Robots in medicine
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net
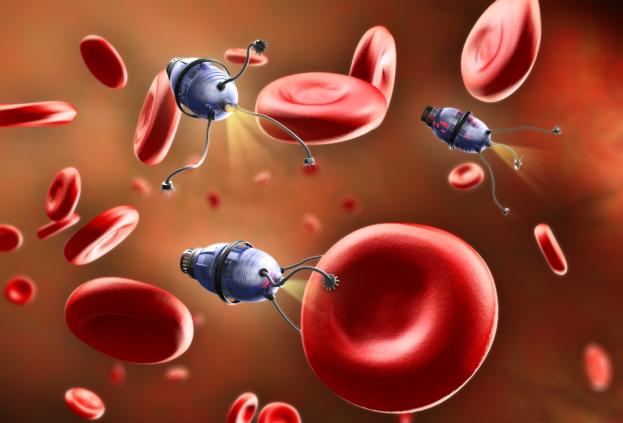
Today, research groups around the world trying to find the concept of using robots in medicine. Although correct, perhaps, to say "have hit upon." Judging by the number of development and interest of various research groups, it can be argued that the main direction was the establishment of medical micro-robots. This may also include robots and with the prefix "nano". And the first successes in this area have been made recently, only eight years ago.
In 2006 a group of researchers led by Silvana Martel first in the world held a successful experiment by running a tiny robot the size of a ball from a pen into the carotid artery of live pigs. At the same time the robot moves on all assigned "Waypoints". And over the past few years since mikrorobototehnika some progress forward.
One of the main goals for engineers today is to create medical robots that will be able to move not only on major arteries, but also in a relatively narrow blood vessels. This would allow for complex treatments without such traumatic surgery.
But this is not the only potential advantage of micro-robots. In the first place, they would be useful in the treatment of cancer, specifically delivering the drug directly to the malignancies. The value of such a possibility is difficult to overestimate: the chemotherapy drugs are given through a drip, dealing a severe blow to the body. In fact, it is a strong poison that affects multiple internal organs, and for the company, the tumor itself. This compares with a carpet bombing to destroy the small single target.
The task of creating such microrobots located at the junction of a number of scientific disciplines. For example, from the point of view of physics - how to make such a small object to move independently in a viscous liquid, which for him is the blood? From the point of view of engineering - how to provide the robot with energy and how to track the movement of the body of a tiny object? From the point of view of biology - the materials used for the manufacture of robots so that they do no harm to the human body? And ideally, the robots must be biodegradable, it was not necessary yet to solve the problem of their withdrawal from the body.
One example of how micro-robots can "contaminate" the patient's body is "bioraketa».
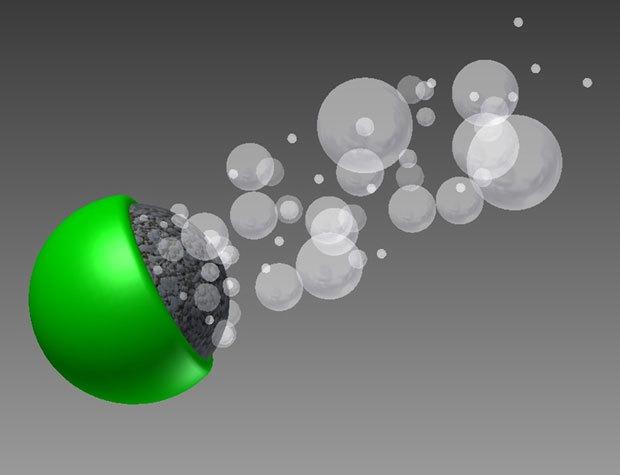
This embodiment is a microrobot titanium core, surrounded by a sheath of aluminum. Robot 20 microns diameter. The aluminum reacts with water in the course of which the surface of the shell formed hydrogen bubbles which push the whole construction. In water, this "bioraketa" floats in a second distance equal to its diameter 150. This can be compared to a man two meters tall, which is a second swims 300 meters, 12 swimming pools. Operates a chemical engine about 5 minutes by the addition of gallium, reduces the intensity of the formation of the oxide film. That is, the maximum cruising range of about 900 mm in water. The direction of movement of the robot is set by an external magnetic field, and you can use it to spot drug delivery. But only after drying out "charge", in a patient would be a scattering microspheres with an aluminum shell, which is not beneficial to the human body, as opposed to biologically neutral titanium.
Micro-robots have to be so small that simply scaled to the desired size traditional technologies will not work. No standard parts suitable size also did not produce. And even if it were made, they simply would not have come to such specific needs. And because the researchers, as it has many times in the history of inventions, seeking inspiration from nature. For example, the same bacteria. At the micro, and the more the nanoscale are completely different physical laws. In particular, water is a very viscous liquid. Therefore it is necessary to use other engineering solutions for the movement of micro-robots. Bacteria often solve this problem with the help of cilia.
Earlier this year, a group of researchers from the University of Toronto has created a prototype microrobot length of 1 mm from the external magnetic field and is equipped with two grippers. The developers managed to use it to build a bridge. Also this robot can be used not only for drug delivery, but also for the mechanical repair of tissue in the circulatory system and organs.
Muscular robots h4> Another interesting trend in mikrorobototehnike - robots, driven by muscles. For example, there is such a project: electricity stimulated muscle cell, to which is attached a robot whose "backbone" is made of hydrogel.
This system essentially replicates the natural solution occurring in many mammalian organisms. For example, in the human body muscle contraction is transmitted through the bones of the tendon. This Biorobot when the cell is reduced under the influence of electricity, the "backbone" of bends and crossbars that serve as legs, attracted to each other. If one of them is in flexion "ridge" is moved a shorter distance, the robot moves toward this "foot».
There is another vision of what should be the medical micro-robots: soft, repetitive forms of various living creatures. For example, is such a robo-bee (RoboBee).
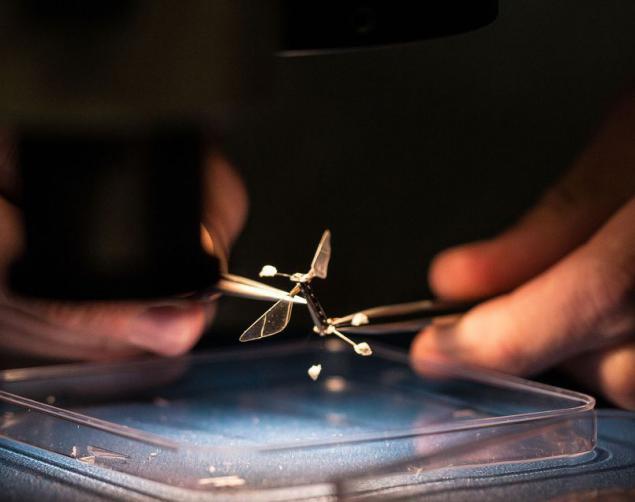

However, it is not intended for medical purposes, and for a number of others: pollination, search and rescue, detection of toxic substances. Authors of the project, of course, not blindly copy the anatomical features of the bees. Instead, they carefully analyze all kinds of "design" of organisms of different insects, adapting and implementing them in the mechanics.
Or another example of the use of naturally occurring "structures" - microrobot in a bivalve. He moves with the help of flapping "wings", thus creating a jet stream. At a rate of about 1 mm, it can float within the human eyeball. Like most other medical robots, the "clam" as an energy source uses an external magnetic field. But there is an important difference - it just gets the energy to move, the field itself it does not move, unlike most other types of micro-robots.
Big robots h4> Of course, only one microrobots park is not limited to medical equipment. In science fiction movies and books medical robots are usually presented in the form of replacement surgeon man. Like, it's kind of a big device that quickly and accurately produce all kinds of surgical manipulations. It is not surprising that this idea was implemented one of the first. Of course, modern surgical robots are not able to replace the whole person, but stitching them already quite trust. They are also used as an extension of the surgeon's hands as paddles.
However, the medical community does not cease debate about the use of such machines. Many experts are of the opinion that the особых benefits such robots do not give , and due to its high price существенно increase the cost of medical services . On the other hand, there is a исследование, according to which patients with prostate cancer who underwent surgical operation with a robot assistant in the future requires less intensive use of hormonal drugs and radiotherapy. In general, it is not surprising that the efforts of many scientists were aimed at the creation of micro-robots.
Interesting project is Robonaut (Robonaut), telemedicine robot designed to assist astronauts. This is still a pilot project, but this approach can be used not only to provide such an important and expensive in training people how astronauts. Telemedicine robots can be used to assist in various remote areas. Of course, it would be appropriate only if it would be cheaper to install in the infirmary of a deaf taiga or mountain settlement robot than to keep a paramedic on the payroll.
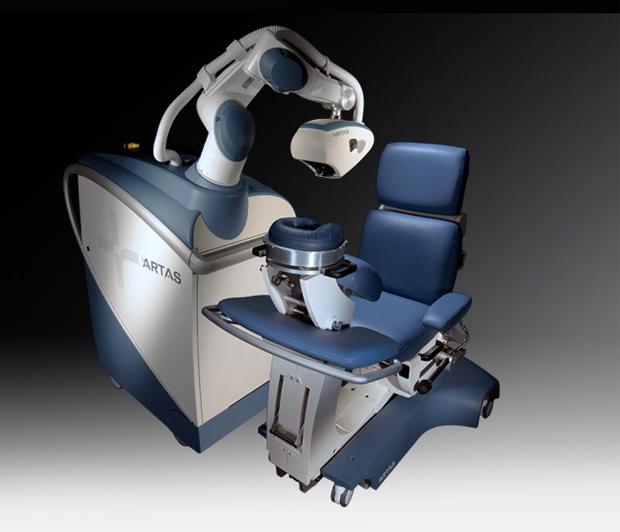
And this medical robot even more highly specialized, it is used to treat baldness. ARTAS is engaged in automatic "digging" the hair follicles of the scalp of the patient, based on high-resolution photos. Then the doctor-hand man introduces "harvest" in the bald areas.
Still, the world of medical robots are not as monotonous as it may seem inexperienced person. Moreover, it is actively growing, comes the accumulation of ideas, experimental results, looking for the most effective approaches. And who knows, maybe even in our lifetime the word "surgeon" shall mean the doctor is not with a scalpel, and a jar of micro-robots, which will be enough to swallow or introduce drip.
Source: geektimes.ru/company/asus/blog/242432/
Tags
See also
10 humanoid robots created in the likeness of human abilities and emotions
Technology, change the order of things
Test drive the robot vacuum cleaners
Photos from the opening of the fighting robots "Bronebot 2016"
Robot waiters have caused the closure of several restaurants in China
SAW robot crawls, climbs and swims with only one engine
Robot chef prepares recipes from the Internet!
Robots-customs officers will identify the contraband
Robot octopus floats in the open sea
The Japanese have created a robot that warns about the unpleasant mouth odor