Wing mechanization
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net
Many of those who flew on a cruise ship, and sat by the window next to the airplane wing saw before take-off (or landing) wing like "crushes". From the rear edge of the "crawl" the new plane, slightly curving down. And when the run after landing on the upper surface of the wing rises something like a nearly vertical plates. This is the mechanization of the wing elements.

Man has always sought to fly faster. And that he gets:-). "Higher, faster - always!" Speed - the subject of aspirations and a stumbling block. At an altitude quickly - it's good. But during takeoff and landing anyway. Most take-off speed is not necessary. Until her plane (especially if it's a big heavy liner) dials, no band is not enough, plus restrictions on the strength of the chassis. Landing speed especially should not be very large. Or chassis destroyed or crew piloting can not cope with. And running after landing will be rather big, which collect such large airfields:-).
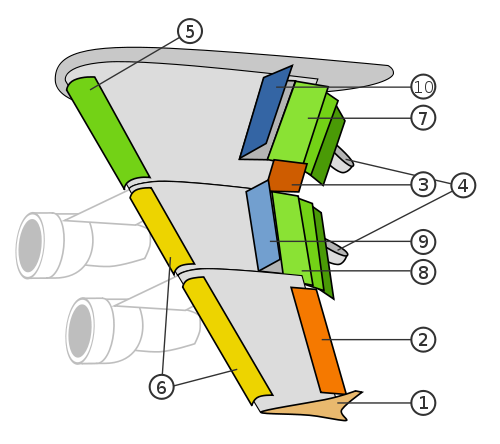
Here man and his handy-savvy trick:-). The solution was found, in general, without much difficulty. This runway mechanization of the wing.

Mechanization includes flaps, slats, spoilers, spoilers, flaperons active boundary layer control system and so on. E., For clarity, we give a well-known figure:

FLAPS
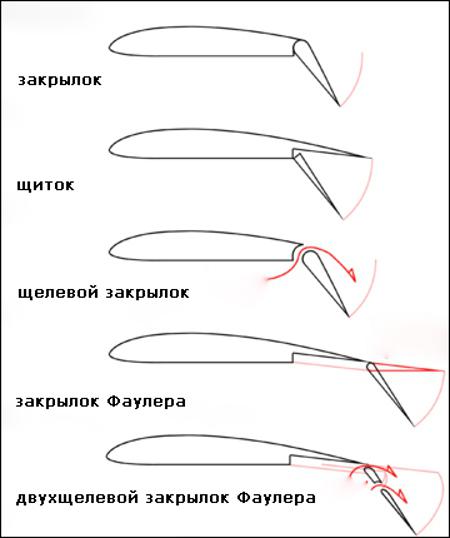
Flaps - the first invented varieties of high-lift devices, they are also the most effective.

Flaps are always on the wing trailing edge and always fall down and, moreover, may be made earlier. They help to improve our plane load-bearing capacity of the wing during takeoff, landing, climb and other maneuvering. The working language act as sails during takeoff and landing when the parachute))
Depending on the type of aircraft, different schemes are used:

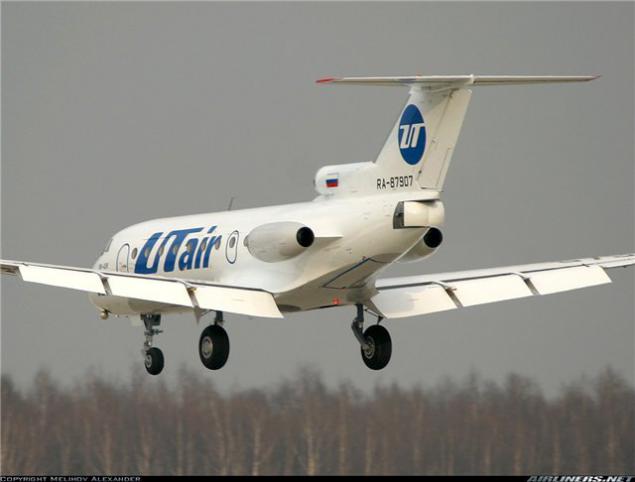
Yak-40 landing with flaps:

Slats
The next element of mechanization of the wing - the slats. To extend the capabilities of the aircraft flying at high angles of attack (and therefore at a lower rate) and slats were invented.
Normal slat slit in the issued state:
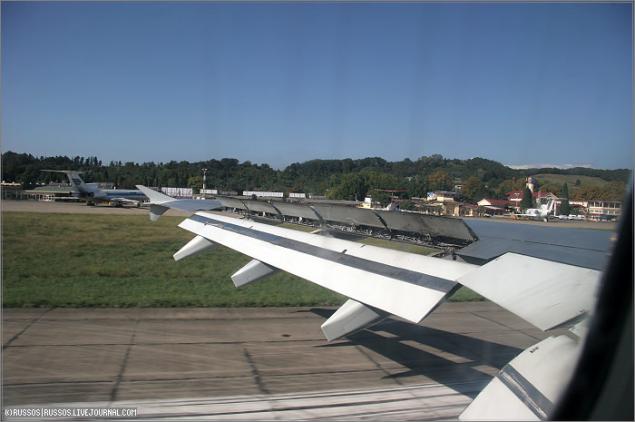

You've probably seen the planes after leaving the band does not smoothly rise up and do it intensively, rather abruptly nose in the air. This is just a plane with existing slats.

Design and principle of operation similar to the slats slotted flaps, only set, of course, on the front edge of the wing.
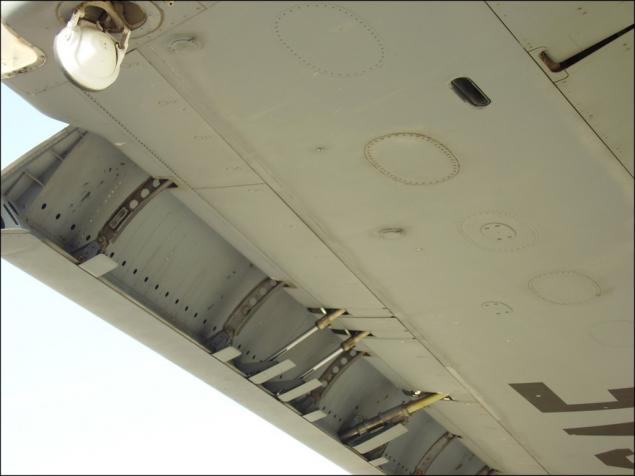
Tu-154 taxiing, issued with slats:
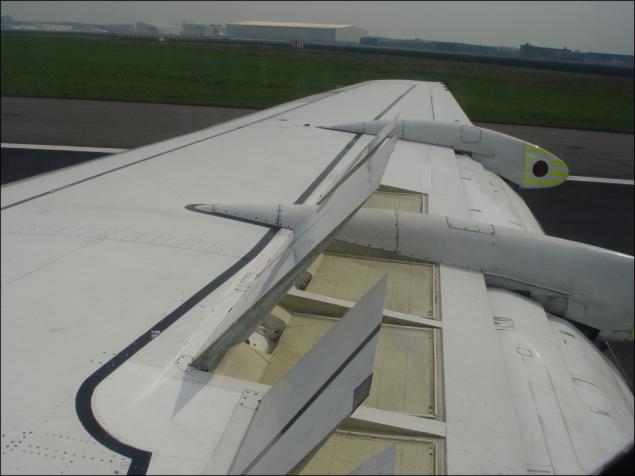

Slats and flaps usually work in the complex. However, for different types of aircraft may be specific modes of their separate work. Such as air refueling.
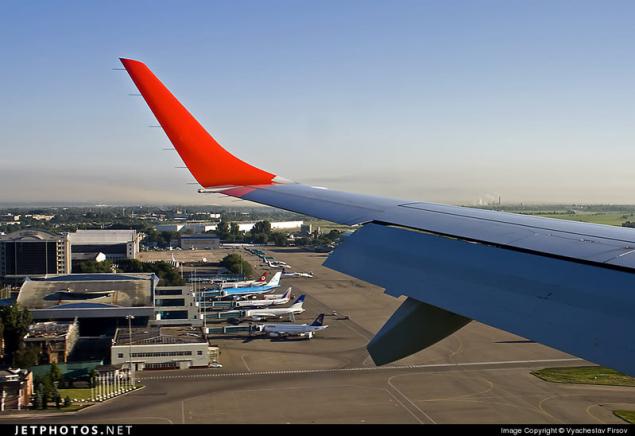

That's probably all of the elements related to the concept of landing mechanization of the wing. These elements allow the aircraft to feel confident on takeoff and landing, and at the same time is quite impressive (I wonder) look

Aileron
And now for the remaining elements of the wing shown in the figure at the beginning of stati.Elerony.
I had them to lift devices do not. This cross-bodies aircraft control, ie control via heel. They operate differentially. One wing up, down to the second. However, there is such a thing as flaperons, slightly "rodnyaschee":-) ailerons with flaps. This so-called "drooping ailerons." They are not only deflected to the opposite side, but, if necessary and also to one. In this case they act as flaps. They are used often, mostly on light aircraft.
Spoilers
The next element - spoilers. This planar elements on the upper wing surface, which are raised (deflected) to the flow. Thus inhibition of this flow occurs, as a consequence of an increase in pressure on the upper surface of the wing, and further, it is understood that reducing the lift of the wing. Spoilers are sometimes called authorities direct lift control.
Slowing spoilers:
Depending on the destination, and the surface area of the console, its location on the wing, and so on. D. Divided into spoilers spoilers and ailerons, spoilers
The effect of the interceptors used in the process of piloting and for braking. In the first case they work (rejected) paired with ailerons (those that deviate upwards) and aileron-called spoilers. An example of such aircraft controls - TU-154, B-737.
737. Powered left aileron-spoiler for the elimination of the right heel:
In the second case, simultaneous release spoilers allows you to change the vertical speed of the aircraft without changing the pitch angle (ie, without dropping his nose). In this case, they operate as brakes and air called spoilers. SPOILERS commonly used even after landing at the same time Revesz thrust (of course, if there is one:-)). Their main task in this case quickly reduce the lift of the wing and thus squeeze the wheel to the tarmac to be able to effectively inhibit the wheel brakes.
Issued spoilers (planting):
Wingtips
Wingtips are used to increase the effective wing span, reducing the drag created by breaking at the end of the swept wing vortex and, as a consequence, increasing the lifting force on the wing tips. Also, the ending can increase the elongation of the wing, almost no change in its scope.
The use of winglets can improve fuel efficiency in aircraft or flight range from gliders. Currently, the same types of aircraft may have different variants endings.
Here in brief is the mechanization of the wing. It vkrattse.Na fact, this topic is much broader.
If you want to show off your erudition in a narrow circle, you know! most modern aircraft - one wing! A left and right is hemipteran! ))
But today I have too much so occupy your attention. I think that is still to come.

Man has always sought to fly faster. And that he gets:-). "Higher, faster - always!" Speed - the subject of aspirations and a stumbling block. At an altitude quickly - it's good. But during takeoff and landing anyway. Most take-off speed is not necessary. Until her plane (especially if it's a big heavy liner) dials, no band is not enough, plus restrictions on the strength of the chassis. Landing speed especially should not be very large. Or chassis destroyed or crew piloting can not cope with. And running after landing will be rather big, which collect such large airfields:-).

Here man and his handy-savvy trick:-). The solution was found, in general, without much difficulty. This runway mechanization of the wing.

Mechanization includes flaps, slats, spoilers, spoilers, flaperons active boundary layer control system and so on. E., For clarity, we give a well-known figure:


FLAPS
Flaps - the first invented varieties of high-lift devices, they are also the most effective.

Flaps are always on the wing trailing edge and always fall down and, moreover, may be made earlier. They help to improve our plane load-bearing capacity of the wing during takeoff, landing, climb and other maneuvering. The working language act as sails during takeoff and landing when the parachute))
Depending on the type of aircraft, different schemes are used:

Yak-40 landing with flaps:

Slats
The next element of mechanization of the wing - the slats. To extend the capabilities of the aircraft flying at high angles of attack (and therefore at a lower rate) and slats were invented.
Normal slat slit in the issued state:

You've probably seen the planes after leaving the band does not smoothly rise up and do it intensively, rather abruptly nose in the air. This is just a plane with existing slats.

Design and principle of operation similar to the slats slotted flaps, only set, of course, on the front edge of the wing.
Tu-154 taxiing, issued with slats:

Slats and flaps usually work in the complex. However, for different types of aircraft may be specific modes of their separate work. Such as air refueling.

That's probably all of the elements related to the concept of landing mechanization of the wing. These elements allow the aircraft to feel confident on takeoff and landing, and at the same time is quite impressive (I wonder) look

Aileron
And now for the remaining elements of the wing shown in the figure at the beginning of stati.Elerony.
I had them to lift devices do not. This cross-bodies aircraft control, ie control via heel. They operate differentially. One wing up, down to the second. However, there is such a thing as flaperons, slightly "rodnyaschee":-) ailerons with flaps. This so-called "drooping ailerons." They are not only deflected to the opposite side, but, if necessary and also to one. In this case they act as flaps. They are used often, mostly on light aircraft.
Spoilers
The next element - spoilers. This planar elements on the upper wing surface, which are raised (deflected) to the flow. Thus inhibition of this flow occurs, as a consequence of an increase in pressure on the upper surface of the wing, and further, it is understood that reducing the lift of the wing. Spoilers are sometimes called authorities direct lift control.
Slowing spoilers:
Depending on the destination, and the surface area of the console, its location on the wing, and so on. D. Divided into spoilers spoilers and ailerons, spoilers
The effect of the interceptors used in the process of piloting and for braking. In the first case they work (rejected) paired with ailerons (those that deviate upwards) and aileron-called spoilers. An example of such aircraft controls - TU-154, B-737.
737. Powered left aileron-spoiler for the elimination of the right heel:
In the second case, simultaneous release spoilers allows you to change the vertical speed of the aircraft without changing the pitch angle (ie, without dropping his nose). In this case, they operate as brakes and air called spoilers. SPOILERS commonly used even after landing at the same time Revesz thrust (of course, if there is one:-)). Their main task in this case quickly reduce the lift of the wing and thus squeeze the wheel to the tarmac to be able to effectively inhibit the wheel brakes.
Issued spoilers (planting):
Wingtips
Wingtips are used to increase the effective wing span, reducing the drag created by breaking at the end of the swept wing vortex and, as a consequence, increasing the lifting force on the wing tips. Also, the ending can increase the elongation of the wing, almost no change in its scope.
The use of winglets can improve fuel efficiency in aircraft or flight range from gliders. Currently, the same types of aircraft may have different variants endings.
Here in brief is the mechanization of the wing. It vkrattse.Na fact, this topic is much broader.
If you want to show off your erudition in a narrow circle, you know! most modern aircraft - one wing! A left and right is hemipteran! ))
But today I have too much so occupy your attention. I think that is still to come.
Tags
See also
The most desperate landing in history
The aircraft, designed for unusual purposes
Teen flown in a wing of Boeing-737 can amputate hands
Experienced pilot
25 Unusual aircraft
Little-known Soviet aircraft
How to hijack planes from the Soviet Union (8 photos)
Vnukovo crashed passenger aircraft Tu-204 (10 pics + 2 video)
Antennae lightning rods on the aircraft (11 photos)
Loft and Repo
















