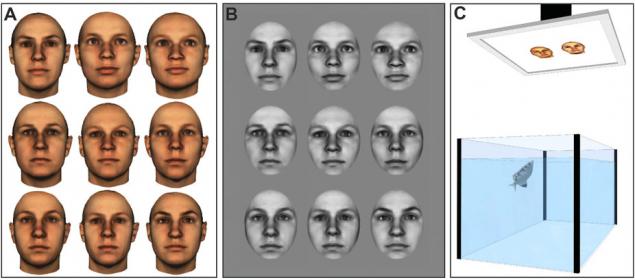
Experiment 1
In the first phase demonstrated one person (the stimulus, CS +) - it was his, according to the scientists, the fish was later to distinguish from several other exhibited together at the next stage of the experiment. By defining the desired object, in accordance with the assigned tasks was to release the fish into it a stream of water, proving that the lesson is mastered. For diligence and proper definition of relevant persons Bryzgunov each time received compensation in the form of portions of delicious food.
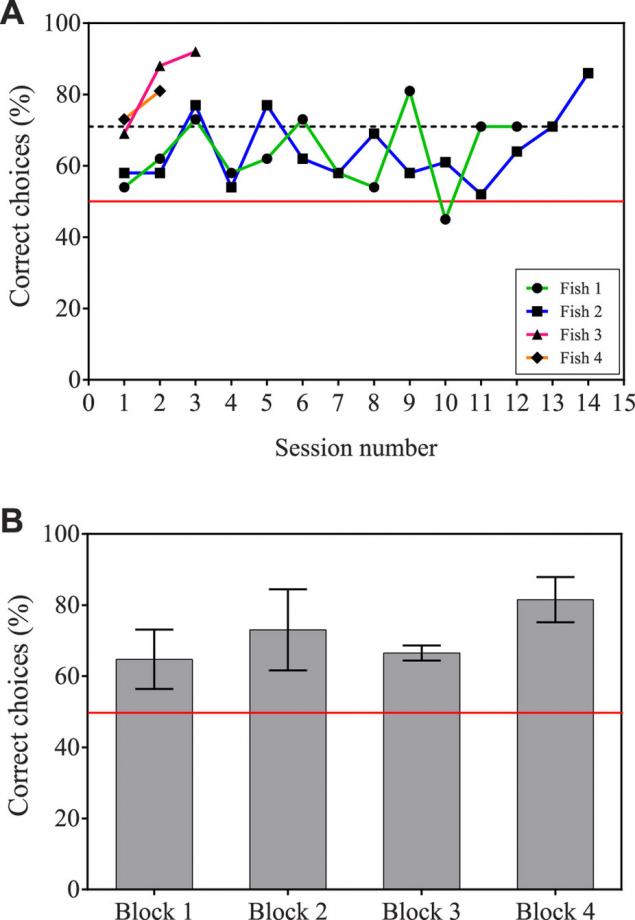
In the first experiment four and Bryzgunov two images of human faces have been used, one of which was taken as a conditioned stimulus (CS +). As noted in the publication of the balance sheet, without exception, the fish learned to distinguish between the CS + in the range 2-14 sessions (Figure below: Fish 1: 12 sessions; Fish 2:. 14 sessions; Fish 3: 3 sessions; Fish 4: 2 sessions) <. br>
Experiment 2
In a second experiment the task was complicated: the pictures exhibited Bryzgunov changed shape of the head, the image brightness and color while maintaining the same persons. It is significant that in this case the fish, after a short training period, have coped with the task.
Apart from the fact of learning fish family Taxotidae scientists have come to a curious conclusion: the percentage of perception and memorization of a black and white image was slightly higher (86%) than non-ferrous (81%).
Thus, using two alternative selection methods, scientists from Oxford showed that Bryzgunov (Toxotes chatareus) are able to learn how to allocate a certain person from a large number of alternative images (experiment 1, 44 persons) and demonstrate such ability, even after the change of colors, shapes head and brightness (experiment 2, 18 facets). This means that Bryzgunov without neocortex, however, has an impressive recognition abilities. Thus demonstrated skills were obtained as a result of the learning process.
publication on Scientific Reports
publication on the website of the University of Oxford
That's all, you had a simple service to select Dronk.Ru sophisticated technology. Do not forget to subscribe to our blog, will be much more interesting ...




< br> Why online retailers give the money for the purchase? Review Xiaomi Mi Air Purifier 2 or how to clean the air of a megacity? Return the money - Choosing a cashback service to Aliexpress
Source: geektimes.ru/company/dronk/blog/277046/

Funny, but the mechanism of compensation that makes the ferocious lion like kittens get on the orders of the trainer sticks on his hind legs and jump through burning rings and working to fish. And it has allowed a group of scientists from Oxford to deliver a series of experiments, a burst of light on the long-running dispute about the nature of the ability of those around us sentient beings to face recognition.
The objectives of the experiment
There are two competing theories about how a person learns the face of others: (a) the ability to recognize is innate, and is achieved through certain parts of the cortex of the neocortex, and (b) the ability to recognize the acquiree and is formed in the process of co-existence with the object recognition.
Research Objective: To determine the ability of fish as sentient beings without the neocortex, to recognize human faces. It is worth noting that attempts to define the role of the neocortex in the human ability to recognize previously been made in experiments with pigeons. The unequivocal answer to this question, in spite of the positive results of experiments that had been received, since, on the one hand, it was proved the existence of the birds of the initial structure of the neocortex, on the other - it is difficult to completely exclude the possibility that hundreds of years of living together with a man in pigeons did not develop device that allows to recognize faces. The "counterweight" to the birds, the fish do not have the neocortex, and not in a position for the time of its existence, the possibility of direct contact with a person is unlikely to have developed over time, any specific recognition tools.
The training Bryzgunov (Toxotes chatareus) of Taxotidae family not only learned to recognize human faces, but also in order to eliminate any doubts about this, clearly showed the participants of the experiment, as well learned lessons learned.
They live "wisdom" of the family Bryzgunov ray-finned fish in the fresh waters of Australia, India, Polynesia and the Philippines. A group of scientists drawn from Oxford these small fish just for its distinctive way to produce food: to fly over water extraction are amazingly accurately hit released from the mouth water spray from a distance of 1-2 meters. Fallen grasshoppers, flies and mosquitoes become easy prey, and even in "difficult" times do not leave the populations of these fish without food. It is not known which of the group of experts came up with the idea to use in experiments Bryzgunov unique abilities, but in the end the result fully confirmed the expectations.
Experiment and the results

For the experiment in the immediate vicinity of the aquarium was placed waterproof display on which the serial output color and black-and-white images of several human faces.

Experiment 1
In the first phase demonstrated one person (the stimulus, CS +) - it was his, according to the scientists, the fish was later to distinguish from several other exhibited together at the next stage of the experiment. By defining the desired object, in accordance with the assigned tasks was to release the fish into it a stream of water, proving that the lesson is mastered. For diligence and proper definition of relevant persons Bryzgunov each time received compensation in the form of portions of delicious food.
In the first experiment four and Bryzgunov two images of human faces have been used, one of which was taken as a conditioned stimulus (CS +). As noted in the publication of the balance sheet, without exception, the fish learned to distinguish between the CS + in the range 2-14 sessions (Figure below: Fish 1: 12 sessions; Fish 2:. 14 sessions; Fish 3: 3 sessions; Fish 4: 2 sessions) <. br>

Experiment 2
In a second experiment the task was complicated: the pictures exhibited Bryzgunov changed shape of the head, the image brightness and color while maintaining the same persons. It is significant that in this case the fish, after a short training period, have coped with the task.
Apart from the fact of learning fish family Taxotidae scientists have come to a curious conclusion: the percentage of perception and memorization of a black and white image was slightly higher (86%) than non-ferrous (81%).
Thus, using two alternative selection methods, scientists from Oxford showed that Bryzgunov (Toxotes chatareus) are able to learn how to allocate a certain person from a large number of alternative images (experiment 1, 44 persons) and demonstrate such ability, even after the change of colors, shapes head and brightness (experiment 2, 18 facets). This means that Bryzgunov without neocortex, however, has an impressive recognition abilities. Thus demonstrated skills were obtained as a result of the learning process.
publication on Scientific Reports
publication on the website of the University of Oxford
That's all, you had a simple service to select Dronk.Ru sophisticated technology. Do not forget to subscribe to our blog, will be much more interesting ...




< br> Why online retailers give the money for the purchase? Review Xiaomi Mi Air Purifier 2 or how to clean the air of a megacity? Return the money - Choosing a cashback service to Aliexpress
Source: geektimes.ru/company/dronk/blog/277046/
Tags
See also
Scientists at Cambridge University have developed a game to help treat patients with schizophrenia
Scientists at Cornell University have created a prototype of the "quantum" of the future of money
Engineers have developed an alloy that changes color
Who and why turned the fight against the dams around the world?
The salt of human tears
Smokers have lower body mass index: nicotine suppresses appetite
Good mood impairs memory
"Smart" glasses will help to restore sight
You and your work *