How to help save energy and water at home around the world
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net
Unlike "active" - energy-efficient - at home, "passive" puts in the priority is not the production of alternative energy, and minimize costs. Its power consumption by 40-90 per cent less than a conventional building types. This house itself heats itself in winter and cool in summer. The look is "passive" house in different ways. The article presents the 13 "thrifty" homes from around the world.
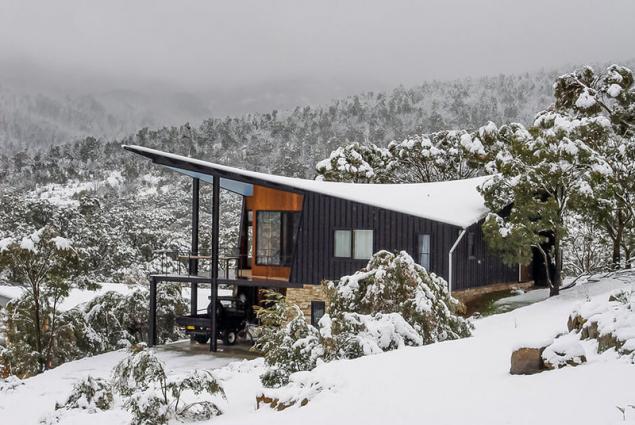

Australia - trendsetter in the world of energy-efficient construction, and this ski lodge in the mountains on the lake Krekenbek - a reference sample of the Australian "passive" houses. The ground floor is recessed into the hill: the land - a good heat insulator. Wide glass facades facing the sun - do not have to include the artificial light during the day. The floor is polished concrete, the day it absorbs heat from the sun, and at night gives.
In the concrete, in the case of heavy frosts, hidden water heating system running from the stove. Another distinctive feature of Australian houses in cold regions - parabolic roof. They protect from the wind, which is "dispersed" to 150 km / h.
Orientation meeting envy: this hut decorated with natural stone and teak, huge bath and sauna in the Japanese style - just an extension to rest. The main house is not visible, but it is close.

Australian neighbors with passion "face off" energy efficiency ratings of their homes. This house is owned by a family with two children, the most effective in your street (9 stars, the energy savings of about 80 percent). In addition to traditional methods of "passive" housing like rooflights and concrete floors, is involved and several original.
For example, the ventilation tube leaving a meter into the ground - make a U-turn under the lawn. Soil temperature in summer is lower than the air outside - it keeps it at the level of 15-17 degrees Celsius. The fan exhausts the warm air into the tube, it has returned a few degrees colder. This system allows the owners to do without air conditioning.
Another feature of the project - "reverse finish 'walls as if turned inside out, inside the brick remains in its original form, and closes the outside insulation, drywall, paneling or metal profile. This scheme reduces the thermal conductivity of the walls.
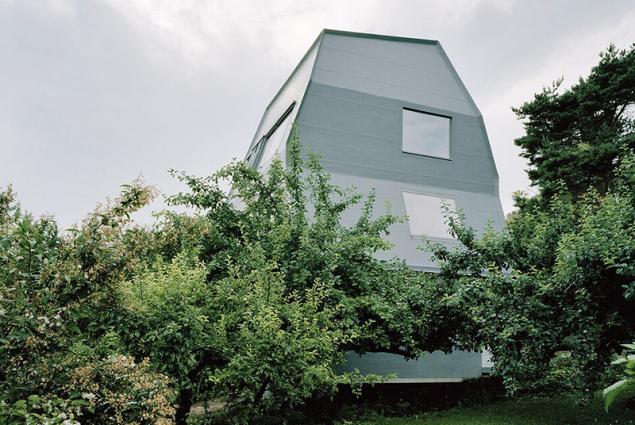

Germany - also a leading article "passive" building, with its recognizable handwriting is not satisfied with the hunt for the sunlight, focusing on the thermal insulation of walls, windows and doors. The walls of homes in Baden-Württemberg, for example, are decorated with rubber. Artificial rubber helps keep the heat in the building without additional heating. The building is essentially "semi-finished" - it is completely built in a factory and assembled on site from 136 items. All furniture is built.
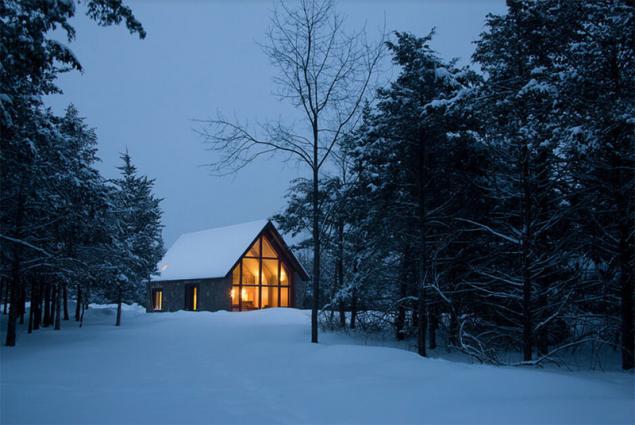

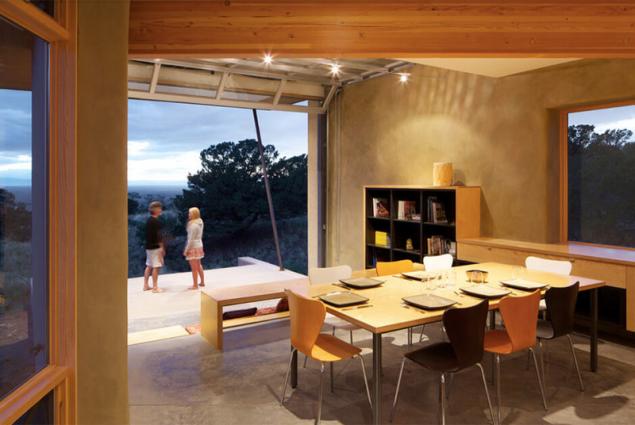
Here is the first certified "passive" house in New York, one of the most energy efficient in the world. Architects assure that the building consumes 90 percent less energy than an average house the same square footage in these parts. The house is located two hours away from New York. Its design - echoes typical upstate "Shed" architecture
. But there are some differences - for example, orientirovnny south glass facade, through which housing receives maximum sunlight and heat. He replaces the street lighting in the evening.
The stone walls of the house are finished with wood. Gabled roofs without attic is considered optimal for the air circulation in the house. Under the soft roof - thick sandwich panels. The concrete floor radiant elements are built. Bedrooms are on the second floor - there is cooler, which has a beneficial effect on sleep
.
"Passive" home often confused with eco-houses, but this is not the same thing. The latter, incidentally, can be enormously energy-intensive. But there are, and happy coincidences. This home in southern Colorado - just one
. There is a whole "gentleman's set" of energy-efficient homes, large glass facade, concrete floors, solar panels on the roof ... The real highlight of this project - the thick walls of straw blocks. Both sides are covered with wire mesh and plastered, and the inside - textured clay mixture. The frame house is made of pillars and beams, and all the space between them is covered with straw. If completely honest, as a heat insulator straw - not the best material, but more environmentally friendly than you can imagine
.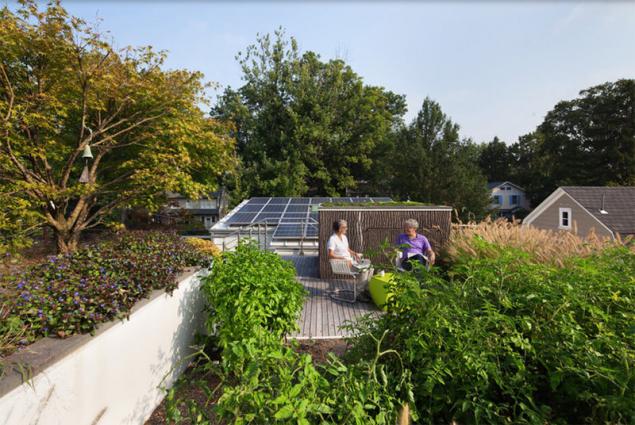
On the roof of the house a couple of Americans smashed the garden. Here the hosts are grown tomatoes, beets, turnips, leeks, lettuce, basil and other herbs, vegetables. Gardening season lasts about nine months of the year. In this step a couple of extravagant inspired not utter destitution, and concern for the environment. Bulk roof acts as an insulator - in the house warm in the winter, in the summer - cool. For watering the garden is rainwater that collects in the barrel Stormwater. And in the second half of the rooftop solar modules. But the real vine growing inside the house.

Damon Gray 10 years collecting wooden karkasniki in British Columbia. And by the time he decided to build his house, he saw for himself the tree should stay away. Mildew and mold in humid climates will shorten the life of wooden structures up to thirty years. And Damon has decided to build a house for the ages, in addition to reduce the electricity bill to zero.
The situation is more complicated that the owner refused to from the two-storey structure - and this is one of the most effective forms of "passive" houses. After experimenting with the plans, Damon stopped at the corner of the building design. In preparation, he found that if you change the angle of the house at 15 degrees, it improves energy efficiency by 25 percent.
The rooftop solar panels are located. Solid overhangs here too there is no coincidence - they do not give the house warm in the summer without further conditioning. Additional insulation for $ 4,000 promised a monthly 200-dollar savings on heating. In all the calculations and testing of materials from the owner took four year.
The best material in a humid climate proved to concrete. According to Damon, good insulation keeps the temperature in the building regardless of the weather outside. Humidity in the room is also constant - 45-50 percent
.
Simple but effective energy saving technology by French engineers. The glass facade of the house near Paris decorated folding panels made of bamboo. When sunlight is necessary to put in the room, the panels are removed, if needed shade - windows hidden behind bamboo siding. Wood paneling and modern windows keep the heat very well. The assembly is complemented by solar modules.
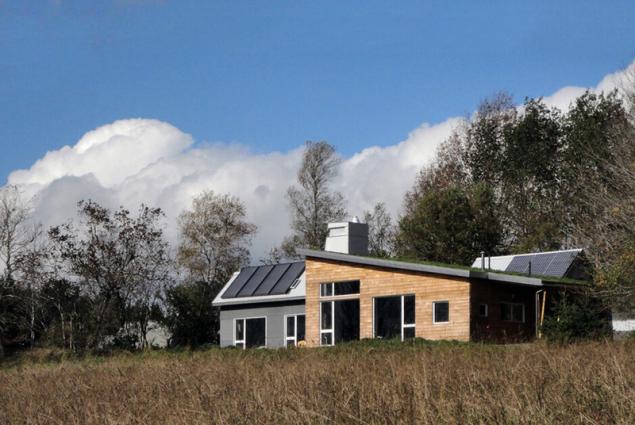

Once architects wife Kate Robertson and Jennifer Corson restored 200-year-old farmhouse in Nova Scotia and well studied area with spectacular views. Later, the owner of the land put up land (just over 18 hectares) on the sale of several plots. Kate and Jennifer, a long time do not hesitate to have acquired one of the largest sites. More on the project stage, the couple decided to build a house, independent of the overall network. Architects led not need, and not a particular consciousness, and professional gambling.
Part of the roof is made of energy-efficient green home, it is also the experience for experience. Special functionality, it can not be held - rain here a little, and more effective materials can be used for thermal insulation. Most just have a good roof is insulated and covered with metal sheets. Ibid located and solar photovoltaics and thermal panels - tanks with ice-glycol, which is heated by the sun and swirling, transfers heat hot-water tanks
. Another circuit with glycol pipes buried in the ground (it keeps a constant temperature of about 15 degrees Celsius) - it is used for the needs of ventilation: cools the incoming air in summer or heat in the winter. The frame house is insulated recycled newsprint (it took almost 7 tons!), Closed OSB-plates and unpretentious concrete panels. The wall thickness reaches 45 cm.
Charged solar missing five dark days. Standby generator uses a family of not more than three times a year.

In recent years, New Zealand students - future architects - take one award after the other in the field of sustainable construction. Wool, cane, recycled wood - it is not only they use in their experimental designs. The house in the photo is not made of the former freight container, as it may seem, but of the original SIP panels: metal layers sandwiched between a layer of insulation
. This project - reporting work of students 3 and 4 courses on "stand-alone housing for low-income families." The complex area of 104 square meters consists of two combined houses, each with two rooms. This team structure, which can easily relocate to another place. Cost of the complex amounted to 1400 dollars for energy-efficient buildings -for square meter is a little.
Inside the houses are decorated with plywood from inexpensive local pine. Ventilation in the house is a natural - for air circulation flaps meet, valves and shutters. Concrete floors in the house: this material accumulates heat during the day and slowly releases it at night. Particular attention New Zealanders traditionally pay zero waste home. All the used water from the house enters the tank for irrigation of small vegetable gardens.
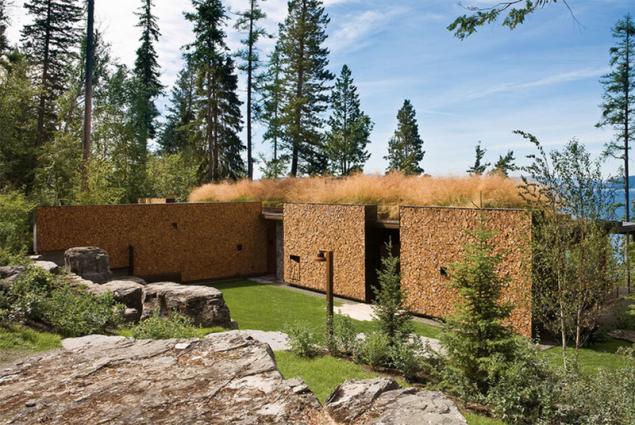

The architect of this grassy Arthur Andersson house once built a "passive" house without air conditioning in the hot Arizona, so plan your housing without central heating in the cool Montana was already possible to say, a matter of honor. In fact, it is a complex of buildings - the main house, guest house, home, living room and a separate summer kitchen. Unusual country residence situated on a hillside overlooking Lake Flathead Lake.
In winter, the main house is heated using a wood-burning stove to heat it is rarely necessary - saves an innovative insulation system walls. Sami walls consist of two layers of stone, between which put the waterproofing layer. Outside their cover design of steel frames, scored spruce and pine logs, blow dried in an oven. Woodpile stacked so tightly that act as fully breathable insulation. Well, the grass on the roof, not only is (along with the soil layer) for thermal and acoustic insulation of the roof, but also helps the buildings blend with the landscape.

Cottage in Butovo - an example of an eco-house with the "passive" features. In this house on 500 square meters of living architect Olga Makarova with her husband Vladimir, parents, two kids, a cat and a dog. Landlords argue that building a house cost in the end cheaper than buying 100-meter apartment in the capital. Architect advance understand what may turn into a life of several families under the same roof, so it has designed seven bathrooms and four kitchens (the smallest - in the basement)
. Huge window in the central part of the house - a central element of energy-saving strategy: even in the most sunny days, it fills the entire range of light. The house is oriented to the sun: a living room with a window on the floor looking south. Glass covered with reflective film which retains part of the UV rays, and retains heat. Instead of curtains in many rooms - plants. The materials used in the finishing of the maximum natural: larch, cork, plaster
. The house is built of brick, for the preservation of environmentally responsible heat basalt insulation, facade facing brick. Of the benefits of civilization - a boiler, gas, warm water floor. Yes, this is not "passive" house in its pure form, but in our climate, its energy efficiency is impressive. It is difficult to imagine what the bill came to the hosts for heating 500 "squares" with the help of electricity.
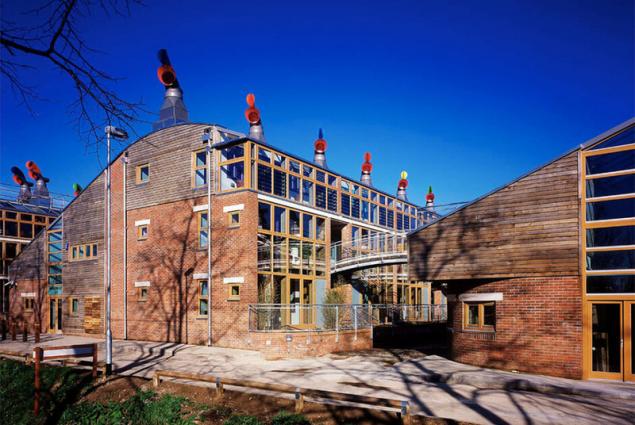

BedZED - a power efficient block in the London suburbs, the fruit of cooperation "green" architects and ambitious developers. 99 townhouses built according to all the principles of energy and resources: thick walls, excellent heat insulation, triple-glazed windows, re-use of building materials, landscaped terraces, etc. Colorful pipes on the roofs of houses - a ventilation outlets
. Due to the heat recovery system, none of the villas in this quarter does not heat the street - all the heat from the equipment and human activity goes towards heating. In the quarter, principally do not burn oil and gas boiler running on wood waste. Her one is enough for all 99 block sections - all thanks to the "passive" building technologies: savings in heating is 90 percent. Most of the electricity is generated by solar panels.

Australia - trendsetter in the world of energy-efficient construction, and this ski lodge in the mountains on the lake Krekenbek - a reference sample of the Australian "passive" houses. The ground floor is recessed into the hill: the land - a good heat insulator. Wide glass facades facing the sun - do not have to include the artificial light during the day. The floor is polished concrete, the day it absorbs heat from the sun, and at night gives.
In the concrete, in the case of heavy frosts, hidden water heating system running from the stove. Another distinctive feature of Australian houses in cold regions - parabolic roof. They protect from the wind, which is "dispersed" to 150 km / h.
Orientation meeting envy: this hut decorated with natural stone and teak, huge bath and sauna in the Japanese style - just an extension to rest. The main house is not visible, but it is close.

Australian neighbors with passion "face off" energy efficiency ratings of their homes. This house is owned by a family with two children, the most effective in your street (9 stars, the energy savings of about 80 percent). In addition to traditional methods of "passive" housing like rooflights and concrete floors, is involved and several original.
For example, the ventilation tube leaving a meter into the ground - make a U-turn under the lawn. Soil temperature in summer is lower than the air outside - it keeps it at the level of 15-17 degrees Celsius. The fan exhausts the warm air into the tube, it has returned a few degrees colder. This system allows the owners to do without air conditioning.
Another feature of the project - "reverse finish 'walls as if turned inside out, inside the brick remains in its original form, and closes the outside insulation, drywall, paneling or metal profile. This scheme reduces the thermal conductivity of the walls.

Germany - also a leading article "passive" building, with its recognizable handwriting is not satisfied with the hunt for the sunlight, focusing on the thermal insulation of walls, windows and doors. The walls of homes in Baden-Württemberg, for example, are decorated with rubber. Artificial rubber helps keep the heat in the building without additional heating. The building is essentially "semi-finished" - it is completely built in a factory and assembled on site from 136 items. All furniture is built.

Here is the first certified "passive" house in New York, one of the most energy efficient in the world. Architects assure that the building consumes 90 percent less energy than an average house the same square footage in these parts. The house is located two hours away from New York. Its design - echoes typical upstate "Shed" architecture
. But there are some differences - for example, orientirovnny south glass facade, through which housing receives maximum sunlight and heat. He replaces the street lighting in the evening.
The stone walls of the house are finished with wood. Gabled roofs without attic is considered optimal for the air circulation in the house. Under the soft roof - thick sandwich panels. The concrete floor radiant elements are built. Bedrooms are on the second floor - there is cooler, which has a beneficial effect on sleep
.

"Passive" home often confused with eco-houses, but this is not the same thing. The latter, incidentally, can be enormously energy-intensive. But there are, and happy coincidences. This home in southern Colorado - just one
. There is a whole "gentleman's set" of energy-efficient homes, large glass facade, concrete floors, solar panels on the roof ... The real highlight of this project - the thick walls of straw blocks. Both sides are covered with wire mesh and plastered, and the inside - textured clay mixture. The frame house is made of pillars and beams, and all the space between them is covered with straw. If completely honest, as a heat insulator straw - not the best material, but more environmentally friendly than you can imagine
.

On the roof of the house a couple of Americans smashed the garden. Here the hosts are grown tomatoes, beets, turnips, leeks, lettuce, basil and other herbs, vegetables. Gardening season lasts about nine months of the year. In this step a couple of extravagant inspired not utter destitution, and concern for the environment. Bulk roof acts as an insulator - in the house warm in the winter, in the summer - cool. For watering the garden is rainwater that collects in the barrel Stormwater. And in the second half of the rooftop solar modules. But the real vine growing inside the house.

Damon Gray 10 years collecting wooden karkasniki in British Columbia. And by the time he decided to build his house, he saw for himself the tree should stay away. Mildew and mold in humid climates will shorten the life of wooden structures up to thirty years. And Damon has decided to build a house for the ages, in addition to reduce the electricity bill to zero.
The situation is more complicated that the owner refused to from the two-storey structure - and this is one of the most effective forms of "passive" houses. After experimenting with the plans, Damon stopped at the corner of the building design. In preparation, he found that if you change the angle of the house at 15 degrees, it improves energy efficiency by 25 percent.
The rooftop solar panels are located. Solid overhangs here too there is no coincidence - they do not give the house warm in the summer without further conditioning. Additional insulation for $ 4,000 promised a monthly 200-dollar savings on heating. In all the calculations and testing of materials from the owner took four year.
The best material in a humid climate proved to concrete. According to Damon, good insulation keeps the temperature in the building regardless of the weather outside. Humidity in the room is also constant - 45-50 percent
.

Simple but effective energy saving technology by French engineers. The glass facade of the house near Paris decorated folding panels made of bamboo. When sunlight is necessary to put in the room, the panels are removed, if needed shade - windows hidden behind bamboo siding. Wood paneling and modern windows keep the heat very well. The assembly is complemented by solar modules.

Once architects wife Kate Robertson and Jennifer Corson restored 200-year-old farmhouse in Nova Scotia and well studied area with spectacular views. Later, the owner of the land put up land (just over 18 hectares) on the sale of several plots. Kate and Jennifer, a long time do not hesitate to have acquired one of the largest sites. More on the project stage, the couple decided to build a house, independent of the overall network. Architects led not need, and not a particular consciousness, and professional gambling.
Part of the roof is made of energy-efficient green home, it is also the experience for experience. Special functionality, it can not be held - rain here a little, and more effective materials can be used for thermal insulation. Most just have a good roof is insulated and covered with metal sheets. Ibid located and solar photovoltaics and thermal panels - tanks with ice-glycol, which is heated by the sun and swirling, transfers heat hot-water tanks
. Another circuit with glycol pipes buried in the ground (it keeps a constant temperature of about 15 degrees Celsius) - it is used for the needs of ventilation: cools the incoming air in summer or heat in the winter. The frame house is insulated recycled newsprint (it took almost 7 tons!), Closed OSB-plates and unpretentious concrete panels. The wall thickness reaches 45 cm.
Charged solar missing five dark days. Standby generator uses a family of not more than three times a year.

In recent years, New Zealand students - future architects - take one award after the other in the field of sustainable construction. Wool, cane, recycled wood - it is not only they use in their experimental designs. The house in the photo is not made of the former freight container, as it may seem, but of the original SIP panels: metal layers sandwiched between a layer of insulation
. This project - reporting work of students 3 and 4 courses on "stand-alone housing for low-income families." The complex area of 104 square meters consists of two combined houses, each with two rooms. This team structure, which can easily relocate to another place. Cost of the complex amounted to 1400 dollars for energy-efficient buildings -for square meter is a little.
Inside the houses are decorated with plywood from inexpensive local pine. Ventilation in the house is a natural - for air circulation flaps meet, valves and shutters. Concrete floors in the house: this material accumulates heat during the day and slowly releases it at night. Particular attention New Zealanders traditionally pay zero waste home. All the used water from the house enters the tank for irrigation of small vegetable gardens.

The architect of this grassy Arthur Andersson house once built a "passive" house without air conditioning in the hot Arizona, so plan your housing without central heating in the cool Montana was already possible to say, a matter of honor. In fact, it is a complex of buildings - the main house, guest house, home, living room and a separate summer kitchen. Unusual country residence situated on a hillside overlooking Lake Flathead Lake.
In winter, the main house is heated using a wood-burning stove to heat it is rarely necessary - saves an innovative insulation system walls. Sami walls consist of two layers of stone, between which put the waterproofing layer. Outside their cover design of steel frames, scored spruce and pine logs, blow dried in an oven. Woodpile stacked so tightly that act as fully breathable insulation. Well, the grass on the roof, not only is (along with the soil layer) for thermal and acoustic insulation of the roof, but also helps the buildings blend with the landscape.

Cottage in Butovo - an example of an eco-house with the "passive" features. In this house on 500 square meters of living architect Olga Makarova with her husband Vladimir, parents, two kids, a cat and a dog. Landlords argue that building a house cost in the end cheaper than buying 100-meter apartment in the capital. Architect advance understand what may turn into a life of several families under the same roof, so it has designed seven bathrooms and four kitchens (the smallest - in the basement)
. Huge window in the central part of the house - a central element of energy-saving strategy: even in the most sunny days, it fills the entire range of light. The house is oriented to the sun: a living room with a window on the floor looking south. Glass covered with reflective film which retains part of the UV rays, and retains heat. Instead of curtains in many rooms - plants. The materials used in the finishing of the maximum natural: larch, cork, plaster
. The house is built of brick, for the preservation of environmentally responsible heat basalt insulation, facade facing brick. Of the benefits of civilization - a boiler, gas, warm water floor. Yes, this is not "passive" house in its pure form, but in our climate, its energy efficiency is impressive. It is difficult to imagine what the bill came to the hosts for heating 500 "squares" with the help of electricity.

BedZED - a power efficient block in the London suburbs, the fruit of cooperation "green" architects and ambitious developers. 99 townhouses built according to all the principles of energy and resources: thick walls, excellent heat insulation, triple-glazed windows, re-use of building materials, landscaped terraces, etc. Colorful pipes on the roofs of houses - a ventilation outlets
. Due to the heat recovery system, none of the villas in this quarter does not heat the street - all the heat from the equipment and human activity goes towards heating. In the quarter, principally do not burn oil and gas boiler running on wood waste. Her one is enough for all 99 block sections - all thanks to the "passive" building technologies: savings in heating is 90 percent. Most of the electricity is generated by solar panels.
Tags
Personal development
psychology
women
men
relationships
life
happiness
harmony
love
children
money
wealth
success
See also
Lemonade around the world: as a refreshing in the summer heat on the other side of the globe.
How does a cup of coffee around the world
How to eat breakfast in the different countries of the world (50 photos)
How to celebrate Easter around the world
How does the hospital food around the world. You'll be amazed to discover the difference!
How are school lunches in different countries
Look like student dormitories in different countries
As in different countries held elections
That is what an apartment can be rented for $ 1,500 a month in different countries ... contrasts Wow!
Here's how to see the justice in the different countries of the world. The paintings, which opened my eyes to many things ...