17 major scientific discoveries of 2013.
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net
Over the past year much of humanity has reached 2013, there was a lot of important scientific discoveries - from the intergalactic neutrinos and invisible brain to create a tiny "organelles". Before you - the 17 most important scientific discoveries of the outgoing year.
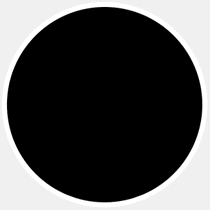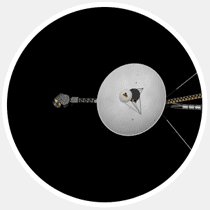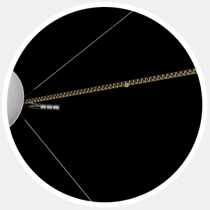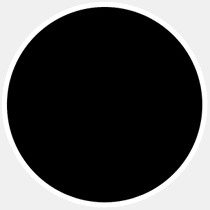
1. «Voyager 1" has gone beyond the solar system way out of the solar system can not be considered an ordinary achievement. For 36 years NASA spacecraft "Voyager 1" increases the distance between himself and the Sun, moving away from him at a speed of 17 km / s. Scientists knew that sooner or later, "Voyager 1" reaches the periphery of the heliosphere, which surrounds the solar system and determine its borders, but when he crosses this barrier, it is known was not there. After months of uncertainty, NASA in September this year, has made an official statement: "Voyager 1" is the first object created by man, which came out in interstellar space. " So, we are already there.
2. to open a short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) in the DNA of bacteria have their own version of the adaptive immune system, but as a CRISPR system is not aimed at the hostile your immune system protein antigens. Instead CRISPR grasps and removes specific DNA sequences using appropriate RNA strands. System CRISPR easily manipulated in January, scientists first reported about the removal, adding, activation and repression of target genes in human cells, mouse, rat, zebrafish, bacteria, fruit flies, yeast, nematodes and crops, showing tremendous opportunities for the application of the opening. For scientists looking for new tools is often the most important is the versatility and ease of use. CRISPR convenient to both sides, and many scientists believe that the discovery has the potential to revolutionize molecular biology.
3. The Milky Way is full of habitable worlds 76,425,088
In November, the astronomers said that 22% of stars similar to our Sun, the Milky Way has a potentially habitable planets around their orbits. Dimensions distant planets comparable to the Earth. This remarkable finding suggests that our galaxy may be more than two billion habitable planets, and the nearest such a planet may be just 12 light years from Earth. Perhaps there - a twin of the Earth? It is still unknown, but thanks to the telescope, "Kepler" we have all the data to find out, it remains only to analyze them. Perhaps his second home, we have already found.

4. interface brain-to-brain in February, researchers announced that they have successfully established a link between the brain two rats: the signals from the brain of a rat helped second rat to solve complex problems in real time, with the animals were on a distance of thousands of kilometers from each other. A few months later, such a link was established between the human brain and rats, but only a month later, scientists published the results of the first successful experiment of establishing communication between the brains of two people. The era of unification of minds does not seem far off.
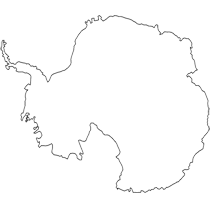
5. There is life on the edge of the world in the lake Uillans is life. Millions of years of tiny lake of liquid water hidden at a depth of hundreds of meters beneath the Ross Ice Shelf in Antarctica is isolated from the outside world, and scientists, and to explore its depths there was no way. This year, a group of researchers led by John Prisca glaciologist at the University of Montana was able to drill a tunnel to the lake Uillans and find life - as Prisca and his colleagues were the first people in history who discovered living organisms in the lake on the edge of the world.
6. The doctors cured of HIV child born sick in March the doctors announced the grand event in medicine - the child was able to cure HIV infection. Dr. Deborah Persaud presented a report on this at the 20th Annual Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections.
8. Neurologists made invisible brain new technology allows scientists to make fully transparent medulla. It has become one of the most important achievements in the field of neuroanatomy in recent decades and it is easy to understand why.

7. The newly discovered skull can reduce the evolutionary tree of humanity beautifully preserved skull age of 1, 8 million years old, found in Dmanisi, Georgia, may be evidence that the evolutionary tree creatures of the genus Homo may have far fewer branches, than previously thought. In a report published in October, it said that a team of researchers led by David Lordkipanidze Georgian anthropologist has found first in the history perfectly preserved skull of a hominid. If you compare the skull with four other skulls found nearby, it becomes clear that the earliest known members of the branches of Homo (Homo habilis, Homo Rudolfensis and Homo erectus), perhaps nothing from each other do not differ. It is likely that they were all part of the same developing branches eventually led to modern humans.
9. The rover «Curiosity» confirmed that Mars once might have life 19,991,410
In March, NASA scientists have published perhaps the most compelling evidence to date that the Red Planet could be home to life. Earlier this year, «Curiosity» drilled several samples of sedimentary rocks near the old riverbed in the crater Gale. In this area there are a series of lines, similar to the dry river bed that can testify to the fact that the planet once had water. Using the on-board computers of the rover, NASA scientists have analyzed these samples for some of the critical elements necessary for life, including sulfur, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus and carbon. Currently, the rover moves to its main scientific objective - Mount Eolida (aka Mount Sharp), five kilometers high, located in the center of the crater Gale. There he will try to find other proofs of the existence of life.

10. The Death of anonymity genome Few things in the world can be more personal than your DNA. For this reason, in projects such as the database of the human genome, we have always respected the privacy of the participants. By studying the individual characteristics of individuals donated their DNA samples, the researchers maintain standards "genomic anonymity." Those days are now officially over. In January, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have shown that the similarity of volunteers, donating personal data - its genome - can only be determined at the public availability of information. Lead researcher on the project Yaniv Erlich told how this method works, explained the implications of his discovery, and why it can change our attitude to genetic data.

11. The researchers discovered neutrinos from another galaxy Physics Observatory "Ice Cube" at the South Pole this year, was drilled in the Antarctic glacier hole depth of 2, 5 km and took it 28 neutrinos - those mysterious and extremely powerful subatomic particles that pass right through solid matter. These particles may have been born outside our solar system, it is possible that outside of our galaxy. Perhaps for this discovery, researchers will receive the Nobel Prize.
12
DNA extracted from the well-preserved 400,000-year-old femur complicates our understanding of human evolution. First, anatomists thought that the bone belonged to the Neanderthal, but further study led to the assumption that the bone belonged to even his predecessor, and the representative of a separate branch of the hominid, known under the name denisovan. Conclusions leading anthropologists are redefining the past several hundred thousand years of human evolution. It is possible that there are many extinct human populations that may interbreed and thus exchanging DNA.

13

14

15
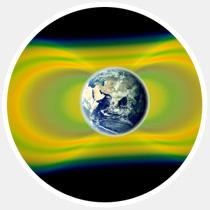
16
17
In May, the researchers got stem cells from cloned human embryos. This controversial new technology may lead to new treatments for diseases such as Parkinson's disease or diabetes - as well as a step to bring us closer to human reproductive cloning.
via factroom.ru

1. «Voyager 1" has gone beyond the solar system way out of the solar system can not be considered an ordinary achievement. For 36 years NASA spacecraft "Voyager 1" increases the distance between himself and the Sun, moving away from him at a speed of 17 km / s. Scientists knew that sooner or later, "Voyager 1" reaches the periphery of the heliosphere, which surrounds the solar system and determine its borders, but when he crosses this barrier, it is known was not there. After months of uncertainty, NASA in September this year, has made an official statement: "Voyager 1" is the first object created by man, which came out in interstellar space. " So, we are already there.

2. to open a short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) in the DNA of bacteria have their own version of the adaptive immune system, but as a CRISPR system is not aimed at the hostile your immune system protein antigens. Instead CRISPR grasps and removes specific DNA sequences using appropriate RNA strands. System CRISPR easily manipulated in January, scientists first reported about the removal, adding, activation and repression of target genes in human cells, mouse, rat, zebrafish, bacteria, fruit flies, yeast, nematodes and crops, showing tremendous opportunities for the application of the opening. For scientists looking for new tools is often the most important is the versatility and ease of use. CRISPR convenient to both sides, and many scientists believe that the discovery has the potential to revolutionize molecular biology.
3. The Milky Way is full of habitable worlds 76,425,088
In November, the astronomers said that 22% of stars similar to our Sun, the Milky Way has a potentially habitable planets around their orbits. Dimensions distant planets comparable to the Earth. This remarkable finding suggests that our galaxy may be more than two billion habitable planets, and the nearest such a planet may be just 12 light years from Earth. Perhaps there - a twin of the Earth? It is still unknown, but thanks to the telescope, "Kepler" we have all the data to find out, it remains only to analyze them. Perhaps his second home, we have already found.

4. interface brain-to-brain in February, researchers announced that they have successfully established a link between the brain two rats: the signals from the brain of a rat helped second rat to solve complex problems in real time, with the animals were on a distance of thousands of kilometers from each other. A few months later, such a link was established between the human brain and rats, but only a month later, scientists published the results of the first successful experiment of establishing communication between the brains of two people. The era of unification of minds does not seem far off.

5. There is life on the edge of the world in the lake Uillans is life. Millions of years of tiny lake of liquid water hidden at a depth of hundreds of meters beneath the Ross Ice Shelf in Antarctica is isolated from the outside world, and scientists, and to explore its depths there was no way. This year, a group of researchers led by John Prisca glaciologist at the University of Montana was able to drill a tunnel to the lake Uillans and find life - as Prisca and his colleagues were the first people in history who discovered living organisms in the lake on the edge of the world.

6. The doctors cured of HIV child born sick in March the doctors announced the grand event in medicine - the child was able to cure HIV infection. Dr. Deborah Persaud presented a report on this at the 20th Annual Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections.

8. Neurologists made invisible brain new technology allows scientists to make fully transparent medulla. It has become one of the most important achievements in the field of neuroanatomy in recent decades and it is easy to understand why.

7. The newly discovered skull can reduce the evolutionary tree of humanity beautifully preserved skull age of 1, 8 million years old, found in Dmanisi, Georgia, may be evidence that the evolutionary tree creatures of the genus Homo may have far fewer branches, than previously thought. In a report published in October, it said that a team of researchers led by David Lordkipanidze Georgian anthropologist has found first in the history perfectly preserved skull of a hominid. If you compare the skull with four other skulls found nearby, it becomes clear that the earliest known members of the branches of Homo (Homo habilis, Homo Rudolfensis and Homo erectus), perhaps nothing from each other do not differ. It is likely that they were all part of the same developing branches eventually led to modern humans.
9. The rover «Curiosity» confirmed that Mars once might have life 19,991,410
In March, NASA scientists have published perhaps the most compelling evidence to date that the Red Planet could be home to life. Earlier this year, «Curiosity» drilled several samples of sedimentary rocks near the old riverbed in the crater Gale. In this area there are a series of lines, similar to the dry river bed that can testify to the fact that the planet once had water. Using the on-board computers of the rover, NASA scientists have analyzed these samples for some of the critical elements necessary for life, including sulfur, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus and carbon. Currently, the rover moves to its main scientific objective - Mount Eolida (aka Mount Sharp), five kilometers high, located in the center of the crater Gale. There he will try to find other proofs of the existence of life.

10. The Death of anonymity genome Few things in the world can be more personal than your DNA. For this reason, in projects such as the database of the human genome, we have always respected the privacy of the participants. By studying the individual characteristics of individuals donated their DNA samples, the researchers maintain standards "genomic anonymity." Those days are now officially over. In January, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have shown that the similarity of volunteers, donating personal data - its genome - can only be determined at the public availability of information. Lead researcher on the project Yaniv Erlich told how this method works, explained the implications of his discovery, and why it can change our attitude to genetic data.

11. The researchers discovered neutrinos from another galaxy Physics Observatory "Ice Cube" at the South Pole this year, was drilled in the Antarctic glacier hole depth of 2, 5 km and took it 28 neutrinos - those mysterious and extremely powerful subatomic particles that pass right through solid matter. These particles may have been born outside our solar system, it is possible that outside of our galaxy. Perhaps for this discovery, researchers will receive the Nobel Prize.
12
DNA extracted from the well-preserved 400,000-year-old femur complicates our understanding of human evolution. First, anatomists thought that the bone belonged to the Neanderthal, but further study led to the assumption that the bone belonged to even his predecessor, and the representative of a separate branch of the hominid, known under the name denisovan. Conclusions leading anthropologists are redefining the past several hundred thousand years of human evolution. It is possible that there are many extinct human populations that may interbreed and thus exchanging DNA.

13

14

15

16
17
In May, the researchers got stem cells from cloned human embryos. This controversial new technology may lead to new treatments for diseases such as Parkinson's disease or diabetes - as well as a step to bring us closer to human reproductive cloning.
via factroom.ru
Tags
See also
Circus
Free science. NASA's scientific work laid out in the open access
The best scientific photography 2013
The greatest scientific discoveries of 2014.
10 recent cosmic discoveries that no one can explain
European Centre for Nuclear Research
10 most important discoveries in biology
TOP 3 space science discoveries of 2013
The brain is not a computer!