Conquerors of the other planets (25 photos)
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net

This year, the world's attention has been drawn to Mars, where the Americans were taken and where they successfully used their Planetary Spirit and Opportunity.
Our share, as is often the case in recent years, it remains only to share the joy of the Americans and console ourselves that we once were able to run the machines on other planets.

(One of the shops VNIITM)
The main developer of the chassis for planetary rovers (wheels, engines, drive, suspension, steering them) in the Soviet Union was (and remains so far in Russian) Leningrad VNIITransmash (VNIITM). This institution developed mainly chassis for tanks, so that was accumulated extensive experience in the field of transport-road, because the common property in the tank and planetary rovers - movement on unprepared terrain.


(STR-1 robot for cleaning the roof of Chernobyl radioactive waste)
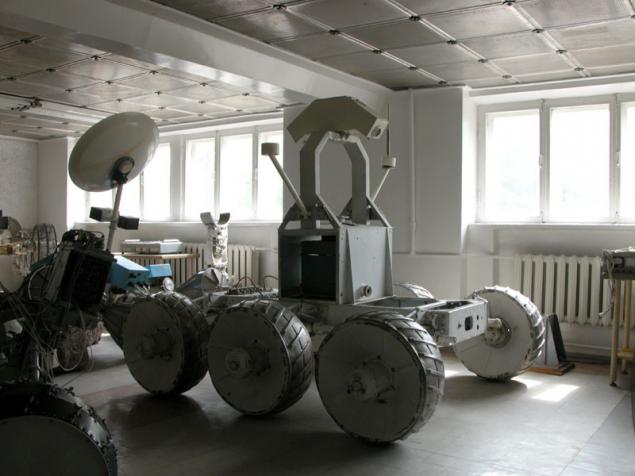
It was created and tested a lot of variety of devices - Lunokhod 1 and 2 (1970), walking planetary rovers sent to Mars in 1971, jumping to Phobos (1988), a robot for cleaning the roof of the destroyed Chernobyl Unit (1986), planetary rovers for a failed expedition Mars-96, several planetary rovers in cooperation with foreign organizations (in recent years), etc.
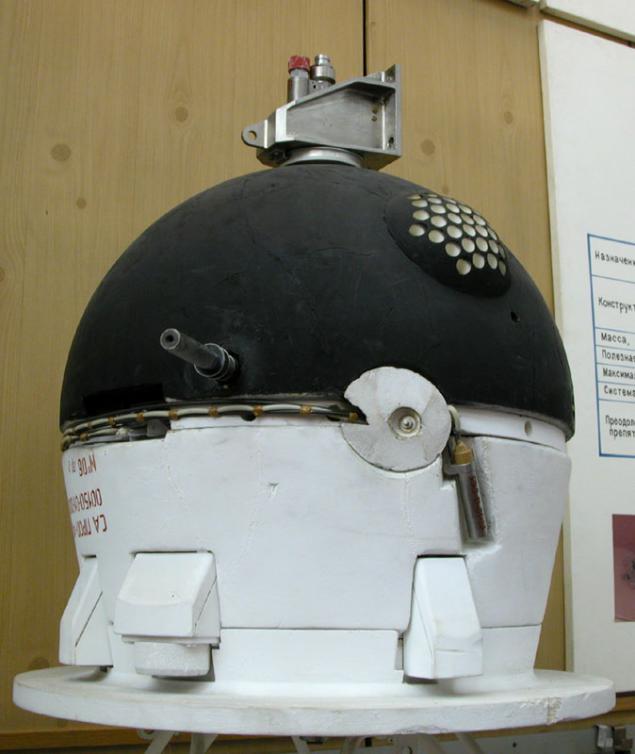

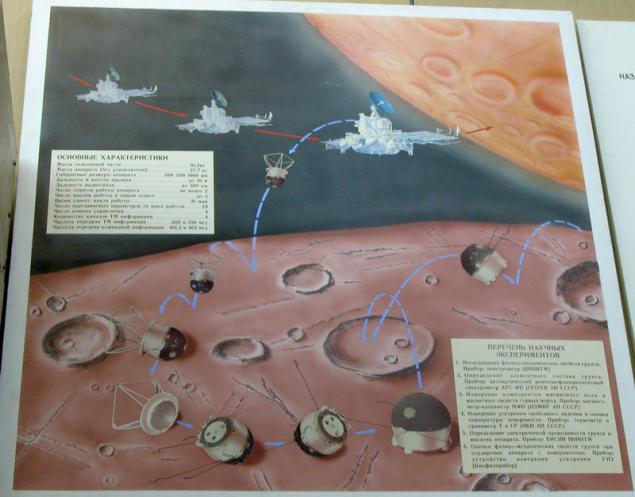
(Leaping apparatus for the study of Phobos)

(Walking machine for Mars exploration PROP v M, 1971)
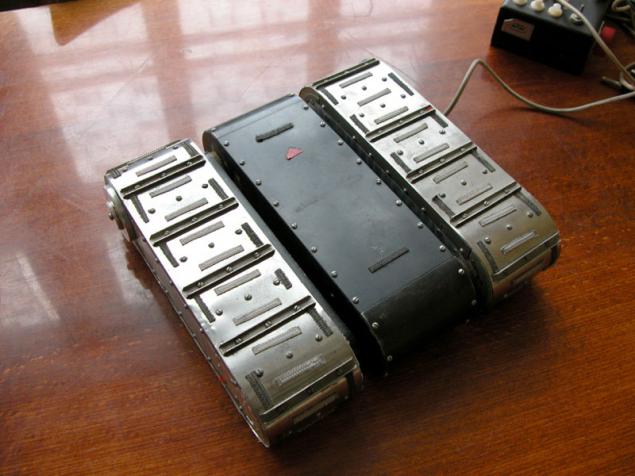

(TRACK-walking rover)
Wheel of planetary rovers must simultaneously combine many requirements - to say a few words about each one article is not enough. So let's look at a few options in VNIITM wheels created since the time of Lunokhod to the present day, highlighting their main features.
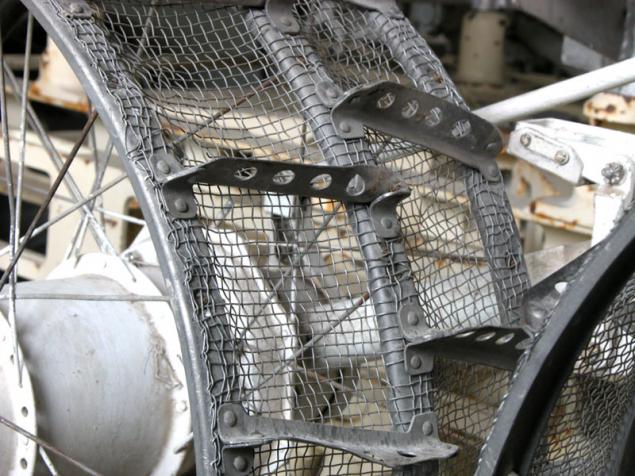
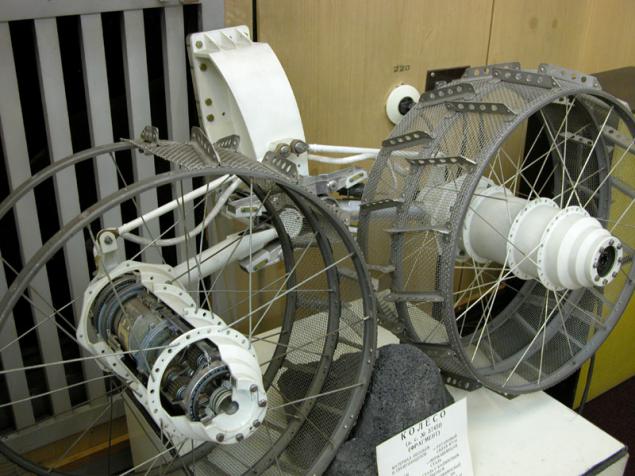

(Wheels Lunokhod)
Wheel rover can already be considered a classic. Most of the subsequent models and real planetary rovers anything, but borrowed from them. Wheels consist of three titanium rims fastened on a steel mesh with lugs of the same titanium. Reliance on a solid surface occurs on average the rim on the same soft ground rim penetrates deeply and then running the grid.
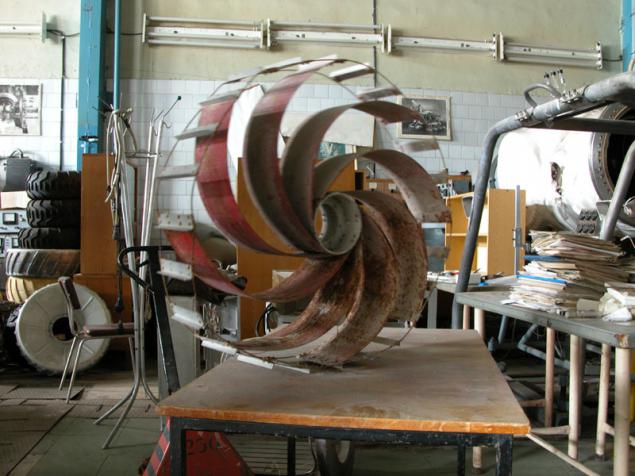


(Trial versions of wheels for Lunokhod)
These are the two wheels for a trial version Lunokhod. Podressorivaetsya wheel, in one case by a resilient metal strip in the other - with the help of springs along an axis of the cylindrical wheel.
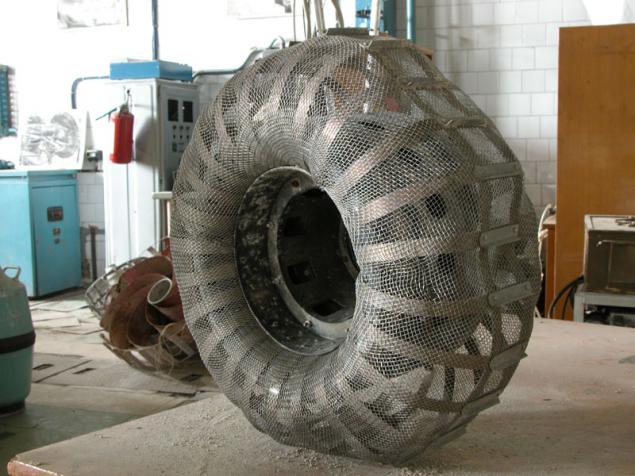

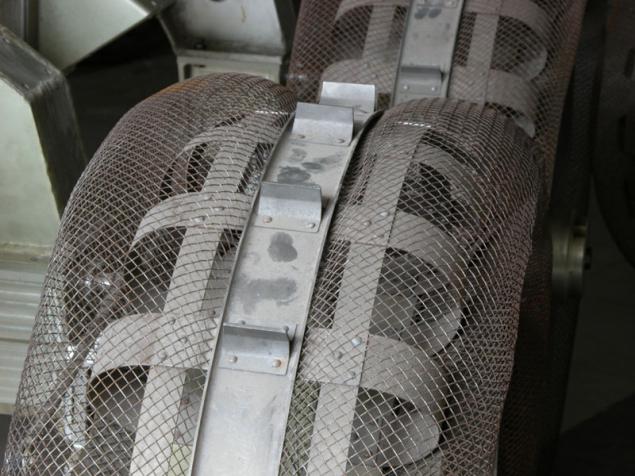
(Trial versions of wheels for Lunokhod)
Another option - is the outer surface of the wheel is made of elastic mesh, but a net placed flat springs that work when under the stress prominaetsya grid. Profile wheel prevents lateral slipping. Lugs (middle) operate mainly by subsidence grid on solid ground.
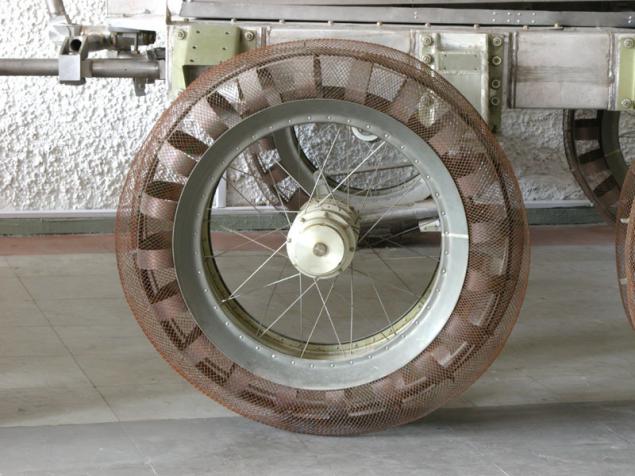


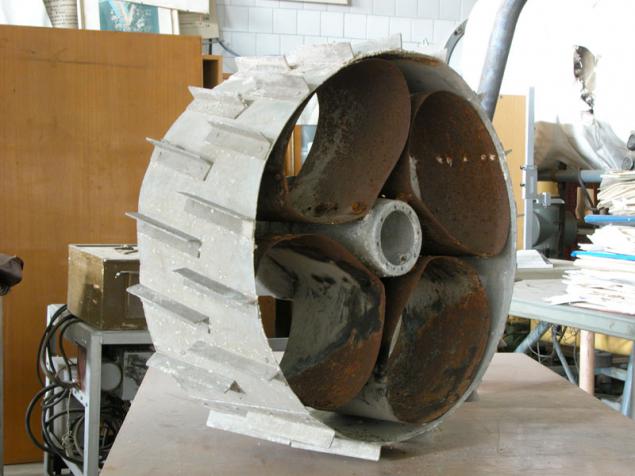
(Trial versions of wheels for Lunokhod)
For planets with strong gravity (Mars, Earth) on flimsy mesh abandoned in favor of a continuous surface with lugs (sheath wheel). In the case of the rovers, scientists proceeded from the first photographs of "Viking" where the surface of Mars looks rocky.
These wheels are used later in the project IARES (1993) and PP-1 (1986)
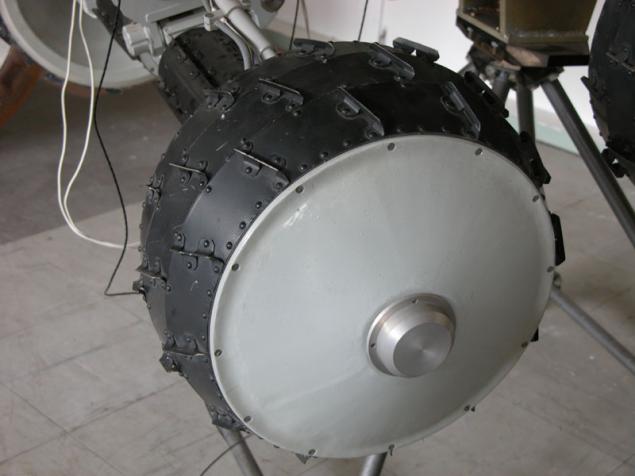

(Wheel IARES)
As can be seen, in all designs attempt to provide good adhesion to the primer (lugs, mesh), light weight (no solid discs and possibly grid spokes or solid but hollow wheel), cushioning (needles, springs, etc.) measures against lateral sliding (convex or concave characteristic profile).
Almost all wheel Planetary wheel is a single (often even sealed) module, which also includes reducer, motor, brake, the necessary sensors. Such a module called "motor-wheel." The use of motor-wheels allows, along with the suspension, to provide equal load on all wheels and efficient use of capacity on uneven terrain, with the wheels hang in the air, etc.
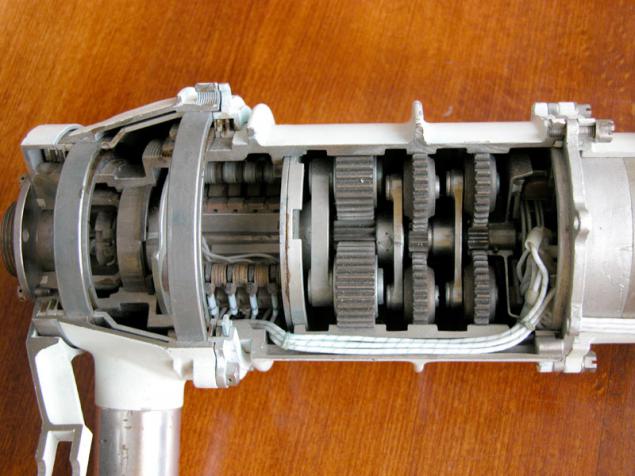
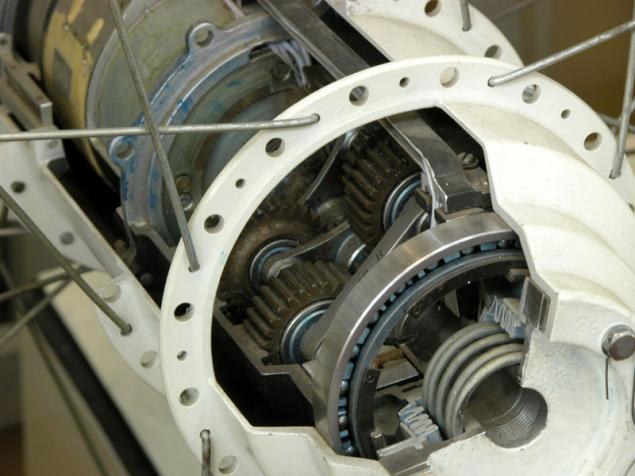
(Motor-wheel sectional)
If we consider the paddle wheels in general, the question arises - why planetary rovers, Lunokhod in particular, as the wheels?
First, until the last moment did not preclude the use of the tracks. In the case of 8-wheel rover it would not require a full review of the structure. Secondly, reducing the load on the ground. Finally, reliability - performance at failure of several wheels.
In the event of jamming the drive wheels Lunokhod contain special release mechanism. Pyrotechnic charge on command from Earth could kill the shaft and as a result of faulty locked wheels would be driven. Four wheel so it would be impossible. Fortunately, this possibility has not been used even once.
Make independent suspension for each motor-wheel. This allows to overcome the small protrusions and depressions avoiding strong banks of the whole machine and overloading the individual engines. Ideally each wheel at any given time should touch the ground, and with approximately the same loads from interacting with it. This is achieved not only the mechanics, but also the electronic part, estimates the load on the engine and suspension. The mechanical part of the suspension is usually performed in the form of levers, wherein the elastic element as used torsions - steel or titanium rods, which constitute the "spring" of the torsion. Using hydraulics problematic, due to the strong temperature variations on the surface of planets.

(Torsion)
Instructive story of the death of the Lunokhod-2 - it set a new trim-tilt sensor (the entire unit automation Lunokhod-2 was developed in triplicate - for manned machine).
The sensor in the Lunokhod-1 was developed by VNIITM, but felt that the machine-building enterprise should mind his own business and the development of new sensor assigned to another organization.
The new sensors are used antifreeze. However, it was not considered a small force of gravity on the moon. As a result, immediately after the lunar landing, the sensor proved to be inoperative. But this sensor should be protected from tipping Lunokhod - automatically stop it, if the slope is too large (in passing - gives an idea of the geometry of the lunar surface). Here he showed that Lunokhod stands at an angle of 40 degrees before the exit of the lander.
Had to go without encoder, focusing only on what is seen through the camera - skyline and simple level - Kata metal ball. All went well, but in the third month Lunokhod drove into a fairly large crater. He stood there with open solar battery and recharged. When it came time to leave the crater, underestimated the angle of inclination. As a result, the machine is caught by solar battery, it was ground, leading to a drop in power. Attempts to shake off the ground only exacerbated the situation - the ground to keep the inner compartment. Thus ended his life Lunokhod 2.
Incidentally, the Lunokhod-1 even less fortunate - at the start of the launcher exploded. So the Lunokhod-1 that has been on the moon - not quite the first moonwalker.
In any case, Lunokhod 2 on the moon was much greater distance - 40 km 3 months than Lunokhod 1 - 10 km. for 10 months. Affected the experience gained researchers and drivers.
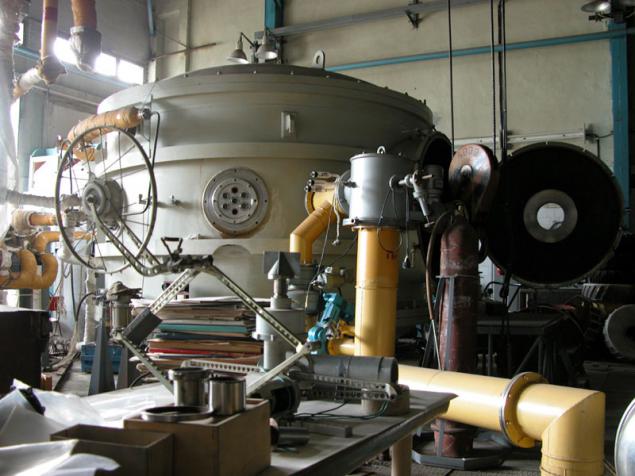
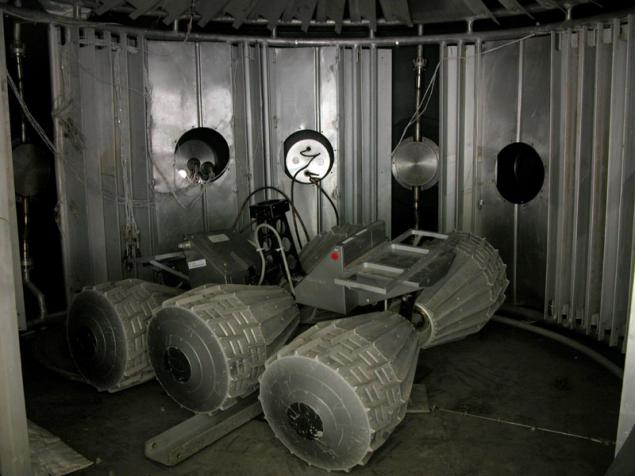


(Camera to simulate the atmosphere of planets and rover in it)
Large turning radius becomes a problem when near a rock or crevice where the unit may splozti when turning.
The most common solution is borrowed from tracked vehicles: making various wheel speed on the left and right side of the machine (in the simplest case, using the brakes), it can be deployed virtually on the spot.
This approach also simplifies the construction, increases reliability, since it does not need to do castor. A well-known example - the "Lunokhod" (1970).
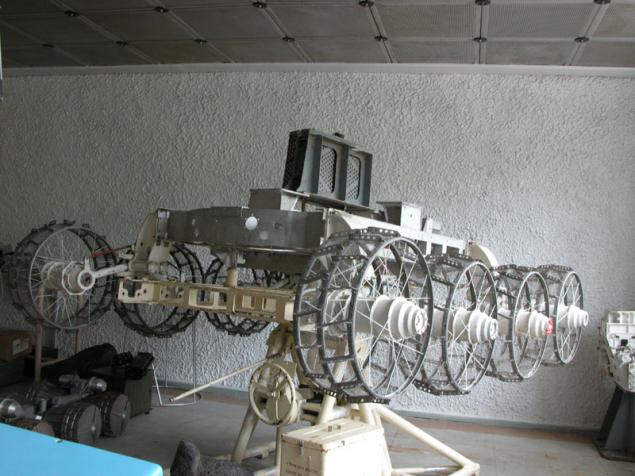

(Chassis for Lunokhod)
Planetary tested in Central Asia, in Kamchatka (in areas with fresh eruptions) - that was a great variety of forms of relief ... It was not known in advance what the soil, for example, on the moon. There have been suggestions that the soil is suspended and Lunokhod can simply drown. Therefore, tests were also carried out on the snowfields - where snow filled volcanic sand.
On planets where now possible to deliver planetary rovers, there is a set of stones, rocky ledges, craters. What future for the walking machine probably will not be a problem (see, most people easily overcomes obstacles that are insurmountable for the wheels) for today's planetary rovers problem is very urgent.
Imagine a situation where the normal car runs into one flange on the large stone. There is a roll of the whole machine and the machine runs the risk of capsize. For planetary rovers such behavior is unacceptable, because the suspension is arranged much more difficult - when one of the wheels moving the stone, the other can take the machine completely horizontally.
But even this may not save, if the stone will be at the bottom of the Planetary and "sit down on his belly." Therefore, ground clearance (clearance) are trying to do the maximum. Increase clearance, in turn, can lead to instability of the device - the center of gravity as low as possible (even projects were put batteries inside the motor-wheels, but it leads to other problems).
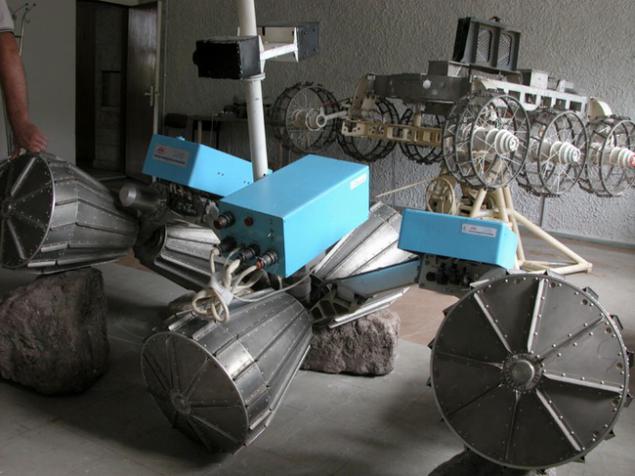
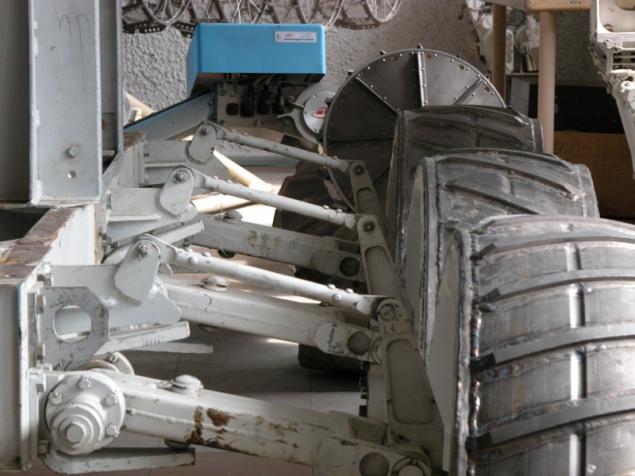
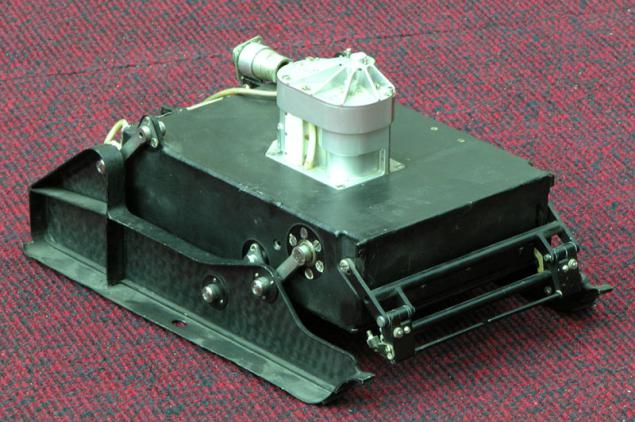
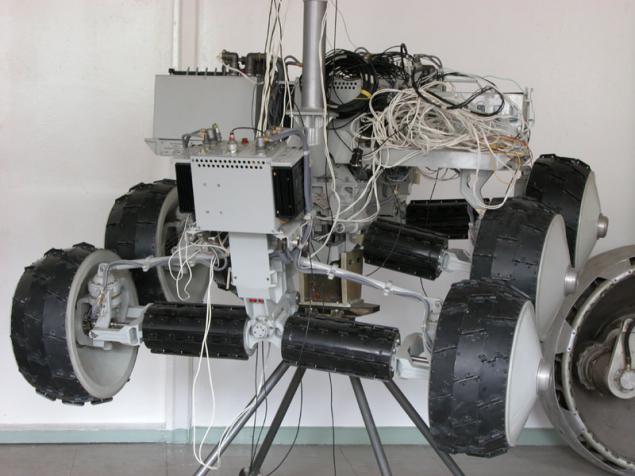
An interesting solution is illustrated by perhaps the most perfect system, which was developed VNIITM titled "Peace" (1988), "Lama» (1994-1995), J-Rover (1996).
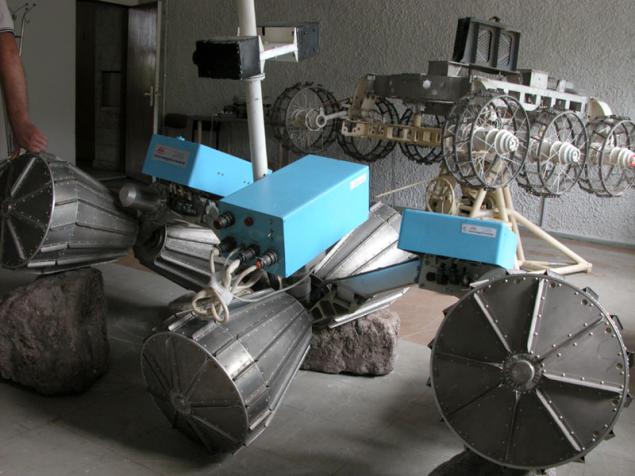

(World / LAMA / J-Rover)
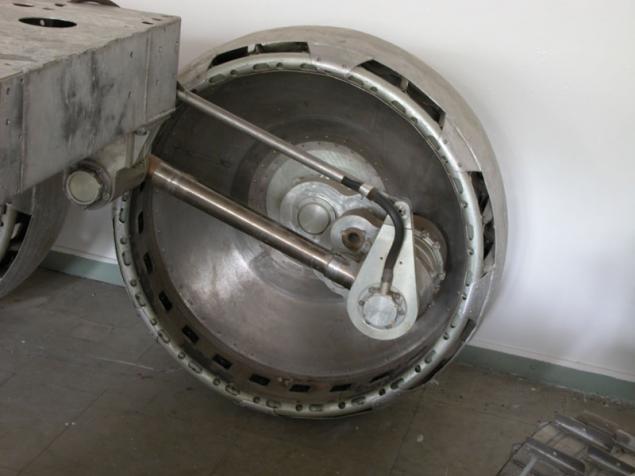
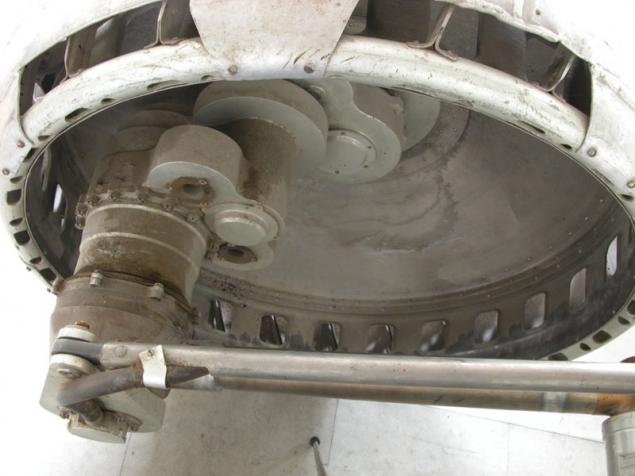
There is virtually no clearance - not the bottom, instead of him - bevel geared wheel. If by them gets rock jam occurs because lugs are located along the entire length of the wheel. There are, however, and the lack of -ostaetsya little space to accommodate a payload (a possible solution - to place the battery inside the wheel). In another development - IARES - instead of bevel gears is typically used in conjunction with rollers, also having lugs.
(IARES)
Interestingly, the bevel gears were at one time bought from VNIITM McDonald Douglas, who were going to do planetary rovers. However, the American rovers developed at JPL, who went their own way. In the same era Lunokhod development on both sides conducted in secrecy, so that was completely independent.
Each pair of wheels may be independently rotated at an angle of about 40 degrees, and move up and down relative to the other pair. Among other things, this allows a compact folded planetary rovers during transport in a spaceship.
Another possibility of the wheel unit is, oddly enough, the pacing. Due to the additional engine section can slightly move off from each other. Alternately blocking one pair of wheels and pushing forward other pairs can be, though not fast, but easy to overcome the obstacle.
Another option pacing has been implemented in the car «EOSAIII-1" (1978).


(EOSA III-1. Note: The lugs are closed tin)
Here, each of the six wheels can operate in two modes - roll (rotation around the center) or walk (rotation around a point offset from the center of the wheel)
All.
Source
-
Tags
See also
If instead of the moon were other planets of the Solar System
China - is not just another country, it's another planet
Stephen Hawking urges humanity to colonize other planets to survive
NASA will send a mini-satellites CubeSat to other planets
And what if the moon were in place other planets? Thanks to the wonderful photos is easy to ...
How would look a modern metropolis on other planets
7 signs that other planets might harbor life
Evolution of the aliens in the movie
Big Secret dealers
Funny and unusual flash mobs