As the bats were to bomb Japan (12 pictures)
 Bashny.Net
Bashny.Net
December 7, 1941 a dental surgeon Lytle Adams (Lytle S. Adams) was on leave. On this day, he, like millions of other Americans, was shocked by the news of the tragedy at Pearl Harbor. Finding an adequate response to the attack doctor remembered the bats.
The fact that your vacation Adams spent in the southwest United States and literally just visited Carlsbad Caverns, where just saw a mouse: "I was extremely impressed by the flight of these creatures and thought - why not equip millions of bats with incendiary bombs and do not throw them off the plane? What could be more devastating than a way to bombing? "- Recalled Dr. course of his thoughts after the war.


And then, in 1941, Adams returned to the caves of Carlsbad, to take "on trial" a few bats, and then began to read everything he could find about the mammals of the order bat.
He learned that in the world there are about 1000 species, and that each bat lives about 30 years. And what is the most common in North America are svobodnohvostye bats (Tadarida pumila), which in one night can catch more than a thousand mosquitoes or insect the size of a mosquito. And at a body weight of 9 grams able to carry the load almost 3 times heavier than himself.
January 12, 1942 Adams sent the White House a proposal to study the possibility of using bats as bombers. It must be said that there is nothing surprising in handling dental surgeon to the President and the government was not there during the war, citizens willingly shared their ideas with the authorities, most of which, of course, defective.

However, the idea of the doctor was held "high-level expertise" and became one of the very few who have received a "green light." Engage in mice-bombers were instructed to military service, was in charge of chemical weapons (Chemical Warfare Service - CWS), in collaboration with the US Air Force. The official history of the CWS, this fact can be easily explained: "President Roosevelt said," OK ", and the project took place." Marked "confidential", of course.
Adams along with his dedicated team of biologists immediately went to work, and start looking to visit places where bats were present in large numbers. Mostly, it was a cave, but a lot of bats inhabited attics, sheds, landfills, and other such places.
"Then we climbed around a thousand caves and three thousand mines, - told the doctor in 1948. - I had to rush to much, so we went during the day and at night. We slept in cars, one after another at the wheel ».

Live bombers fly out of the box - to light (Figure Chris Fauver / afa.org).
The largest of the mice was found Eumops perotiss 50-centimeter wingspan, which theoretically could carry a 450-gram stick of dynamite. However, these mice "in nature" was not enough.
More rasprostranёnnayaAntrozous pallidus could carry 85 grams, but the researchers have decided that it is hardy enough for the project.
Finally, the team of Adams, as one would expect, has chosen svobodnohvostuyu bat, which can be loaded 28 grams.
The largest colony of fruit bats, numbering 20-30 million individuals, were found in a cave Ney (Ney Cave), in Texas. The colony was so great that the animals to leave the cave dense flow, took about five hours.
So catch the mice in the required amount using the network was not working. Several hundred prisoners were placed in refrigerated vans (to get them to "hibernate" hibernate), and several povёz Adams in Washington, in order to demonstrate how they are fake bomb.

Container canister within which the bats were thrown from the plane with a parachute. During the fall it was heated - mouse wake - opens and releases the instigators (photo from biomicro.sdstate.edu).
In March 1943, with the participation of Staff of the US Air Force experiment was conducted entitled "Verification method of dispersal arsonists» («Test of Method to Scatter Incendiaries»), whose aim was "to establish the possibility of using bats for the delivery of small incendiary bombs to enemy targets" .
Before we talk about the experiment, we note that the construction of tiny incendiary bombs to bats engaged Dr. Visser (LF Fisser). He produced two prototypes of different sizes and weights - oblong objects from nitrocellulose, filled with kerosene.
One bomb weighed 17 grams and burned for 4 minutes with a 25-centimeter flame. Other weighing 28 grams burned for 6 minutes with a 30-centimeter flame. The operation of the device powered mechanical igniter that fires with the slowdown: copper dichloride eroded steel wire, stick drummer in a tense situation.
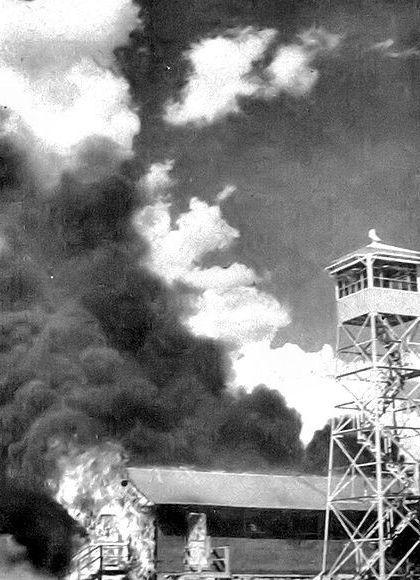

The result, I think, a successful trial.
The bomb was fixed on the chest of a bat by means of surgical clamps and some thin tethers (among others assumed that these mice will gnaw leash and leave the bombs).
Returning to the experiment to test the arsonists. 180 mice with dummy bombs were loaded into cardboard container that was thrown from the plane. The container is automatically opened in the air at an altitude of about 300 meters, and liberated the mouse fly with bombs hidden in their favorite places. Like, everything turned out as planned.
For the next test in Carlsbad Caverns was caught about 3, 5 thousand bats. May 21, 1943 of 5 containers packed with dummy bombs dropped from B-25s at the height of 1, 5 kilometers.
These tests were successful: most of the animals are not able to wake up from the end of "hibernation", not flew, fell and broke. In general, there were many complications: cartons are not functioning properly, surgical clamps tore the delicate skin of mice and so on.
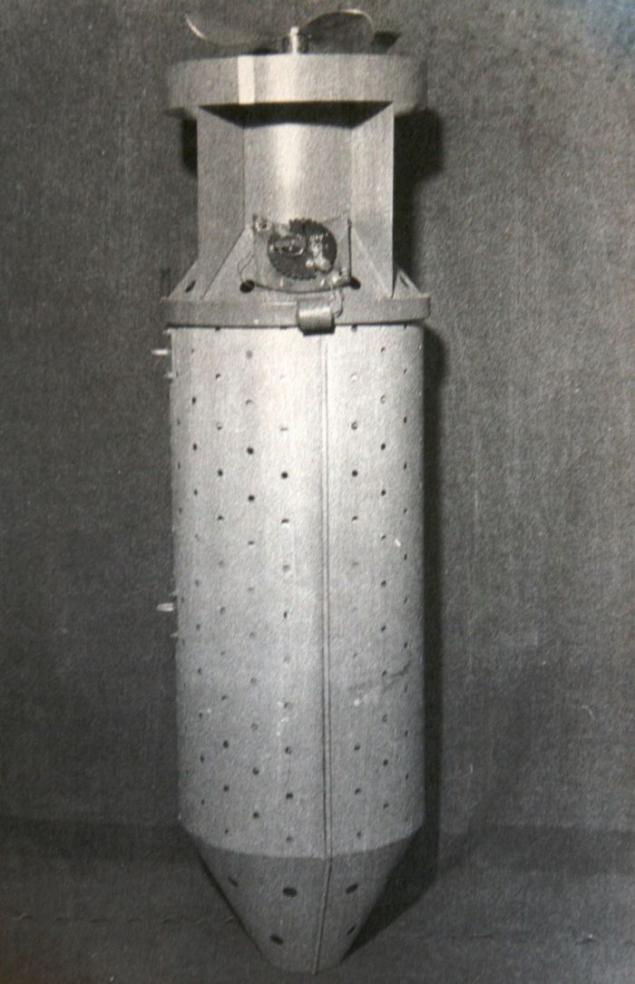
Each compartment should contain 40 bats, each containing 17 or 28 grams of napalm.
Army tests ended May 29, 1943. "Bats used in the experiment, weighed an average of 9 grams. Without any problems they could carry 11 grams, 18 grams - satisfactory, but 22 grams, proved they can not afford, "- wrote in his report on the trials Captain Carr (Carr).
In subsequent experiments involved about 6000 mice. War, it became clear that it takes a new parachute that the delay time will print container canister, new mounts for bombs, Simplified igniter and the like.
In his secret report, dated June 8, 1943, Captain Carr briefly reported that "tests have been completed after a fire destroyed much of the test material».
Captain "forgot" to mention that during the test village simulates Japanese settlement was burned down. The fact that, due to staff negligence left the door open, and some bats fled with these incendiary bombs and set fire to a hangar with the vehicle General.

Reaction warlord history is silent, but soon after the incident, in August 1943, the army gave the project the Navy, who somehow renamed the "X-rays» (Project X-Ray).
In October, 1943 the Marines secured the four caves to grab the mouse, if necessary - for one night could easily catch a million.
The first "sea" experiments with mice-bombers began in December. During the tests, the animals made about 30 arson and, according to historian Robert Sherrod (Robert Sherrod), «four of them demanded the intervention of professional firefighters».
Full-scale trials have been scheduled for August 1944, however, when Fleet Admiral Ernest King (Ernest J. King) knew that the bats will not be ready for a fight, at least until mid-1945, he abruptly stopped all work on the project that by the time "ate" about $ 2 million.
The surgeon-dentist Adams, until recently, worked on "X-rays", very angry. He argued that arson committed bats bombers might have been more devastating than the atomic bomb that was razed to the ground Hiroshima and Nagasaki.

Another one of such experiments attempt to use pigeons to control planning bomb. Who saw the Danish film "Beat the first, Freddy!" Will understand and appreciate the idea. The idea is not bad, but you never know what might be in a dove in his head?
By design, planned and controlled depth charge «Pelican» Use pigeons were reliable radar and radio guidance. A trained pigeon could push beak on a specific point on a map projected on a special lens and thus to influence the route bombs.
SWOD Mk-7 "Pelican" - homing antiship planning to bomb a semi-active radar homing. Developed within the framework of SWOD the US Navy in World War II. It was successfully tested in 1943, but in the arms of the fleet has not arrived because of the potential to develop a vastly superior characteristics homing bomb - then ASM-N-2 Bat ...
B-24s Libarator three bombs Pelican

The bomb was developed in 1942, the program SWOD. It was assumed that its main function will be defeated with long range submarines surfaced. Exact bombing on a relatively small submarines was an easy task for ocean patrol aircraft, and the US Navy had hoped to solve the problem by creating smart bombs. It is also planned to use the bomb to effectively defeat surface ships.
"Pelican" was first tested in December 1942, becoming the world's first tested homing weapon. Structurally, the bomb was a wooden glider fuselage developed by the Bureau of Standards (Bureau of Standards), which were suspended under the different types of bombs. At the head of the bomb was mounted semi-active homing head, receiving the reflected beam is mounted on the carrier aircraft radar AN / APS-2.
Initially it was assumed that the main bomb warhead will be 357-pound depth charges, but eventually the bomb was developed under a 1000 lb (450 kg) and 1,500-pound (650 kg) bombs. The lighter version designated as «Pelican Mk-II», heavier - «Pelican Mk-III». Patrol Bomber PV-1P, elected as a carrier could carry under the wings of two Mk-II or one Mk-III in the bomb bay.

Bomb tests were successful, but in 1943 reached a level of miniaturization of electronics, enabling a compact radar is located at the very bomb, that is to make a planning bomb fully active homing. In the future, the emergence of such weapons, the Navy refused to accept SWOD Mk 7 weapons, justifying refusal to insufficient range and the need for a carrier aircraft to come close to the goal. Bomb-making «Pelican» used tests, attention has shifted to the military ASM-N-2 Bat.
And now the most interesting, though weird, to say the least: for that Bombay offers organic management system with the help of specially trained pigeons.
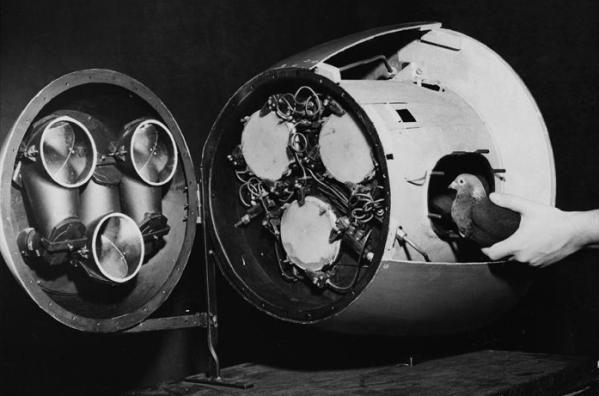
In early 1942, the US Navy received a proposal from Dr. Skinner used to induce controlled bombs trained pigeons.
According to the proposed concept, the pigeon had to be pre-trained to recognize areas on aerial photography and press beak attacked the position of the object. Through a hole in the map, located exactly on the site of the attacked object to pigeon feed fed. Thus, the pigeon got used to recognize and push beak on a well-defined object in the picture.
Put in a bomb homing pigeon would see through the lens system around the area, and noticed an object which he had been taught to recognize it on the map, it would be poking its beak. Special electrically conductive screen on which was projected before the dove image areas would be perceived as the movement of the beak autopilot commands and transmit them servos bomb. It was assumed that the dove's beak holding for the purposes will thus inducing a bomb right on target.
Despite the criticism of the fleet to the proposal, a specific budget has been allocated to the test. Conducted in 1943, tests have shown performance concept, but its main drawback - the need for careful preliminary exploration and the long training pigeons for combat use - led to the closure of the program in April 1945, without any practical applications.
Formally, the bomb "Pelican" with a dove as a seeker, can be considered the first cyborg, designed for use in military applications.
The fact that your vacation Adams spent in the southwest United States and literally just visited Carlsbad Caverns, where just saw a mouse: "I was extremely impressed by the flight of these creatures and thought - why not equip millions of bats with incendiary bombs and do not throw them off the plane? What could be more devastating than a way to bombing? "- Recalled Dr. course of his thoughts after the war.


And then, in 1941, Adams returned to the caves of Carlsbad, to take "on trial" a few bats, and then began to read everything he could find about the mammals of the order bat.
He learned that in the world there are about 1000 species, and that each bat lives about 30 years. And what is the most common in North America are svobodnohvostye bats (Tadarida pumila), which in one night can catch more than a thousand mosquitoes or insect the size of a mosquito. And at a body weight of 9 grams able to carry the load almost 3 times heavier than himself.
January 12, 1942 Adams sent the White House a proposal to study the possibility of using bats as bombers. It must be said that there is nothing surprising in handling dental surgeon to the President and the government was not there during the war, citizens willingly shared their ideas with the authorities, most of which, of course, defective.

However, the idea of the doctor was held "high-level expertise" and became one of the very few who have received a "green light." Engage in mice-bombers were instructed to military service, was in charge of chemical weapons (Chemical Warfare Service - CWS), in collaboration with the US Air Force. The official history of the CWS, this fact can be easily explained: "President Roosevelt said," OK ", and the project took place." Marked "confidential", of course.
Adams along with his dedicated team of biologists immediately went to work, and start looking to visit places where bats were present in large numbers. Mostly, it was a cave, but a lot of bats inhabited attics, sheds, landfills, and other such places.
"Then we climbed around a thousand caves and three thousand mines, - told the doctor in 1948. - I had to rush to much, so we went during the day and at night. We slept in cars, one after another at the wheel ».

Live bombers fly out of the box - to light (Figure Chris Fauver / afa.org).
The largest of the mice was found Eumops perotiss 50-centimeter wingspan, which theoretically could carry a 450-gram stick of dynamite. However, these mice "in nature" was not enough.
More rasprostranёnnayaAntrozous pallidus could carry 85 grams, but the researchers have decided that it is hardy enough for the project.
Finally, the team of Adams, as one would expect, has chosen svobodnohvostuyu bat, which can be loaded 28 grams.
The largest colony of fruit bats, numbering 20-30 million individuals, were found in a cave Ney (Ney Cave), in Texas. The colony was so great that the animals to leave the cave dense flow, took about five hours.
So catch the mice in the required amount using the network was not working. Several hundred prisoners were placed in refrigerated vans (to get them to "hibernate" hibernate), and several povёz Adams in Washington, in order to demonstrate how they are fake bomb.

Container canister within which the bats were thrown from the plane with a parachute. During the fall it was heated - mouse wake - opens and releases the instigators (photo from biomicro.sdstate.edu).
In March 1943, with the participation of Staff of the US Air Force experiment was conducted entitled "Verification method of dispersal arsonists» («Test of Method to Scatter Incendiaries»), whose aim was "to establish the possibility of using bats for the delivery of small incendiary bombs to enemy targets" .
Before we talk about the experiment, we note that the construction of tiny incendiary bombs to bats engaged Dr. Visser (LF Fisser). He produced two prototypes of different sizes and weights - oblong objects from nitrocellulose, filled with kerosene.
One bomb weighed 17 grams and burned for 4 minutes with a 25-centimeter flame. Other weighing 28 grams burned for 6 minutes with a 30-centimeter flame. The operation of the device powered mechanical igniter that fires with the slowdown: copper dichloride eroded steel wire, stick drummer in a tense situation.

The result, I think, a successful trial.
The bomb was fixed on the chest of a bat by means of surgical clamps and some thin tethers (among others assumed that these mice will gnaw leash and leave the bombs).
Returning to the experiment to test the arsonists. 180 mice with dummy bombs were loaded into cardboard container that was thrown from the plane. The container is automatically opened in the air at an altitude of about 300 meters, and liberated the mouse fly with bombs hidden in their favorite places. Like, everything turned out as planned.
For the next test in Carlsbad Caverns was caught about 3, 5 thousand bats. May 21, 1943 of 5 containers packed with dummy bombs dropped from B-25s at the height of 1, 5 kilometers.
These tests were successful: most of the animals are not able to wake up from the end of "hibernation", not flew, fell and broke. In general, there were many complications: cartons are not functioning properly, surgical clamps tore the delicate skin of mice and so on.

Each compartment should contain 40 bats, each containing 17 or 28 grams of napalm.
Army tests ended May 29, 1943. "Bats used in the experiment, weighed an average of 9 grams. Without any problems they could carry 11 grams, 18 grams - satisfactory, but 22 grams, proved they can not afford, "- wrote in his report on the trials Captain Carr (Carr).
In subsequent experiments involved about 6000 mice. War, it became clear that it takes a new parachute that the delay time will print container canister, new mounts for bombs, Simplified igniter and the like.
In his secret report, dated June 8, 1943, Captain Carr briefly reported that "tests have been completed after a fire destroyed much of the test material».
Captain "forgot" to mention that during the test village simulates Japanese settlement was burned down. The fact that, due to staff negligence left the door open, and some bats fled with these incendiary bombs and set fire to a hangar with the vehicle General.

Reaction warlord history is silent, but soon after the incident, in August 1943, the army gave the project the Navy, who somehow renamed the "X-rays» (Project X-Ray).
In October, 1943 the Marines secured the four caves to grab the mouse, if necessary - for one night could easily catch a million.
The first "sea" experiments with mice-bombers began in December. During the tests, the animals made about 30 arson and, according to historian Robert Sherrod (Robert Sherrod), «four of them demanded the intervention of professional firefighters».
Full-scale trials have been scheduled for August 1944, however, when Fleet Admiral Ernest King (Ernest J. King) knew that the bats will not be ready for a fight, at least until mid-1945, he abruptly stopped all work on the project that by the time "ate" about $ 2 million.
The surgeon-dentist Adams, until recently, worked on "X-rays", very angry. He argued that arson committed bats bombers might have been more devastating than the atomic bomb that was razed to the ground Hiroshima and Nagasaki.

Another one of such experiments attempt to use pigeons to control planning bomb. Who saw the Danish film "Beat the first, Freddy!" Will understand and appreciate the idea. The idea is not bad, but you never know what might be in a dove in his head?
By design, planned and controlled depth charge «Pelican» Use pigeons were reliable radar and radio guidance. A trained pigeon could push beak on a specific point on a map projected on a special lens and thus to influence the route bombs.
SWOD Mk-7 "Pelican" - homing antiship planning to bomb a semi-active radar homing. Developed within the framework of SWOD the US Navy in World War II. It was successfully tested in 1943, but in the arms of the fleet has not arrived because of the potential to develop a vastly superior characteristics homing bomb - then ASM-N-2 Bat ...
B-24s Libarator three bombs Pelican

The bomb was developed in 1942, the program SWOD. It was assumed that its main function will be defeated with long range submarines surfaced. Exact bombing on a relatively small submarines was an easy task for ocean patrol aircraft, and the US Navy had hoped to solve the problem by creating smart bombs. It is also planned to use the bomb to effectively defeat surface ships.
"Pelican" was first tested in December 1942, becoming the world's first tested homing weapon. Structurally, the bomb was a wooden glider fuselage developed by the Bureau of Standards (Bureau of Standards), which were suspended under the different types of bombs. At the head of the bomb was mounted semi-active homing head, receiving the reflected beam is mounted on the carrier aircraft radar AN / APS-2.
Initially it was assumed that the main bomb warhead will be 357-pound depth charges, but eventually the bomb was developed under a 1000 lb (450 kg) and 1,500-pound (650 kg) bombs. The lighter version designated as «Pelican Mk-II», heavier - «Pelican Mk-III». Patrol Bomber PV-1P, elected as a carrier could carry under the wings of two Mk-II or one Mk-III in the bomb bay.

Bomb tests were successful, but in 1943 reached a level of miniaturization of electronics, enabling a compact radar is located at the very bomb, that is to make a planning bomb fully active homing. In the future, the emergence of such weapons, the Navy refused to accept SWOD Mk 7 weapons, justifying refusal to insufficient range and the need for a carrier aircraft to come close to the goal. Bomb-making «Pelican» used tests, attention has shifted to the military ASM-N-2 Bat.
And now the most interesting, though weird, to say the least: for that Bombay offers organic management system with the help of specially trained pigeons.

In early 1942, the US Navy received a proposal from Dr. Skinner used to induce controlled bombs trained pigeons.
According to the proposed concept, the pigeon had to be pre-trained to recognize areas on aerial photography and press beak attacked the position of the object. Through a hole in the map, located exactly on the site of the attacked object to pigeon feed fed. Thus, the pigeon got used to recognize and push beak on a well-defined object in the picture.
Put in a bomb homing pigeon would see through the lens system around the area, and noticed an object which he had been taught to recognize it on the map, it would be poking its beak. Special electrically conductive screen on which was projected before the dove image areas would be perceived as the movement of the beak autopilot commands and transmit them servos bomb. It was assumed that the dove's beak holding for the purposes will thus inducing a bomb right on target.
Despite the criticism of the fleet to the proposal, a specific budget has been allocated to the test. Conducted in 1943, tests have shown performance concept, but its main drawback - the need for careful preliminary exploration and the long training pigeons for combat use - led to the closure of the program in April 1945, without any practical applications.
Formally, the bomb "Pelican" with a dove as a seeker, can be considered the first cyborg, designed for use in military applications.
Tags
See also
Orgy bats
Baby bats (21 photos)
Bat-Panda
What kind of brown trees? (9 photos)
This town is more like a decoration to the film
50 bats
A little about bats
"The bat" and 5 exercises for a perfect neck
Riddle of the day
Interesting facts about bats

















