How to build a spacecraft without leaving the office
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net
Sputnik DX1, born to be the first private spacecraft Russia, late for this title, but for the development company he will always be the firstborn. Around the year it was created, more than six months is expected to launch, and finally took his place in the rocket "Soyuz 2.1b».
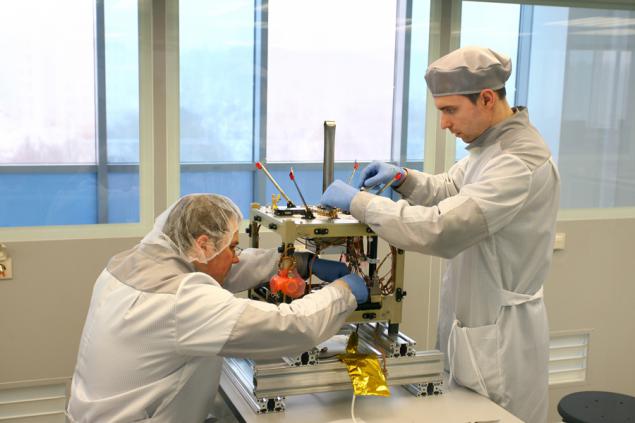

What you need to build your spacecraft? What challenges have to be solved? How much it all cost? Answers to these questions have to find up to the moment when the satellite was sent to Baikonur.
Many of the "Aerospace Dahuria" has already had experience creating spacecraft and were ready to go, but in order to form a cohesive team was required to pass along all stages of the spacecraft. Only shareable positive and negative experiences, having the entire process from concept to launch and operation, it is safe to talk about the company's willingness to further achievements. It was, perhaps, the main motive of creating DX1. But the important role played and the more prosaic factors: it was necessary to write and test the software system, ready to use on other satellites of the company; earn chain suppliers and subcontractors; prepare the assembly site.
Typically, satellites are created for specific tasks or orders. The company does not have those, so decided to develop a universal platform based on the possibility of launching a satellite Roscosmos "Meteor-M №2». Immediately laid the capabilities of this platform to implement projects as the company and to order. When choosing a platform concept based on a number of parameters:
1) weight up to 100 kg - the so-called Class "microsatellites»;
2) scalability - the ability to change the dimensions of the platform, without changing the basic elements and avionics, and as a consequence - the total software;
3) a wide range of applications - fitting of precision targeting platform that allows the satellites, for example, to capture images of the Earth's surface, or to carry out astrophysical problems.

The result was a draft DX1 - «Dauriya pilot first." In order not to run a simple technological demonstrator, equipped with a satellite signal receiving unit AIS - so he got a commercial application and the possibility of partial or full cost recovery. But this device must confirm the ability of exceeding the needs of the payload.
AIS unit energy consumption is not high, which allowed to do without opening the solar panels. This simplified the design, operation and management easier. But even so, the satellite is able to produce energy is three times more than he really needed.
Onboard radio operates in two bands: VHF and S. Obtaining permission to use them over the territory of Russia took almost as much as the creation of the device.
Main specifications DX1 seen from the table:
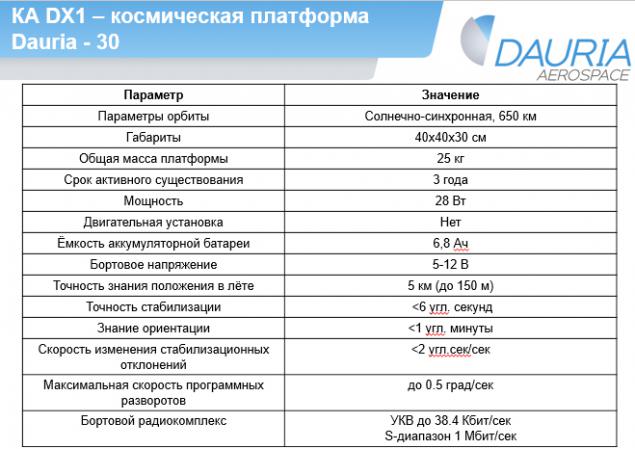
Ranking in orbit up to hundreds of meters, and the pointing accuracy of up to 6 seconds of arc - a characteristic suitable for shooting the surface of the Earth or planetary astronomy. Such opportunities laid for the future, with the expectation of future challenges.
Birth unit began with an assessment of what to offer the modern world industry. Traveled bunch exhibitions and forums worldwide. Looking for industrial grade components, ie, suitable for use in industry in the world. Space or military components are orders of magnitude more expensive, contrary to the ideology of the planned business. And with the advent of sanctions only added to the difficulties.
But now, and industrial electronics capable of performing the task space. Actually, do not stop using its state-owned companies and the Russian Space Agency. On the "Phobos-Grunt" it did not work, but in the near-Earth space satellites in "non-space" components work up to ten years. Roscosmos enjoys the electronics because there is simply no other: its microelectronics are often not ready to offer necessary and foreigners «Space" and "Military» a > just do not sell.
"Dauriya" consciously goes to "industrialize" considering additional methods of protection in space: a thick layer of aluminum shielding, redundancy, hardware and software.
As a result, on-board machine DX1 looked like a piece of the tank, but in general the satellite turned out pretty easy, for its size - 22 kg. (Joke about positive buoyancy). Filling the onboard computer is already flying practice on an experimental satellite NASA.
The architecture is based on a satellite carrying an aluminum frame, and the walls act as solar panels. Devices are mounted on the top and bottom panels and uprights. Frame rout own drawings. About 3D-printing thought, but while there are fears that the metal seal will not give the required accuracy, and be much more expensive cutters, so we wait until the technology develops to the desired quality.
The bad news is the fact that it is often supplied components do not meet the published specifications. So check all before installing the unit. Sometimes we had to be smart. For example gyroscopes orientation systems tested for astronomical mount. Lucky that one of the engineers in their spare time, space conquest close, engaged in the contemplation of long-range.
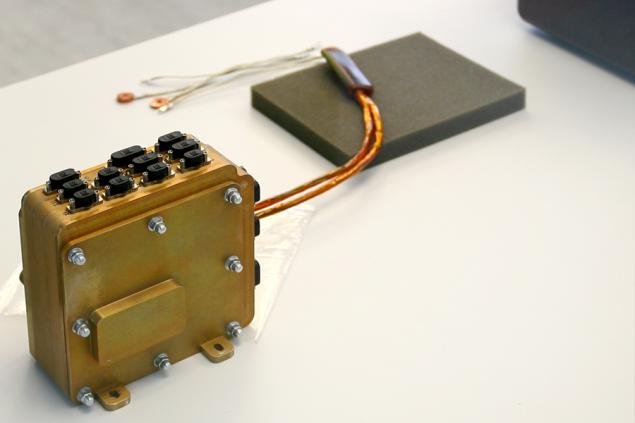
The photo - solar sensor is tested under the rays of an artificial "sun»:

Another device, which I have high hopes - a star sensor. Russia, by the way of production. It is seen on the opposite faces antennas apparatus. It should be used for the orientation of the stars and the determination of the position of the satellite. Actually it is a black and white camera is low resolution, but it is the only camera on the satellite, so I hope our specialists exhort them to remove the Moon in New Moon. This shooting and image transfer is theoretically possible, but will have to try. This will be the best proof of efficiency unit.
Although the company to no one accountable for the development of DX1, but engineers decided to conduct the full range of tests that must withstand the spacecraft Roscosmos. To this end created layout dimensions and weight for vibrodynamic tests. He was to confirm the reliability of the design of the satellite, its willingness to endure congestion during the launch of the launch vehicle. Upon successful completion of the tests, the layout is the first exhibit of the future museum of private Russian astronautics. He managed to light up in several TV stories and photos (this remark to the most attentive, who might surprise twisted pair on the spacecraft).
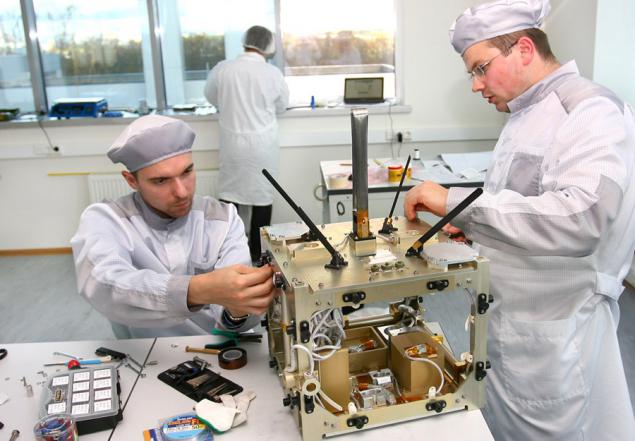

Another layout - Antennas - tested in an anechoic chamber, which allows to estimate the propagation of radio waves in conditions close to the space. There are also confirmed by designers incorporated features.
Finally, it is already fully assembled spacecraft checked in thermal vacuum chamber. This stage of testing will assess the readiness of the unit to operate in conditions of space heat and cold. There was revealed a defect: it turned out that, while stationary, satellite severely overheated on the sunny side. In principle, it is not fatal - enough to run the machine in the "kebab", ie rotate regularly, substituting different facets of the sun. But such a regime would not allow to perform a series of operations for future prospective missions. Therefore the problem was solved in a constructive way - replace the brackets solar panels with aluminum to copper. The thermal conductivity of copper is higher, so the excess heat must "leak" in the body and dissipate on the shady side.
General maintenance of the thermal regime on spacecraft - is an art as something to tell about it separately. All elements of the satellite, except antennas and solar panels before testing was wrapped in vacuum-screen insulation - "gold foil". Unlike electronics, here found a quality domestic manufacturer - Research Institute of CWA Pereiaslavl. First, our specialist in thermal regime has mastered the skills of sewing and drew a full pattern. On it did draft insulation and came to our office on a full fitting.
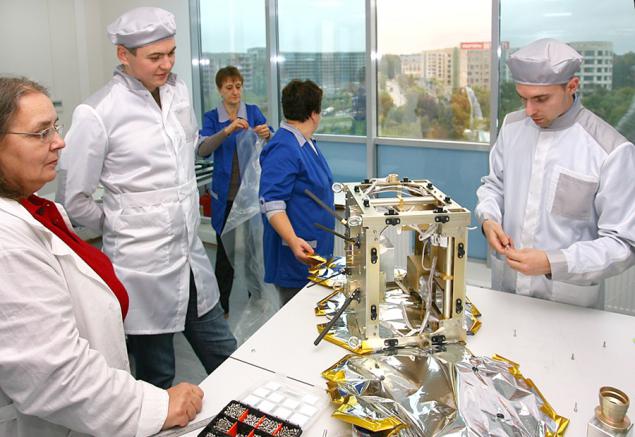

Suit villages not once, but as a result of our cavalier went on parade at Baikonur.
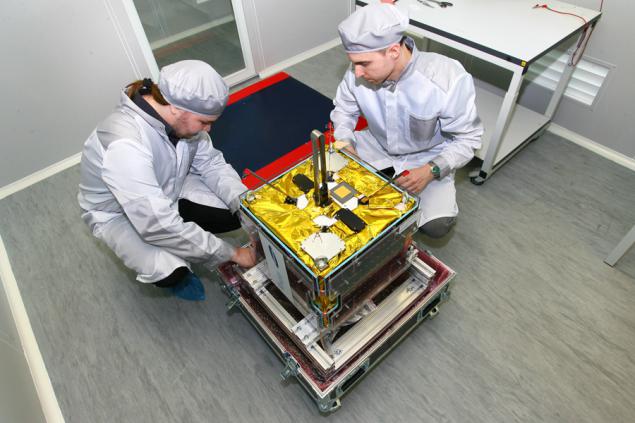

Before we launch ourselves almost spoiled the start - so qualitatively tightened satellite to the booster module that transferring the cable must pass through the team at office. As a result, the bare wire shorted to chassis and battery discharge ...
Prior to the start less than three weeks before the Baikonur over 2 thousand. Km, spare parts in Moscow. Roscosmos postponed the launch of more than a year, so we have to wait another and no one would. The bill went on his watch have time to fix it or not? First flight to Baikonur on Saturday to help our guys went with the spare cable. Still carried a massive layout of the device - a metal disc, which would replace the satellite, if it was removed. The program is written in advance of the missile, so any discrepancy weight could destroy the entire launch.
Replace anything but the cable is not physically have time. Sputnik was removed from the upper stage, replace the cable, battery charge - kept within two days. Next, it was necessary to check the performance of the instrument - to make sure that no short circuit burned out some chip. Abnormalities were identified and resolved to fly.
Photography workshop at Baikonur can not show, so here Baikonurskaya gopher :)

How to fly, and how to work DX1 soon find out. In its work, the specialists of "Daura" sure. The rocket "Soyuz" reliable. The upper stage "Fregat" also works as a clock. Now the main thing that did not disappoint components, and we will be space.
As a bonus, direct speech project manager DX1, Alexander Malinin: to begin designing DX1, we certainly did not know where it might lead. Of course, before that, everyone in the team is more or less the task of developing the spacecraft, but to make the spacecraft from the first sketch to the last bolt - did not do none of the engineers.
Planning began on the system used in the US for most of the spacecraft. The last stage PDR and CDR, the machine at first glance rubbings. At this stage, was made an important mistake, one of the systems, in particular the APS was poorly designed, which negatively affected the later stages of design and production. Then he had to adjust the system to existing dimensions and constraints to change that it was too late.
General view of the spacecraft design was chosen in the early design stage, so more methane in this respect we were not. But the production process of the structure itself was delayed for months. After all, in order to make a small piece of aluminum, it had to detail draws in the drawings to make restrictions on tolerances and roughness. These are the realities of domestic metalworking companies, 3D models ready to work units, and their quality is poor.
But here, designing spacecraft was completed and began to come to the office of the first copies of the flight instruments and process samples. Began stage autonomous, followed and integrated tests of instruments and spacecraft systems. With some devices had fewer complications, with some much more. It turned out that not all devices are working as it is stated in the documentation on it. Had in the course of solving these problems and modify the part that depended on us, whether it's cable or interface configuration.
With lёtnymi cables for spacecraft entered a different story. Everything at least once, but have worked with them before and it is taken for granted. But now that we ourselves had to develop them. This was for us a completely new challenge that no one had never encountered. But we were able to cope with it and gain the required competence, albeit at the cost of a few months. We totally have bought the necessary accessories: wire screens, adhesives, potting, connectors, housings, etc. And independently produced and tested them.
Passing a difficult test phase consisting of an integrated stand, our designer started assembling the spacecraft. Due to the fact that those who designed the spacecraft, the same people, and gathered it, the process went cheerfully. It was not necessary to produce the extra documentation between the services, because these services were to face the same people.
Gathering spacecraft we switched to comprehensive testing of spacecraft, and further to TVI. And at this point I clearly realized, test and debug components spacecraft separately and do the same on the spacecraft assembly, are completely different things. First, nothing is not working, as softvarnom and at hardvarnogo levels. But, the work goes on, and that's the spacecraft began to function the way we wanted it. Not quickly, gradually, day by day. But started!
To say that the enthusiasm to create your own CA was great - it's nothing to say. We worked 12-14 hours a day, sometimes seven days a week. There were days when everything goes wrong, and time is running out. In these days of hands fall and faith in their own strength and success weakens. But tomorrow, nastaёt new day, and you again steadily approaching their offspring to a natural end.
Now, having completed all the stages of development of the spacecraft, I can say that we are much more experienced, confident, and most importantly, a much more ambitious in terms of professional people.
Now it remains for us the most important thing, to run the spacecraft and received from him the first signal. It would seem a trifle in comparison with what we have already done. But this is a trifle long-awaited and hard-earned, that it is worth to pursue the case!
P.S. I think the text will cause many issues. I shall warn that all the highly technical questions can not answer. Ask engineers to help, but they are now, on the eve of the launch, there is something to do, and the concept of a trade secret has not been canceled. Therefore, if whose questions remain unanswered - understand and forgive me. I>
Source: habrahabr.ru/company/dauria/blog/228431/

What you need to build your spacecraft? What challenges have to be solved? How much it all cost? Answers to these questions have to find up to the moment when the satellite was sent to Baikonur.
Many of the "Aerospace Dahuria" has already had experience creating spacecraft and were ready to go, but in order to form a cohesive team was required to pass along all stages of the spacecraft. Only shareable positive and negative experiences, having the entire process from concept to launch and operation, it is safe to talk about the company's willingness to further achievements. It was, perhaps, the main motive of creating DX1. But the important role played and the more prosaic factors: it was necessary to write and test the software system, ready to use on other satellites of the company; earn chain suppliers and subcontractors; prepare the assembly site.
Typically, satellites are created for specific tasks or orders. The company does not have those, so decided to develop a universal platform based on the possibility of launching a satellite Roscosmos "Meteor-M №2». Immediately laid the capabilities of this platform to implement projects as the company and to order. When choosing a platform concept based on a number of parameters:
1) weight up to 100 kg - the so-called Class "microsatellites»;
2) scalability - the ability to change the dimensions of the platform, without changing the basic elements and avionics, and as a consequence - the total software;
3) a wide range of applications - fitting of precision targeting platform that allows the satellites, for example, to capture images of the Earth's surface, or to carry out astrophysical problems.

The result was a draft DX1 - «Dauriya pilot first." In order not to run a simple technological demonstrator, equipped with a satellite signal receiving unit AIS - so he got a commercial application and the possibility of partial or full cost recovery. But this device must confirm the ability of exceeding the needs of the payload.
AIS unit energy consumption is not high, which allowed to do without opening the solar panels. This simplified the design, operation and management easier. But even so, the satellite is able to produce energy is three times more than he really needed.
Onboard radio operates in two bands: VHF and S. Obtaining permission to use them over the territory of Russia took almost as much as the creation of the device.
Main specifications DX1 seen from the table:

Ranking in orbit up to hundreds of meters, and the pointing accuracy of up to 6 seconds of arc - a characteristic suitable for shooting the surface of the Earth or planetary astronomy. Such opportunities laid for the future, with the expectation of future challenges.
Birth unit began with an assessment of what to offer the modern world industry. Traveled bunch exhibitions and forums worldwide. Looking for industrial grade components, ie, suitable for use in industry in the world. Space or military components are orders of magnitude more expensive, contrary to the ideology of the planned business. And with the advent of sanctions only added to the difficulties.
But now, and industrial electronics capable of performing the task space. Actually, do not stop using its state-owned companies and the Russian Space Agency. On the "Phobos-Grunt" it did not work, but in the near-Earth space satellites in "non-space" components work up to ten years. Roscosmos enjoys the electronics because there is simply no other: its microelectronics are often not ready to offer necessary and foreigners «Space" and "Military» a > just do not sell.
"Dauriya" consciously goes to "industrialize" considering additional methods of protection in space: a thick layer of aluminum shielding, redundancy, hardware and software.
As a result, on-board machine DX1 looked like a piece of the tank, but in general the satellite turned out pretty easy, for its size - 22 kg. (Joke about positive buoyancy). Filling the onboard computer is already flying practice on an experimental satellite NASA.

The architecture is based on a satellite carrying an aluminum frame, and the walls act as solar panels. Devices are mounted on the top and bottom panels and uprights. Frame rout own drawings. About 3D-printing thought, but while there are fears that the metal seal will not give the required accuracy, and be much more expensive cutters, so we wait until the technology develops to the desired quality.
The bad news is the fact that it is often supplied components do not meet the published specifications. So check all before installing the unit. Sometimes we had to be smart. For example gyroscopes orientation systems tested for astronomical mount. Lucky that one of the engineers in their spare time, space conquest close, engaged in the contemplation of long-range.
The photo - solar sensor is tested under the rays of an artificial "sun»:

Another device, which I have high hopes - a star sensor. Russia, by the way of production. It is seen on the opposite faces antennas apparatus. It should be used for the orientation of the stars and the determination of the position of the satellite. Actually it is a black and white camera is low resolution, but it is the only camera on the satellite, so I hope our specialists exhort them to remove the Moon in New Moon. This shooting and image transfer is theoretically possible, but will have to try. This will be the best proof of efficiency unit.
Although the company to no one accountable for the development of DX1, but engineers decided to conduct the full range of tests that must withstand the spacecraft Roscosmos. To this end created layout dimensions and weight for vibrodynamic tests. He was to confirm the reliability of the design of the satellite, its willingness to endure congestion during the launch of the launch vehicle. Upon successful completion of the tests, the layout is the first exhibit of the future museum of private Russian astronautics. He managed to light up in several TV stories and photos (this remark to the most attentive, who might surprise twisted pair on the spacecraft).

Another layout - Antennas - tested in an anechoic chamber, which allows to estimate the propagation of radio waves in conditions close to the space. There are also confirmed by designers incorporated features.
Finally, it is already fully assembled spacecraft checked in thermal vacuum chamber. This stage of testing will assess the readiness of the unit to operate in conditions of space heat and cold. There was revealed a defect: it turned out that, while stationary, satellite severely overheated on the sunny side. In principle, it is not fatal - enough to run the machine in the "kebab", ie rotate regularly, substituting different facets of the sun. But such a regime would not allow to perform a series of operations for future prospective missions. Therefore the problem was solved in a constructive way - replace the brackets solar panels with aluminum to copper. The thermal conductivity of copper is higher, so the excess heat must "leak" in the body and dissipate on the shady side.
General maintenance of the thermal regime on spacecraft - is an art as something to tell about it separately. All elements of the satellite, except antennas and solar panels before testing was wrapped in vacuum-screen insulation - "gold foil". Unlike electronics, here found a quality domestic manufacturer - Research Institute of CWA Pereiaslavl. First, our specialist in thermal regime has mastered the skills of sewing and drew a full pattern. On it did draft insulation and came to our office on a full fitting.

Suit villages not once, but as a result of our cavalier went on parade at Baikonur.

Before we launch ourselves almost spoiled the start - so qualitatively tightened satellite to the booster module that transferring the cable must pass through the team at office. As a result, the bare wire shorted to chassis and battery discharge ...
Prior to the start less than three weeks before the Baikonur over 2 thousand. Km, spare parts in Moscow. Roscosmos postponed the launch of more than a year, so we have to wait another and no one would. The bill went on his watch have time to fix it or not? First flight to Baikonur on Saturday to help our guys went with the spare cable. Still carried a massive layout of the device - a metal disc, which would replace the satellite, if it was removed. The program is written in advance of the missile, so any discrepancy weight could destroy the entire launch.
Replace anything but the cable is not physically have time. Sputnik was removed from the upper stage, replace the cable, battery charge - kept within two days. Next, it was necessary to check the performance of the instrument - to make sure that no short circuit burned out some chip. Abnormalities were identified and resolved to fly.
Photography workshop at Baikonur can not show, so here Baikonurskaya gopher :)

How to fly, and how to work DX1 soon find out. In its work, the specialists of "Daura" sure. The rocket "Soyuz" reliable. The upper stage "Fregat" also works as a clock. Now the main thing that did not disappoint components, and we will be space.
As a bonus, direct speech project manager DX1, Alexander Malinin: to begin designing DX1, we certainly did not know where it might lead. Of course, before that, everyone in the team is more or less the task of developing the spacecraft, but to make the spacecraft from the first sketch to the last bolt - did not do none of the engineers.
Planning began on the system used in the US for most of the spacecraft. The last stage PDR and CDR, the machine at first glance rubbings. At this stage, was made an important mistake, one of the systems, in particular the APS was poorly designed, which negatively affected the later stages of design and production. Then he had to adjust the system to existing dimensions and constraints to change that it was too late.
General view of the spacecraft design was chosen in the early design stage, so more methane in this respect we were not. But the production process of the structure itself was delayed for months. After all, in order to make a small piece of aluminum, it had to detail draws in the drawings to make restrictions on tolerances and roughness. These are the realities of domestic metalworking companies, 3D models ready to work units, and their quality is poor.
But here, designing spacecraft was completed and began to come to the office of the first copies of the flight instruments and process samples. Began stage autonomous, followed and integrated tests of instruments and spacecraft systems. With some devices had fewer complications, with some much more. It turned out that not all devices are working as it is stated in the documentation on it. Had in the course of solving these problems and modify the part that depended on us, whether it's cable or interface configuration.
With lёtnymi cables for spacecraft entered a different story. Everything at least once, but have worked with them before and it is taken for granted. But now that we ourselves had to develop them. This was for us a completely new challenge that no one had never encountered. But we were able to cope with it and gain the required competence, albeit at the cost of a few months. We totally have bought the necessary accessories: wire screens, adhesives, potting, connectors, housings, etc. And independently produced and tested them.
Passing a difficult test phase consisting of an integrated stand, our designer started assembling the spacecraft. Due to the fact that those who designed the spacecraft, the same people, and gathered it, the process went cheerfully. It was not necessary to produce the extra documentation between the services, because these services were to face the same people.
Gathering spacecraft we switched to comprehensive testing of spacecraft, and further to TVI. And at this point I clearly realized, test and debug components spacecraft separately and do the same on the spacecraft assembly, are completely different things. First, nothing is not working, as softvarnom and at hardvarnogo levels. But, the work goes on, and that's the spacecraft began to function the way we wanted it. Not quickly, gradually, day by day. But started!
To say that the enthusiasm to create your own CA was great - it's nothing to say. We worked 12-14 hours a day, sometimes seven days a week. There were days when everything goes wrong, and time is running out. In these days of hands fall and faith in their own strength and success weakens. But tomorrow, nastaёt new day, and you again steadily approaching their offspring to a natural end.
Now, having completed all the stages of development of the spacecraft, I can say that we are much more experienced, confident, and most importantly, a much more ambitious in terms of professional people.
Now it remains for us the most important thing, to run the spacecraft and received from him the first signal. It would seem a trifle in comparison with what we have already done. But this is a trifle long-awaited and hard-earned, that it is worth to pursue the case!
P.S. I think the text will cause many issues. I shall warn that all the highly technical questions can not answer. Ask engineers to help, but they are now, on the eve of the launch, there is something to do, and the concept of a trade secret has not been canceled. Therefore, if whose questions remain unanswered - understand and forgive me. I>
Source: habrahabr.ru/company/dauria/blog/228431/
Tags
See also
How to build a sauna from chopped logs: step by step instructions
How to build a timber frame bath with his hands
Submit reports online is very convenient, because it can be done without leaving your office or home
How to build a firewood tower at the dacha with his hands
How to build a terrace at the dacha with his hands
How to build an affordable eco house with his own hands
How to build a versatile and warm beds
How to build a henhouse with your own hands
How to build a winter garden with his own hands