How to launch satellites
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net
April 12, 1961 the Soviet Union launched the first time in the history of manned spacecraft on board was Yuri Gagarin. Today we show how from the cosmodrome "Baikonur" using rocket "Proton-M" was launched on the second Kazakhstani telecommunications satellite "KazSat-2" (KazSat-2). As the unit was launched into orbit in which it state how and where its management is carried out? Look under the cut
26 photos via science.mirtesen.ru
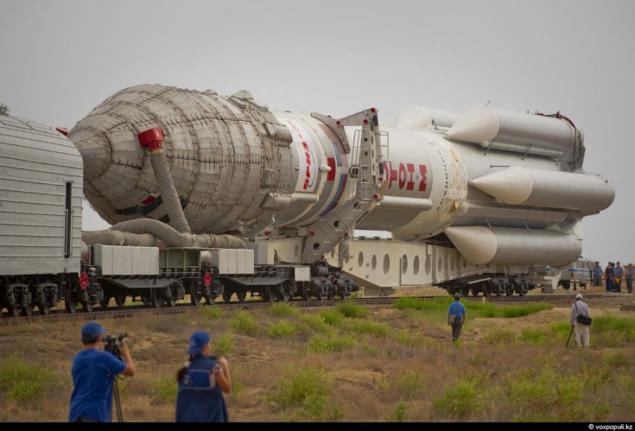

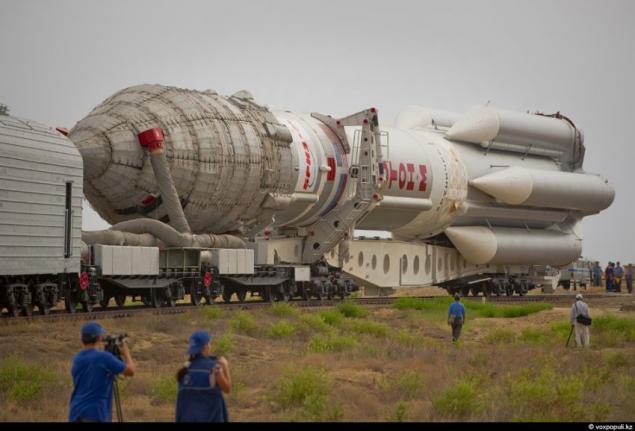
1. The 12 of July of 2011. Camuyu heavy Russian space rocket "Proton-M" with the Kazakh communications satellite №2 and the American SES-3 (OS-2) are taken to the starting position. "Proton-M" run only from the Baikonur "cosmodrome." It is here that there is the necessary infrastructure to service this complex space-rocket system. The Russian side, namely the manufacturer of the device, the Khrunichev space center, ensures that "KazSat-2" will last at least 12 years old.
Since the signing of the agreement on the establishment of a satellite project reworked several times, and the launch was postponed at least three times. As a result of "KazSat-2" was a fundamentally new components and a new control algorithm. But most importantly, the satellite was assembled the latest and highly reliable navigation instruments, manufacturing French company ASTRIUM.
This gyroscopic measuring angular velocity and astrodatchiki. With astrodatchikov satellite orients itself in space by the stars. That failure of navigation equipment led to the first "KazSat" was actually lost in the year 2008, nearly caused an international scandal.

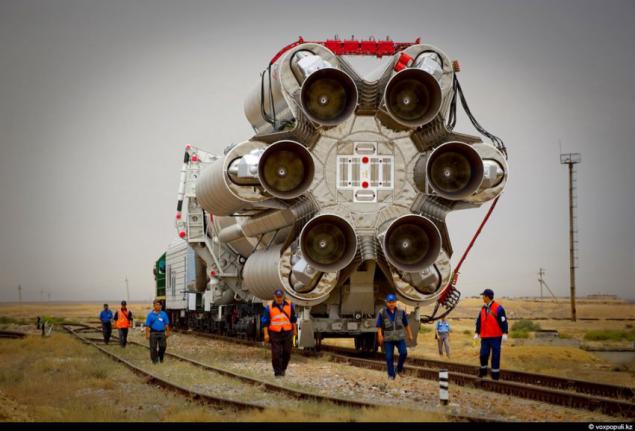
2. Way of missiles attached to her power and temperature control systems, the head portion, where the upper stage "Breeze-M" satellites and takes about 3 hours. The speed of the special train of 5-7 kilometers per hour, the composition serves the team of specially trained drivers.
Another group of security officers inspect the Baikonur tracks. Not the slightest design load could damage the rocket. Unlike its predecessor, "KazSat" has become more energy-intensive.
The number of transmitters increased to 16. On the "KazSat-1" there were 12. A total capacity of the transponder is increased to 4 and a half kilowatts. This will allow the pump to order more of all kinds of data. All these changes are reflected in the cost of the device. It amounted to $ 115 million. The first unit cost Kazakhstan 65 million.

...

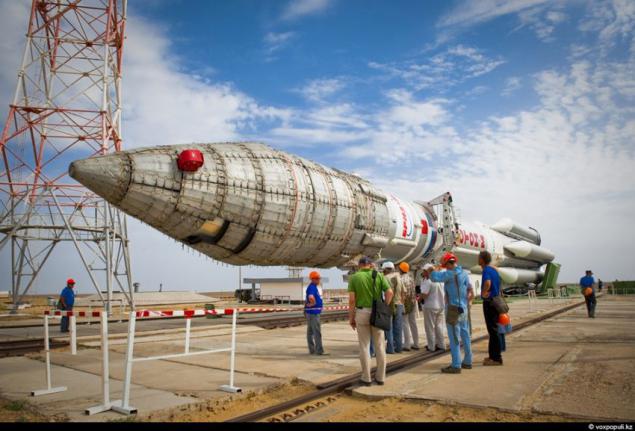
3. For all happening quietly watching the local inhabitants of the steppe. Ships of the Desert)

4. The size and capabilities of the missile actually striking. Its length is 58 m 2, weight 705 tons filled state. At the start craving 6 engines of the first stage rocket is about 1 ths. Tons. This allows the output to the reference near-Earth orbit objects weighing up to 25 tons, and the high geostationary (30 thous. Km. From the surface of the earth) - up to 5 tons. Therefore, the "Proton-M" is indispensable when it comes to the launch of telecommunications satellites.
Victor Lefter, President of the Republican Center of Space Communications:
- Two identical spacecraft just does not happen, because each spacecraft - is a completely new technology. Within a short period, it so happens that you have to change completely new elements. In "KazCate-2" to apply the new advanced technologies, which at that time were. It was placed a piece of equipment manufactured in Europe, in terms of that, where we have been failures in the "KazSat-1". I think that the equipment we have now is working on "KazSat-2" should show good results. It has a fairly good year history
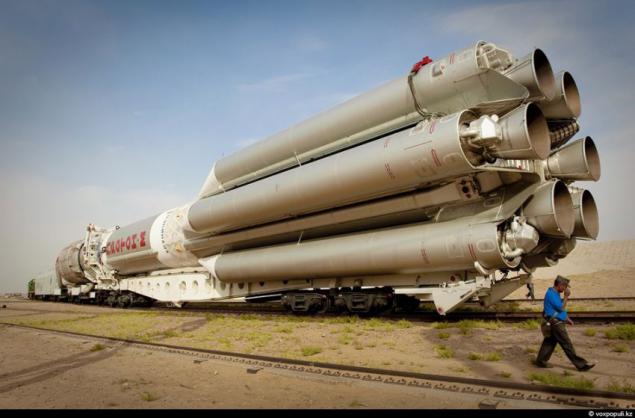

5. The cosmodrome currently has 4 starting positions for rocket "Proton". However, only 3 of them at the sites number 81 and number 200 are in working order. Previous launches of this rocket would only deal with the military because of the fact that working with toxic fuel required hard manual command. Today the complex is demilitarized, although the composition of crews a lot of ex-military, who withdrew the shoulder straps.
The orbital position of the second "KazSat" has become much easier to work with. It is 86 and a half degrees east longitude. Coverage includes the entire territory of Kazakhstan, parts of Central Asia and Russia.
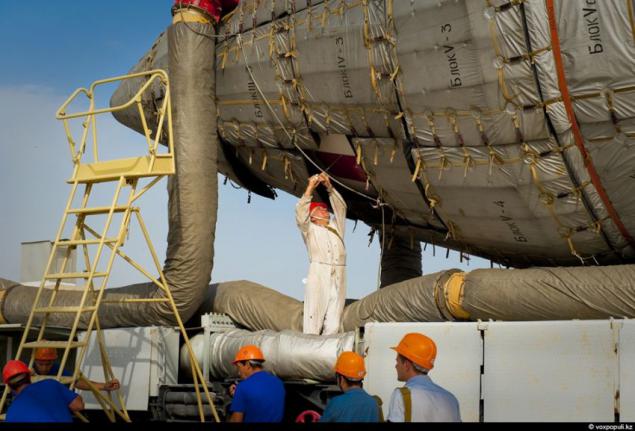

6. The sunsets at the cosmodrome "Baikonur" technology exclusively! Massive construction to the right center of the picture - a "Proton-M" fully supplied to him farm maintenance. Since the removal of the rocket to the launch pad position number 200 and goes up to the start of 4 days. All this is being done to prepare and test systems "Proton-M". Approximately 12 hours before the start of the meeting of the state commission held that gives permission to refuel the rocket fuel. Filling begins 6 hours before the start. From that point, all operations are irreversible.
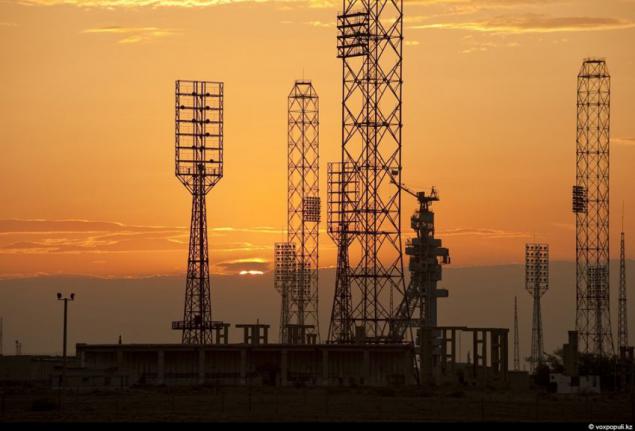

7. What kind of benefit receives our country having its own communications satellite? First of all - is the solution information support in Kazakhstan. His companion will help expand the range of information services for the entire population. This e-government services, the Internet, mobile communication. Most importantly, that Kazakh satellite will partially reject the services of foreign telecommunications companies, providing our operator service relay. We are talking about tens of millions of dollars that will now not go abroad and come to the state budget.
Victor Lefter, President of the Republican Center of Space Communications:
- Kazakhstan has a large territory, in comparison with other countries. And we must understand that in every town, in every village, the village school, we can not apply those communication services that are limited by means of cable and other systems. Spacecraft solves this problem. Almost the whole territory is closed. Moreover, not only the territory of Kazakhstan, but also part of the territory of neighboring states. And satellites - the ability to ensure a stable bond

8. Various modifications rocket "Proton" in operation since 1967 year. Its chief designer was Academician Vladimir Chelomey and its Bureau (now - CB "Salute", a branch of Khrunichev. Khrunichev). You can safely say that all of the impressive Soviet projects for development of near-Earth space and study of objects of the solar system would have been impossible without this rocket. In addition, the "Proton" has a very high level for the reliability of this technique: for all time of its operation was made 370 starts, 44 of them - failed.

9. The only major drawback and "Proton" - a highly toxic fuel components: unsymmetrical dimethyl hydrazine (UDMH), or as it is called "heptyl" and nitrogen tetroxide ("amil"). In places the fall of the first stage (this territory near the town of Dzhezkazgan), there is pollution, which requires costly operations to clean it up.
The situation seriously worsened in the early 2000s, when there was a succession of three rocket accidents. This caused extreme dissatisfaction with the authorities of Kazakhstan, the Russian side demanded more compensation. Since 2001, the modification of the old rocket were replaced with upgraded "Proton-M". There is a digital control system, and the system bleed unburned fuel residues in the upper layers of the ionosphere.
Thus, we managed to significantly reduce damage to the environment. Additionally, it developed, but still remains on the paper draft environmentally safe rocket "Angar" which uses kerosene as fuel components and oxygen and which must gradually replace "Proton-M". By the way, the complex launch vehicle "Angara" on "Baikonur" will be called "Baiterek" (in Kazakh "Topol".)
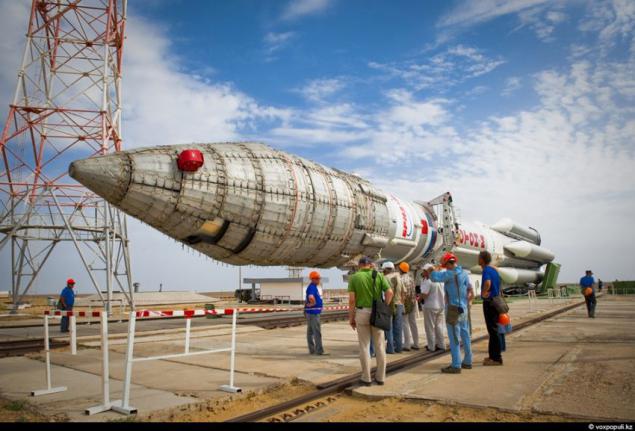

10. It is reliable rockets at one time attracted the Americans. In the 90s it was a joint venture ILS, which positioned the rocket on the American telecommunications systems market. Today, most American civilian communications satellites are launched, "Proton-M" from the cosmodrome in the Kazakh steppe. American SES-3 (owned by SES WORLD SKIES), which is in the head of the rocket along with the Kazakh "KazSat-2" - one of many launched from "Baikonur".
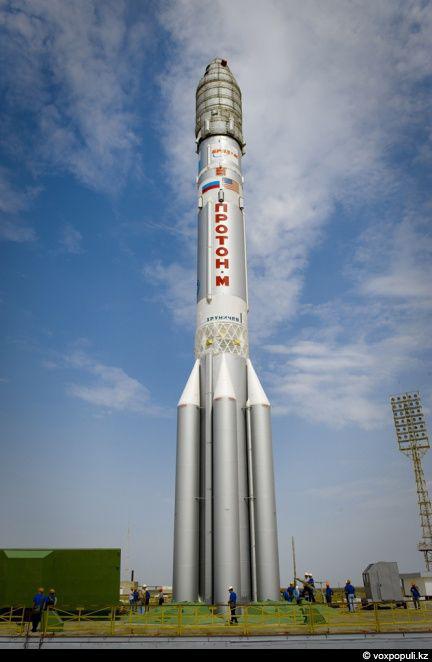

11. In the Russian and American flags, rocket placed Kazakhstan as well as the emblem of the Republican Center of Space Communications - the organization that now owns and operates the satellite.
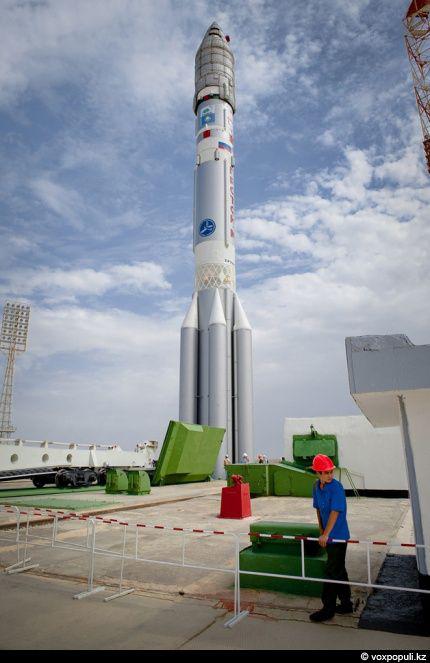

12. July 16, 2011, the year 5:00 16 minutes and 10 seconds in the morning. The climax. Fortunately, everything goes well.

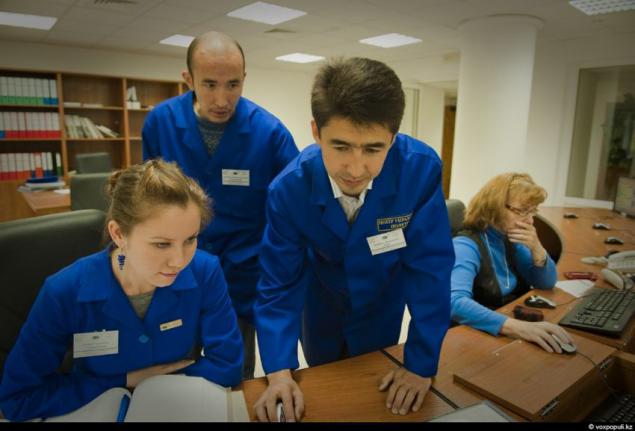
13. Within 3 months after the launch. Young professionals - a leading engineer of the satellite control Bekbolot Azaev, as well as his colleagues, engineers Rimma Kozhevnikova and Assylbek Abdrakhmanov. These guys and run "KazSat-2".

14. Akmola region. A small, up to 2006, unremarkable district center Akkol received wide acclaim 5 years ago, when there was built the country's first MCC - Mission Control Centre orbiting satellites. October is a cold, windy and rainy, but right now there comes the busy season for those people who need to make satellite "KazSat-2" status of a full-fledged and important segment of Kazakhstan's telecom infrastructure.
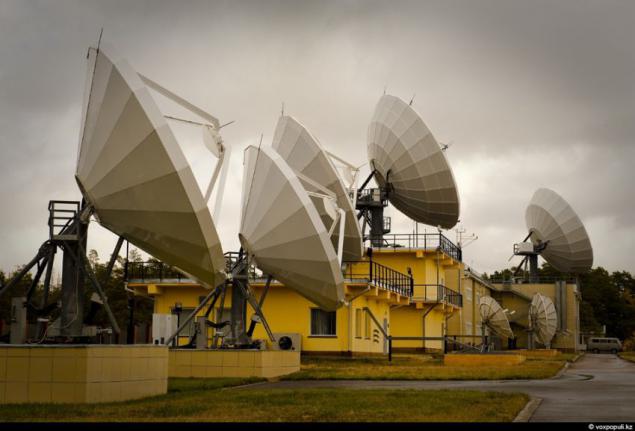

15. After losing the first satellite in 2008, the year in Akkol Satellite Communications Center underwent a major modernization. It allows you to now handle two devices.
Baurzhan Kudabaev, vice president of the Republican Center of Space Communications:
- It was established a special software delivered new equipment. Before you rack-command of the measuring system. This supply of American firm Vertex, as it was in the "KazSat-1", but the new modifications, improved version. Applied development company "Russian Space Systems". Ie all this - the development of today. The new programs, equipment, electronic components. All this improves the performance of our spacecraft
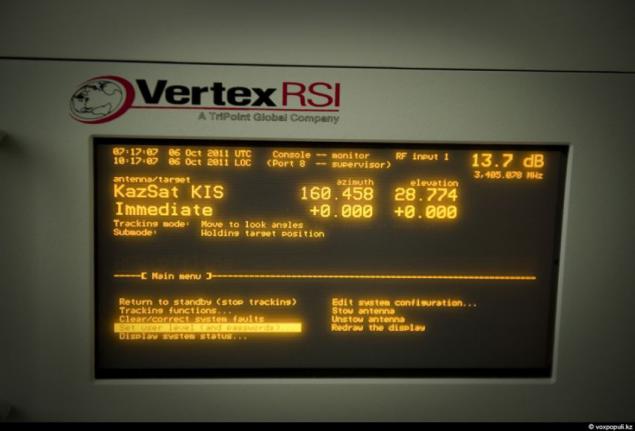
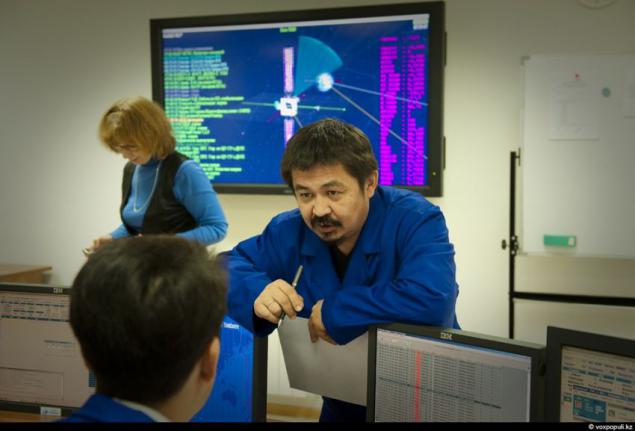
16. Darkhan Maral, head of the mission control center in the workplace. In 2011, the Center came young specialists, graduates of Russian and Kazakh universities. They have learned to work and how to maintain leadership in RTSKS, with the completion of a career is no problem. In 2008, the situation was much sadder. After losing the first satellite, a significant proportion of highly educated people left the center.

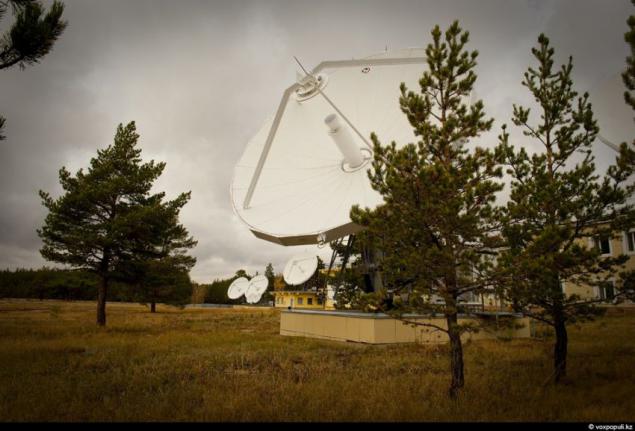
17. October of 2011 was another climax in the work of the Kazakh satellite. He completed his flight tests and started the so-called trial transcripts. Ie it was like a test for the functionality of the satellite manufacturer. There was everything follows. On the "KazSat-2" raised the television signal.
Then, several groups of experts traveled to different regions of Kazakhstan and the measured parameters of the signal, ie, how correctly the signal relays satellite. Observations have arisen, and in the end a special committee adopted an act on the transfer of the satellite to the Kazakh side. Since then, the operation of the unit involved in Kazakh specialists.

18. Until the end of November 2011, the Space Center "Akkol" a large group of Russian experts. They were subcontractors on the project "KazSat-2". These are the leading companies of the Russian space industry: Center. Khrunichev, which designed and built the satellite, Design Bureau "Mars" (which specializes in navigation orbiting satellites), as well as the corporation "Russian Space Systems", which develops software.
The whole system is divided into two components. It is, in fact, the satellite and terrestrial infrastructure management. According to the technology first, the contractor must demonstrate the availability of the system - is equipment installation, debug it, the demonstration features. After all procedures - training of Kazakh specialists.
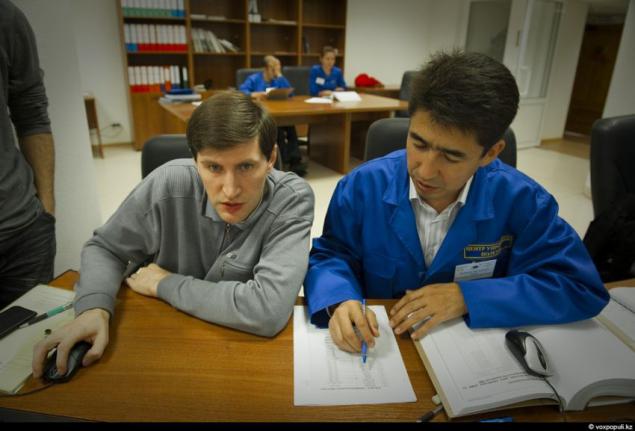

19. Satellite Communications Center in Akkol - this is one of the few places in our country where there are favorable electromagnetic environment. On many tens of kilometers around here there are no sources of radiation. They can create interference and hamper satellite. 10 large parabolic antennas directed into the sky in a single point. There is a great distance from the Earth's surface - that's more than 36-thousand kilometers of hanging a small man-made object - the Kazakh communications satellite "KazSat-2".
Most modern geostationary communications satellites. Ie their orbit is constructed so that as it hangs over one geographic point, and the rotation of the earth has little to this stable position no effect. This allows the on-board transponder to pump large volumes of information confidently take this information in the coverage area on the Earth.
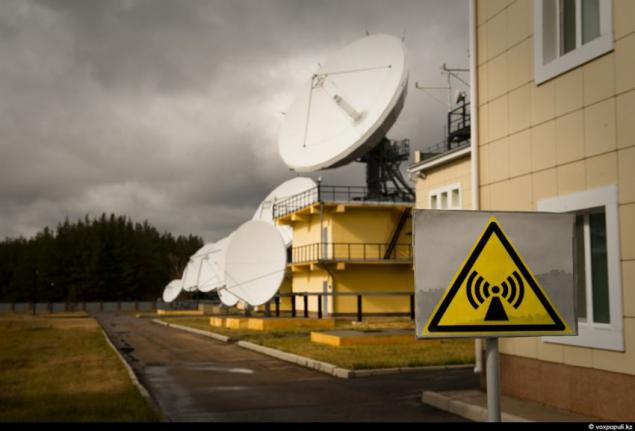

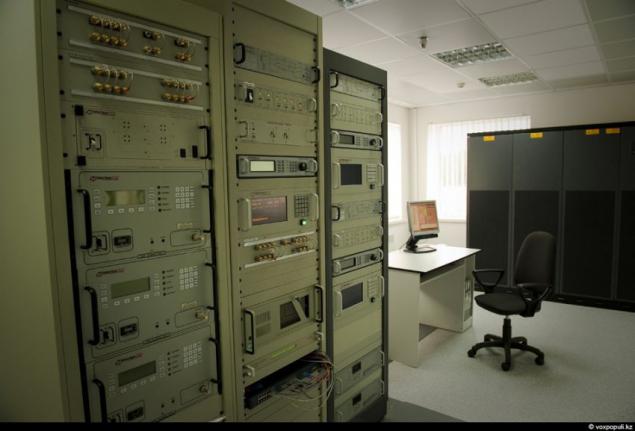
20. Another curious detail. According to the international rules of the tolerance of the satellite from the point of standing can be a maximum of half a degree. For Professionals -uderzhat MCC unit in the given parameters - piece of work that requires highly qualified specialists in ballistics. The center will work 69 people, 36 of them - are technical experts.
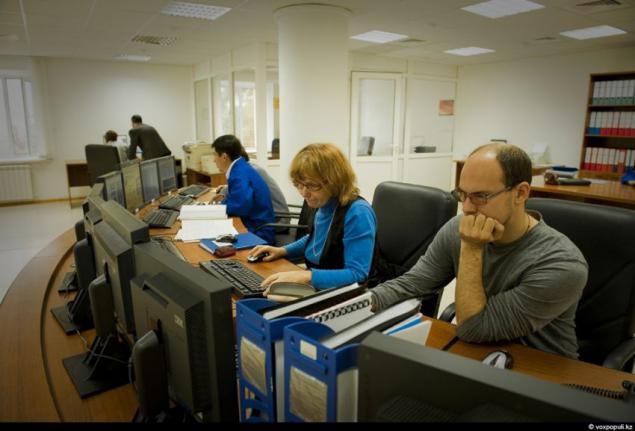

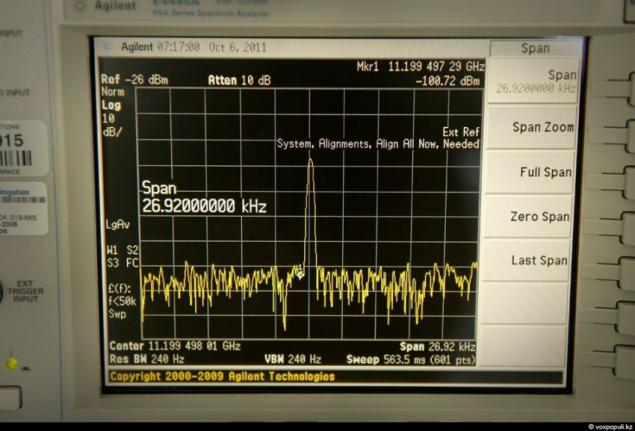
21. This is the main control. On the wall of a large monitor, which receives all the telemetry on the semi-circular table are several computers and telephones. It seems to be very simple ...
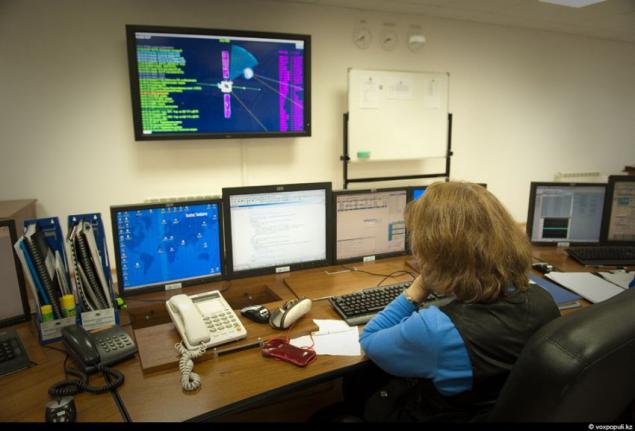

22. ... but it only seems that way. Read in this curve on the oscilloscope being a space object and that the telescope is not visible, it is given not for everyone ...
23. Victor Lefter, President of the Republican Center of Space Communications:
- We will expand Kazakhstan's fleet up to 3, 4, and perhaps even - up to 5 cputnikov. Ie that there was a constant replacement of vehicles, provision was, and that our operators have not experienced such an urgent need to use the products of other countries. So we were provided with their reserves. "
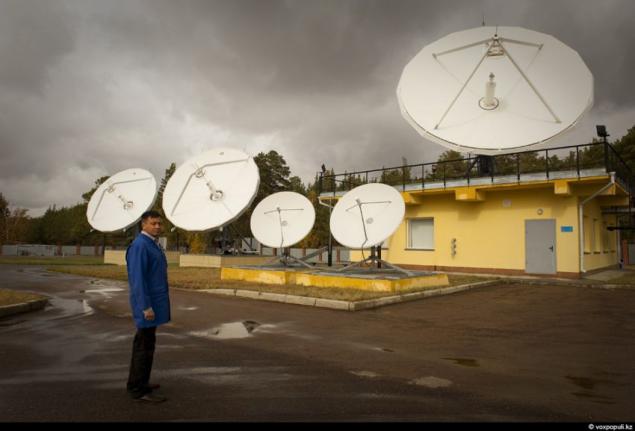

24. Currently, the backup satellite control is carried out from Moscow, where the Space Center. Khrunichev. However, the National Center for Space Communications intends to reserve a flight c Kazakh territory. To do this, now under construction the second MCC. It will be located 30 kilometers north of Almaty.

25. The plans of the National Space Agency of Kazakhstan, coming in 2013, the year the launch of the third satellite "KazSat-3". The contract for its development and production was signed in 2011, the year in France, Air Show in Le Bourget. Sputnik Kazakhstan builds im.Akademika Reshetnev NPO, which is located in the Russian city of Krasnoyarsk.

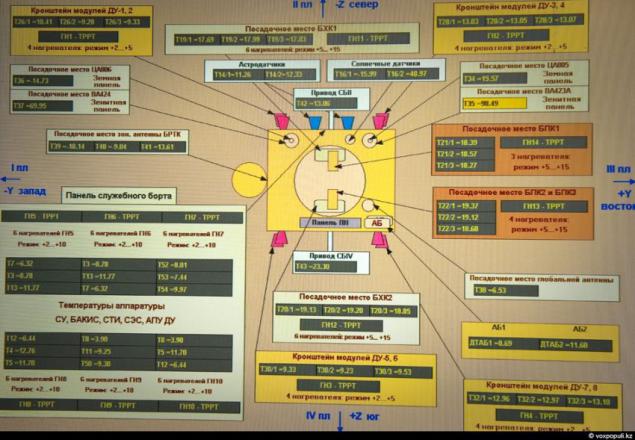
26. The operator interface management department. So it looks like now.
Source:
26 photos via science.mirtesen.ru

1. The 12 of July of 2011. Camuyu heavy Russian space rocket "Proton-M" with the Kazakh communications satellite №2 and the American SES-3 (OS-2) are taken to the starting position. "Proton-M" run only from the Baikonur "cosmodrome." It is here that there is the necessary infrastructure to service this complex space-rocket system. The Russian side, namely the manufacturer of the device, the Khrunichev space center, ensures that "KazSat-2" will last at least 12 years old.
Since the signing of the agreement on the establishment of a satellite project reworked several times, and the launch was postponed at least three times. As a result of "KazSat-2" was a fundamentally new components and a new control algorithm. But most importantly, the satellite was assembled the latest and highly reliable navigation instruments, manufacturing French company ASTRIUM.
This gyroscopic measuring angular velocity and astrodatchiki. With astrodatchikov satellite orients itself in space by the stars. That failure of navigation equipment led to the first "KazSat" was actually lost in the year 2008, nearly caused an international scandal.

2. Way of missiles attached to her power and temperature control systems, the head portion, where the upper stage "Breeze-M" satellites and takes about 3 hours. The speed of the special train of 5-7 kilometers per hour, the composition serves the team of specially trained drivers.
Another group of security officers inspect the Baikonur tracks. Not the slightest design load could damage the rocket. Unlike its predecessor, "KazSat" has become more energy-intensive.
The number of transmitters increased to 16. On the "KazSat-1" there were 12. A total capacity of the transponder is increased to 4 and a half kilowatts. This will allow the pump to order more of all kinds of data. All these changes are reflected in the cost of the device. It amounted to $ 115 million. The first unit cost Kazakhstan 65 million.

...

3. For all happening quietly watching the local inhabitants of the steppe. Ships of the Desert)

4. The size and capabilities of the missile actually striking. Its length is 58 m 2, weight 705 tons filled state. At the start craving 6 engines of the first stage rocket is about 1 ths. Tons. This allows the output to the reference near-Earth orbit objects weighing up to 25 tons, and the high geostationary (30 thous. Km. From the surface of the earth) - up to 5 tons. Therefore, the "Proton-M" is indispensable when it comes to the launch of telecommunications satellites.
Victor Lefter, President of the Republican Center of Space Communications:
- Two identical spacecraft just does not happen, because each spacecraft - is a completely new technology. Within a short period, it so happens that you have to change completely new elements. In "KazCate-2" to apply the new advanced technologies, which at that time were. It was placed a piece of equipment manufactured in Europe, in terms of that, where we have been failures in the "KazSat-1". I think that the equipment we have now is working on "KazSat-2" should show good results. It has a fairly good year history

5. The cosmodrome currently has 4 starting positions for rocket "Proton". However, only 3 of them at the sites number 81 and number 200 are in working order. Previous launches of this rocket would only deal with the military because of the fact that working with toxic fuel required hard manual command. Today the complex is demilitarized, although the composition of crews a lot of ex-military, who withdrew the shoulder straps.
The orbital position of the second "KazSat" has become much easier to work with. It is 86 and a half degrees east longitude. Coverage includes the entire territory of Kazakhstan, parts of Central Asia and Russia.

6. The sunsets at the cosmodrome "Baikonur" technology exclusively! Massive construction to the right center of the picture - a "Proton-M" fully supplied to him farm maintenance. Since the removal of the rocket to the launch pad position number 200 and goes up to the start of 4 days. All this is being done to prepare and test systems "Proton-M". Approximately 12 hours before the start of the meeting of the state commission held that gives permission to refuel the rocket fuel. Filling begins 6 hours before the start. From that point, all operations are irreversible.

7. What kind of benefit receives our country having its own communications satellite? First of all - is the solution information support in Kazakhstan. His companion will help expand the range of information services for the entire population. This e-government services, the Internet, mobile communication. Most importantly, that Kazakh satellite will partially reject the services of foreign telecommunications companies, providing our operator service relay. We are talking about tens of millions of dollars that will now not go abroad and come to the state budget.
Victor Lefter, President of the Republican Center of Space Communications:
- Kazakhstan has a large territory, in comparison with other countries. And we must understand that in every town, in every village, the village school, we can not apply those communication services that are limited by means of cable and other systems. Spacecraft solves this problem. Almost the whole territory is closed. Moreover, not only the territory of Kazakhstan, but also part of the territory of neighboring states. And satellites - the ability to ensure a stable bond

8. Various modifications rocket "Proton" in operation since 1967 year. Its chief designer was Academician Vladimir Chelomey and its Bureau (now - CB "Salute", a branch of Khrunichev. Khrunichev). You can safely say that all of the impressive Soviet projects for development of near-Earth space and study of objects of the solar system would have been impossible without this rocket. In addition, the "Proton" has a very high level for the reliability of this technique: for all time of its operation was made 370 starts, 44 of them - failed.

9. The only major drawback and "Proton" - a highly toxic fuel components: unsymmetrical dimethyl hydrazine (UDMH), or as it is called "heptyl" and nitrogen tetroxide ("amil"). In places the fall of the first stage (this territory near the town of Dzhezkazgan), there is pollution, which requires costly operations to clean it up.
The situation seriously worsened in the early 2000s, when there was a succession of three rocket accidents. This caused extreme dissatisfaction with the authorities of Kazakhstan, the Russian side demanded more compensation. Since 2001, the modification of the old rocket were replaced with upgraded "Proton-M". There is a digital control system, and the system bleed unburned fuel residues in the upper layers of the ionosphere.
Thus, we managed to significantly reduce damage to the environment. Additionally, it developed, but still remains on the paper draft environmentally safe rocket "Angar" which uses kerosene as fuel components and oxygen and which must gradually replace "Proton-M". By the way, the complex launch vehicle "Angara" on "Baikonur" will be called "Baiterek" (in Kazakh "Topol".)

10. It is reliable rockets at one time attracted the Americans. In the 90s it was a joint venture ILS, which positioned the rocket on the American telecommunications systems market. Today, most American civilian communications satellites are launched, "Proton-M" from the cosmodrome in the Kazakh steppe. American SES-3 (owned by SES WORLD SKIES), which is in the head of the rocket along with the Kazakh "KazSat-2" - one of many launched from "Baikonur".

11. In the Russian and American flags, rocket placed Kazakhstan as well as the emblem of the Republican Center of Space Communications - the organization that now owns and operates the satellite.

12. July 16, 2011, the year 5:00 16 minutes and 10 seconds in the morning. The climax. Fortunately, everything goes well.

13. Within 3 months after the launch. Young professionals - a leading engineer of the satellite control Bekbolot Azaev, as well as his colleagues, engineers Rimma Kozhevnikova and Assylbek Abdrakhmanov. These guys and run "KazSat-2".

14. Akmola region. A small, up to 2006, unremarkable district center Akkol received wide acclaim 5 years ago, when there was built the country's first MCC - Mission Control Centre orbiting satellites. October is a cold, windy and rainy, but right now there comes the busy season for those people who need to make satellite "KazSat-2" status of a full-fledged and important segment of Kazakhstan's telecom infrastructure.

15. After losing the first satellite in 2008, the year in Akkol Satellite Communications Center underwent a major modernization. It allows you to now handle two devices.
Baurzhan Kudabaev, vice president of the Republican Center of Space Communications:
- It was established a special software delivered new equipment. Before you rack-command of the measuring system. This supply of American firm Vertex, as it was in the "KazSat-1", but the new modifications, improved version. Applied development company "Russian Space Systems". Ie all this - the development of today. The new programs, equipment, electronic components. All this improves the performance of our spacecraft

16. Darkhan Maral, head of the mission control center in the workplace. In 2011, the Center came young specialists, graduates of Russian and Kazakh universities. They have learned to work and how to maintain leadership in RTSKS, with the completion of a career is no problem. In 2008, the situation was much sadder. After losing the first satellite, a significant proportion of highly educated people left the center.

17. October of 2011 was another climax in the work of the Kazakh satellite. He completed his flight tests and started the so-called trial transcripts. Ie it was like a test for the functionality of the satellite manufacturer. There was everything follows. On the "KazSat-2" raised the television signal.
Then, several groups of experts traveled to different regions of Kazakhstan and the measured parameters of the signal, ie, how correctly the signal relays satellite. Observations have arisen, and in the end a special committee adopted an act on the transfer of the satellite to the Kazakh side. Since then, the operation of the unit involved in Kazakh specialists.

18. Until the end of November 2011, the Space Center "Akkol" a large group of Russian experts. They were subcontractors on the project "KazSat-2". These are the leading companies of the Russian space industry: Center. Khrunichev, which designed and built the satellite, Design Bureau "Mars" (which specializes in navigation orbiting satellites), as well as the corporation "Russian Space Systems", which develops software.
The whole system is divided into two components. It is, in fact, the satellite and terrestrial infrastructure management. According to the technology first, the contractor must demonstrate the availability of the system - is equipment installation, debug it, the demonstration features. After all procedures - training of Kazakh specialists.

19. Satellite Communications Center in Akkol - this is one of the few places in our country where there are favorable electromagnetic environment. On many tens of kilometers around here there are no sources of radiation. They can create interference and hamper satellite. 10 large parabolic antennas directed into the sky in a single point. There is a great distance from the Earth's surface - that's more than 36-thousand kilometers of hanging a small man-made object - the Kazakh communications satellite "KazSat-2".
Most modern geostationary communications satellites. Ie their orbit is constructed so that as it hangs over one geographic point, and the rotation of the earth has little to this stable position no effect. This allows the on-board transponder to pump large volumes of information confidently take this information in the coverage area on the Earth.

20. Another curious detail. According to the international rules of the tolerance of the satellite from the point of standing can be a maximum of half a degree. For Professionals -uderzhat MCC unit in the given parameters - piece of work that requires highly qualified specialists in ballistics. The center will work 69 people, 36 of them - are technical experts.

21. This is the main control. On the wall of a large monitor, which receives all the telemetry on the semi-circular table are several computers and telephones. It seems to be very simple ...

22. ... but it only seems that way. Read in this curve on the oscilloscope being a space object and that the telescope is not visible, it is given not for everyone ...

23. Victor Lefter, President of the Republican Center of Space Communications:
- We will expand Kazakhstan's fleet up to 3, 4, and perhaps even - up to 5 cputnikov. Ie that there was a constant replacement of vehicles, provision was, and that our operators have not experienced such an urgent need to use the products of other countries. So we were provided with their reserves. "

24. Currently, the backup satellite control is carried out from Moscow, where the Space Center. Khrunichev. However, the National Center for Space Communications intends to reserve a flight c Kazakh territory. To do this, now under construction the second MCC. It will be located 30 kilometers north of Almaty.

25. The plans of the National Space Agency of Kazakhstan, coming in 2013, the year the launch of the third satellite "KazSat-3". The contract for its development and production was signed in 2011, the year in France, Air Show in Le Bourget. Sputnik Kazakhstan builds im.Akademika Reshetnev NPO, which is located in the Russian city of Krasnoyarsk.

26. The operator interface management department. So it looks like now.

Source:
Tags
See also
500 seconds
Man in Space!
50 years of the launch of Sputnik
Failure mission U2
"Lighthouse": The first Soviet nuclear disaster
How to run KazEOSat-2
As covered the sky of the USSR from the USA
"Travel in Russia: The Soviet Union today"
Five minutes in the Soviet Union
15 films that will believe in themselves















